Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Vending Machine Route
Guide to Vending Machine Route
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vending machine route
- Understanding vending machine route Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of vending machine route
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vending machine route
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vending machine route
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vending machine route Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential vending machine route Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vending machine route
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vending machine route Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vending machine route
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vending machine route
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vending machine route
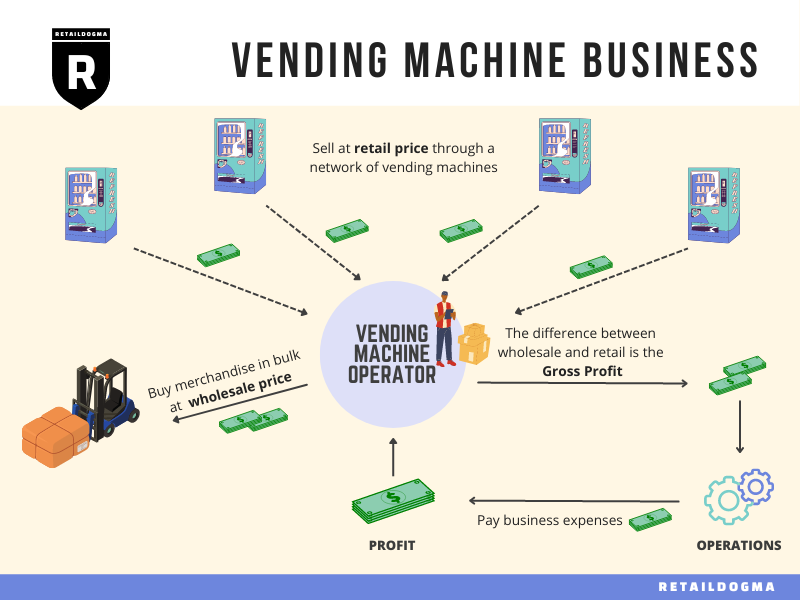
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, the vending machine route has emerged as a vital component for businesses seeking to maximize revenue and enhance customer engagement. This guide serves as an essential resource for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, who are looking to capitalize on the lucrative opportunities presented by vending machines.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding the intricacies of the vending machine route is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions. This comprehensive guide will explore various aspects of the vending machine ecosystem, including types of machines, materials used in manufacturing, quality control processes, and key suppliers. Additionally, we will provide insights into cost considerations and market trends, ensuring you are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of this industry.
By delving into frequently asked questions and addressing common challenges, this guide empowers buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their business objectives. Whether you are looking to expand your current operations or establish a new vending machine venture, the insights presented here will enhance your understanding and guide you toward successful outcomes in the global marketplace. With a focus on actionable insights and practical information, we aim to support your journey in the dynamic world of vending machine routes.
Understanding vending machine route Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Vending Route | Regular visits to replenish stock and maintain machines | Offices, schools, gyms | Pros: Familiar model, predictable revenue. Cons: High labor costs, less flexible. |
| Micro-Market Route | Self-service kiosks with diverse product offerings | Corporate environments, hotels | Pros: Higher margins, variety of products. Cons: Initial setup cost can be high. |
| Mobile Vending Route | Flexible, on-the-go service with trucks or carts | Events, festivals, construction sites | Pros: Adaptable to demand, lower overhead. Cons: Limited inventory, may require permits. |
| Automated Vending Route | Machines equipped with advanced technology (e.g., cashless payments) | Retail spaces, high-traffic locations | Pros: Reduced need for manual labor, increased sales. Cons: Higher upfront costs, tech maintenance needed. |
| Specialty Vending Route | Focused on niche markets (e.g., healthy snacks, local products) | Health-focused companies, local markets | Pros: Targeted customer base, can command premium pricing. Cons: Limited audience, may require extensive marketing. |
Traditional Vending Route
The traditional vending route involves regular, scheduled visits to restock vending machines, ensuring they are operational and well-supplied. This model is widely recognized and often used in settings such as offices, schools, and gyms. For B2B buyers, the predictability of revenue generation is a significant advantage, although it comes with higher labor costs and reduced flexibility in adapting to changing consumer preferences.
Micro-Market Route
Micro-markets feature self-service kiosks that offer a wider array of products, including fresh food and beverages. Typically found in corporate environments and hotels, these setups allow for more extensive product offerings, which can lead to higher profit margins. However, the initial investment can be substantial, requiring careful consideration of location and consumer demand to maximize ROI.
Mobile Vending Route
Mobile vending routes utilize trucks or carts to deliver products directly to consumers at events, festivals, or construction sites. This route offers flexibility and the ability to adapt to customer demand in real-time. While the overhead costs are generally lower than traditional vending, inventory limitations and potential permit requirements can pose challenges for buyers.
Automated Vending Route
Automated vending routes leverage advanced technology, such as cashless payment systems and inventory monitoring, to enhance the vending experience. These machines are suitable for high-traffic retail spaces and can significantly reduce the need for manual restocking. However, the initial investment and ongoing maintenance of the technology can be a barrier for some businesses.
Specialty Vending Route
Specialty vending routes focus on niche markets, offering products like healthy snacks or locally sourced items. This model is particularly appealing to health-conscious companies and local markets looking to differentiate themselves. While it allows for premium pricing due to targeted offerings, the audience may be limited, necessitating effective marketing strategies to attract customers.
Related Video: Explainable AI explained! | #2 By-design interpretable models with Microsofts InterpretML
Key Industrial Applications of vending machine route
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vending machine route | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Automated product dispensing | Reduces labor costs, increases sales efficiency | Machine compatibility with product types, payment systems |
| Healthcare | Medication dispensing | Improves patient compliance, reduces pharmacy workload | Regulatory compliance, secure storage options |
| Education | Snack and beverage services | Enhances student satisfaction, provides convenience | Variety of products, nutritional guidelines |
| Transportation | Travel essentials vending | Meets traveler needs, generates additional revenue | Location analysis, machine durability |
| Corporate Offices | Employee refreshment stations | Boosts employee morale, increases productivity | Product selection, machine maintenance services |
Retail
In the retail sector, vending machines serve as automated product dispensers, allowing businesses to streamline sales processes. These machines can be strategically placed in high-traffic areas to maximize visibility and accessibility. By reducing labor costs associated with staffing, businesses can increase sales efficiency. International buyers should consider machine compatibility with the types of products offered and the integration of various payment systems to cater to diverse consumer preferences.
Healthcare
Vending machines in healthcare settings provide essential medication dispensing solutions, improving patient compliance with prescribed treatments. These machines alleviate the workload of pharmacy staff and ensure that patients have easy access to their medications at all hours. For international B2B buyers, regulatory compliance is crucial, along with secure storage options to maintain the integrity of sensitive products. Suppliers must be equipped to meet stringent health regulations across different countries.
Education
In educational institutions, vending machines that offer snacks and beverages enhance student satisfaction and convenience. By providing quick access to food and drinks, these machines contribute to a positive campus experience and can help maintain student energy levels during long study sessions. Buyers should focus on a variety of products that cater to different dietary needs, ensuring compliance with nutritional guidelines. Additionally, understanding the specific needs of the student demographic is vital for product selection.
Transportation
Vending machines placed in transportation hubs address travelers’ needs for quick access to essentials such as snacks, drinks, and travel necessities. This application not only meets consumer demands but also generates additional revenue for the operators. For buyers in this sector, conducting location analysis is essential to determine the best placement for machines. Durability is also a key consideration, as machines must withstand high usage rates and varying environmental conditions.
Corporate Offices
In corporate environments, vending machines serve as refreshment stations that boost employee morale and productivity. By offering a variety of snacks and beverages, companies can create a more engaging workplace atmosphere. International buyers should prioritize product selection that aligns with employee preferences and consider machine maintenance services to ensure continuous operation. This can lead to improved employee satisfaction and retention, reflecting positively on overall company performance.
Related Video: How to Start a Vending Machine Business, Cost, Tips, How Much You Make
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vending machine route
When selecting materials for the vending machine route, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect performance, durability, and compliance with local standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in vending machine components, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C (1472°F) and can handle moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for vending machines exposed to moisture and food products. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials, and its manufacturing can be complex due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is suitable for components that come into contact with food and beverages, ensuring hygiene and safety. Its compatibility with various media, including acidic and alkaline substances, makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local food safety standards and certifications, such as the FDA in the U.S. or EU regulations. Understanding the grades of stainless steel (like 304 or 316) is crucial, as they have different corrosion resistance levels.
2. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is characterized by its high tensile strength and ability to withstand significant pressure. However, it is less resistant to corrosion, which can be a limitation in humid environments.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for structural components. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion means it often requires protective coatings, which can add to manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is suitable for non-corrosive environments, making it ideal for vending machines that dispense dry goods or in areas with low humidity. Its use in structural components can enhance the overall strength of the vending machine.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify the material’s compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN. In regions with high humidity, additional treatments or coatings may be necessary to enhance corrosion resistance.
3. Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its lightweight nature, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand temperatures up to 100°C (212°F). It is also resistant to many acids and bases.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of polypropylene is its low cost and ease of manufacturing, making it suitable for various components like trays and dispensers. However, it has lower mechanical strength compared to metals and may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is ideal for components that require flexibility and chemical resistance, such as those handling snacks or beverages. Its lightweight nature can reduce shipping costs.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with local plastic regulations and food safety standards. The availability of recycled polypropylene may also be a consideration for sustainability-focused buyers.
4. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a good strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand temperatures of around 400°C (752°F) and moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum’s primary advantage is its lightweight nature, which can reduce transportation costs. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and may not be suitable for high-stress applications without proper reinforcement.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for components requiring a balance of strength and weight, such as machine frames and panels. Its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for machines placed in outdoor or humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet relevant standards such as JIS or EN. Additionally, understanding the alloy grades is essential, as they can significantly impact performance and cost.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for vending machine route | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Components exposed to food and moisture | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components for non-corrosive environments | Cost-effective and strong | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Trays and dispensers for snacks and beverages | Lightweight and low-cost | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
| Aluminum | Frames and panels in humid environments | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | More expensive than carbon steel | Med |
This strategic material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions when sourcing materials for vending machine routes, ensuring compliance with local standards and optimizing performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vending machine route
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance (QA) for vending machines involve several critical stages and standards that ensure the products meet the requirements of international B2B buyers. This section provides an in-depth look at these processes, focusing on actionable insights for buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage involves selecting high-quality materials that are durable and suitable for vending machine construction. Common materials include:
- Metal: Steel and aluminum for the frame and housing, chosen for their strength and corrosion resistance.
- Plastic: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polycarbonate for components like panels and displays.
- Electronic Components: Circuit boards, sensors, and payment systems, which must comply with international electrical standards.
Key Techniques:
– Material Sourcing: Establish relationships with reliable suppliers who provide certified materials.
– Pre-processing: Cutting, machining, and treating materials to enhance durability, such as powder coating for metal parts.
2. Forming
This stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the required components of the vending machine.
- Techniques:
- Stamping: Used for creating metal panels and frames.
- Injection Molding: For producing plastic parts like buttons and trays.
- Laser Cutting: Provides precision in creating complex shapes and designs.
3. Assembly
The assembly process is where all components come together to form the final product.
- Assembly Line Setup: A streamlined process reduces assembly time and enhances efficiency. Workers are trained to handle specific tasks to maintain consistency.
- Modular Design: Many vending machines utilize modular components that can be easily replaced or upgraded, which is a significant selling point for buyers.
4. Finishing
Finishing touches are applied to enhance the aesthetic appeal and functionality of the vending machines.
- Painting and Coating: Protective and decorative finishes are applied to metal surfaces.
- Quality Control Inspections: Each machine undergoes inspection before leaving the production line to ensure it meets design specifications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring that vending machines operate reliably and meet consumer expectations. Here are the core aspects:
International Standards
B2B buyers should look for manufacturers who adhere to international quality standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant in some regions, particularly for machines that dispense food products.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control checkpoints are implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with specifications:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Checks the quality of raw materials and components upon arrival.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors the manufacturing process to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts comprehensive inspections of the finished product to verify functionality and safety.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods vary based on components and regulations but generally include:
- Performance Testing: Ensures that machines function correctly under load.
- Safety Testing: Checks for electrical safety, especially for components like payment systems.
- Durability Testing: Simulates long-term usage to identify potential failure points.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, verifying the quality control of suppliers is essential:
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of supplier facilities to assess compliance with quality standards.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed reports on quality control processes and results from suppliers.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent third-party organizations to conduct inspections and tests to validate supplier claims.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers must be aware of the nuances associated with quality control and certification:
- Cultural Differences: Understand the local manufacturing practices and standards in the supplier’s country. This can influence the quality and reliability of products.
- Documentation: Ensure that all certifications and quality reports are properly documented and easily accessible. These documents should be in a language that the buyer understands.
- Local Regulations: Be aware of specific regulations in your region regarding vending machines, as compliance can vary significantly.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is vital for B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions regarding vending machines. By focusing on high-quality materials, robust manufacturing practices, and thorough quality control, buyers can ensure they invest in reliable products that meet international standards. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers who prioritize quality can lead to long-term success in the vending machine business.
Related Video: The Production Planning Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vending machine route Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of vending machine route sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis will break down the key components of costs, influential pricing factors, and provide actionable insights tailored for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
- Materials: The core materials used in vending machines, such as metal, plastics, and electronic components, significantly impact overall costs. Prices can vary based on the quality and specifications required. Buyers should consider sourcing from local suppliers to mitigate import costs.
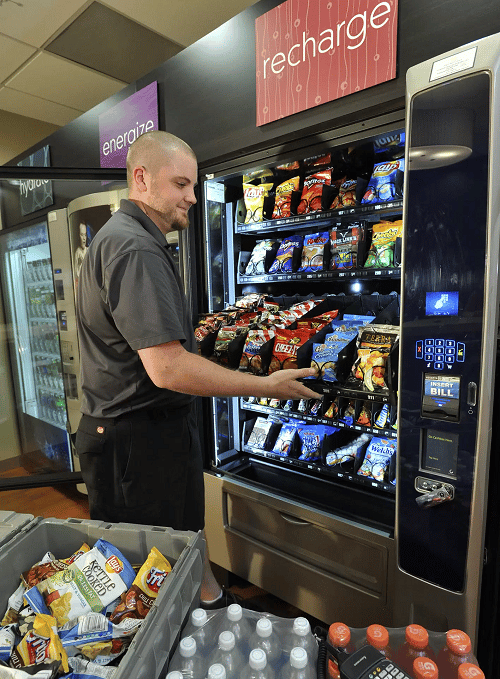

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct labor involved in manufacturing and indirect labor for administrative and operational support. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, buyers can benefit from more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, rent, and maintenance of manufacturing facilities. Understanding the overhead rates of suppliers can provide insight into their pricing structures.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific vending machine designs can be a significant upfront investment. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of customization against potential long-term benefits.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing QC processes ensures the reliability and safety of vending machines. While this may increase initial costs, it can prevent expensive recalls and repairs, leading to better Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can be substantial, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and any tariffs or customs duties should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary widely depending on market competition and supplier reputation. Negotiating terms and understanding market prices can help buyers ensure they are getting fair margins.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) often dictate pricing. Buyers should assess their purchasing power and consider placing larger orders to negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or designs can lead to increased costs. Buyers must weigh the necessity of these customizations against standard offerings.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly influences price. Opting for higher-quality materials can increase initial costs but may lead to lower maintenance expenses over time.
-
Quality/Certifications: Compliance with international standards and certifications can add costs but is crucial for market acceptance and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer premium prices due to their track record, while newer suppliers may be willing to negotiate.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms agreed upon in a contract is essential for managing logistics costs. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total price significantly.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms. Always be prepared to discuss alternatives and express interest in long-term partnerships.
-
Cost Efficiency: Buyers should focus on the Total Cost of Ownership rather than just the purchase price. This includes maintenance, operation, and potential downtime costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing strategies compared to those in Africa or South America due to varying market dynamics.
-
Research Local Suppliers: Local suppliers may offer more competitive prices and lower shipping costs. Conduct thorough market research to identify potential suppliers in your region.
-
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, demand, and raw material costs. Always request updated quotes and be prepared for price negotiations.
By understanding these cost structures, pricing influencers, and practical tips, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing vending machine routes, ensuring they secure the best value for their investments.
Spotlight on Potential vending machine route Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘vending machine route’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vending machine route
When engaging in the vending machine route business, understanding essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed decisions. Below are key specifications and terms that international B2B buyers should be familiar with.
Critical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the quality and type of materials used in the construction of vending machines, such as stainless steel, plastic, or glass.
– Importance: Higher grade materials ensure durability and longevity, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing the machine’s aesthetic appeal. For buyers in regions with harsh weather conditions, this becomes especially pertinent. -
Power Consumption
– Definition: The amount of electrical energy the vending machine uses, typically measured in watts.
– Importance: Understanding power consumption helps buyers estimate operational costs and select energy-efficient models. This is particularly relevant for businesses in regions with high electricity prices. -
Capacity and Size
– Definition: The volume of products a vending machine can hold, often expressed in terms of number of items or cubic meters.
– Importance: Buyers must match the capacity to expected sales volume. Larger machines may be beneficial in high-traffic areas, while smaller models may suffice in less frequented locations. -
Temperature Control
– Definition: The ability of a vending machine to maintain specific temperatures for products, especially for food and beverages.
– Importance: Proper temperature control is essential for product safety and quality. Buyers should ensure machines comply with local health regulations, which vary by region. -
User Interface
– Definition: The design and functionality of the machine’s interaction system, including touch screens, buttons, and payment systems.
– Importance: A user-friendly interface can increase sales by providing a seamless purchasing experience. This is vital in diverse markets, where consumer preferences for technology may vary. -
Payment Options
– Definition: The types of payment methods accepted by the vending machine, such as cash, credit/debit cards, and mobile payments.
– Importance: Offering multiple payment options can enhance customer convenience and boost sales, especially in regions with high mobile payment adoption, like parts of Africa and Europe.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Usage: Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for customized vending machines or replacement parts, as it affects warranty and service agreements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order.
– Usage: Buyers should be aware of MOQs to avoid overcommitting to inventory that may not sell quickly, especially in markets with fluctuating demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services.
– Usage: Crafting a detailed RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, ensuring that buyers get competitive offers tailored to their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of international rules defining the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in the delivery of goods.
– Usage: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international transactions to clarify shipping responsibilities, insurance, and risk of loss. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Usage: Buyers must consider lead times to ensure that their vending machines are operational when needed, particularly for seasonal or event-driven sales. -
Warranty Period
– Definition: The duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the product against defects.
– Usage: Understanding warranty terms helps buyers assess the risk associated with their investment and plan for potential future costs.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their vending machine investments, and enhance operational efficiency in diverse markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vending machine route Sector
The vending machine route sector is experiencing significant evolution driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and increasing emphasis on sustainability. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must understand these dynamics to effectively navigate the market.
Market Overview & Key Trends
Several global drivers are currently shaping the vending machine route market. The rise of cashless payments and digital transactions has transformed traditional vending operations, allowing for more streamlined purchasing experiences. Moreover, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology is enhancing inventory management, enabling operators to monitor stock levels in real-time and optimize supply routes accordingly.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the adoption of AI and machine learning for predictive analytics, which can help businesses forecast demand and tailor their offerings to specific consumer preferences. These technologies are crucial for maximizing operational efficiency and reducing costs, particularly in diverse markets across Africa and South America, where consumer behavior can vary widely.
Sourcing trends are also evolving. There’s a growing demand for localized suppliers who can provide fresh and diverse product offerings, catering to regional tastes. This trend is especially pertinent in the Middle East and Africa, where cultural preferences significantly influence product selection. B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers that can offer flexibility and responsiveness to local market demands.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As environmental concerns gain prominence, sustainability in the vending machine route sector is becoming a critical focus. The environmental impact of traditional vending operations, including energy consumption and waste generation, necessitates a shift towards more sustainable practices. B2B buyers should seek out vending machine manufacturers that prioritize energy-efficient designs and sustainable materials in their products.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers must ensure that their supply chains are transparent and adhere to fair labor practices. This not only mitigates reputational risks but also aligns with the values of increasingly eco-conscious consumers. Certifications such as Fair Trade and organic labels can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to ethical sourcing.
Incorporating ‘green’ materials in vending machine operations—such as biodegradable packaging and recyclable components—can enhance a company’s sustainability profile. Buyers should actively engage with suppliers who invest in sustainable practices and can demonstrate their environmental credentials.
Brief Evolution/History
The vending machine industry has undergone a remarkable transformation since its inception in the late 19th century. Originally designed to dispense simple products like postcards and candy, modern vending machines now offer a wide array of items, including fresh food and beverages. The integration of technology has revolutionized the sector, with innovations like touch screens, mobile payments, and remote monitoring systems becoming standard features. This evolution is not only enhancing consumer convenience but also allowing businesses to optimize their operations, making the vending machine route a vital component of the broader retail landscape.
Understanding these trends and practices is essential for international B2B buyers looking to capitalize on the opportunities within the vending machine route sector while adhering to ethical and sustainable standards.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vending machine route
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for vending machine routes?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the vending industry and their understanding of local markets, particularly in your region. Check for certifications and compliance with local regulations. Request references from existing clients to assess reliability and service quality. Additionally, evaluate their logistical capabilities, including delivery times and response to service issues, as these factors can impact your business operations. -
Can I customize vending machines to suit my market needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for vending machines, including branding, product selection, and machine design. Discuss your specific requirements upfront and ask for samples or mock-ups. It’s essential to ensure that the customization aligns with local consumer preferences and regulatory standards. Be clear about your vision to avoid miscommunication and delays in production. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for vending machines?
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the machine type and customization level. Generally, expect MOQs to range from 5 to 20 units. Lead times also vary, usually from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on customization and supplier capacity. Always confirm these details before placing an order to align your inventory needs with supplier capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing vending machines internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on supplier policies and your negotiation skills. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation (often 30-50%) with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect your investment. Clarify these terms in your contract to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for the vending machines?
Request documentation for quality assurance practices, such as ISO certifications or compliance with international safety standards. A reliable supplier should have a transparent QA process and be willing to share inspection reports. Consider conducting a factory visit or utilizing third-party inspection services to verify that the machines meet your quality expectations before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing vending machines?
Logistics play a crucial role in the successful importation of vending machines. Confirm the supplier’s logistics capabilities, including shipping options and costs. Understand customs regulations in your country to avoid delays and ensure compliance. It’s advisable to partner with a freight forwarder experienced in handling vending machines to navigate any potential challenges efficiently. -
How can I handle disputes with suppliers effectively?
To manage disputes, establish clear communication channels and maintain documentation of all transactions and agreements. Attempt to resolve issues amicably through direct dialogue before escalating matters. If necessary, refer to the dispute resolution clause in your contract, which might include mediation or arbitration. Being proactive in addressing concerns can prevent escalation and foster a better relationship with your supplier. -
What are the common challenges faced when establishing a vending machine route?
Common challenges include identifying the right locations for machines, ensuring consistent product supply, and managing maintenance and servicing. Conduct thorough market research to select high-traffic areas that align with your target audience. Additionally, develop a robust supply chain management strategy to prevent stockouts and ensure timely restocking, which is vital for maintaining customer satisfaction.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vending machine route
In today’s competitive market, effective strategic sourcing is paramount for optimizing the vending machine route business. By leveraging data-driven insights and establishing strong relationships with suppliers, international B2B buyers can enhance product offerings, reduce costs, and improve service quality. Key takeaways include the importance of local market understanding, the benefits of diversified product lines to cater to varying consumer preferences, and the necessity of adopting technology for inventory management and customer engagement.
As buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate this evolving landscape, it’s essential to be proactive in identifying new opportunities and adapting to consumer trends. The integration of sustainable practices and innovative solutions will not only improve operational efficiency but also align with growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly options.
Looking ahead, the vending machine route sector is ripe for transformation. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to capitalize on these trends, invest in strategic sourcing initiatives, and position themselves as leaders in the marketplace. Embrace this journey to enhance your competitive edge and drive long-term success.