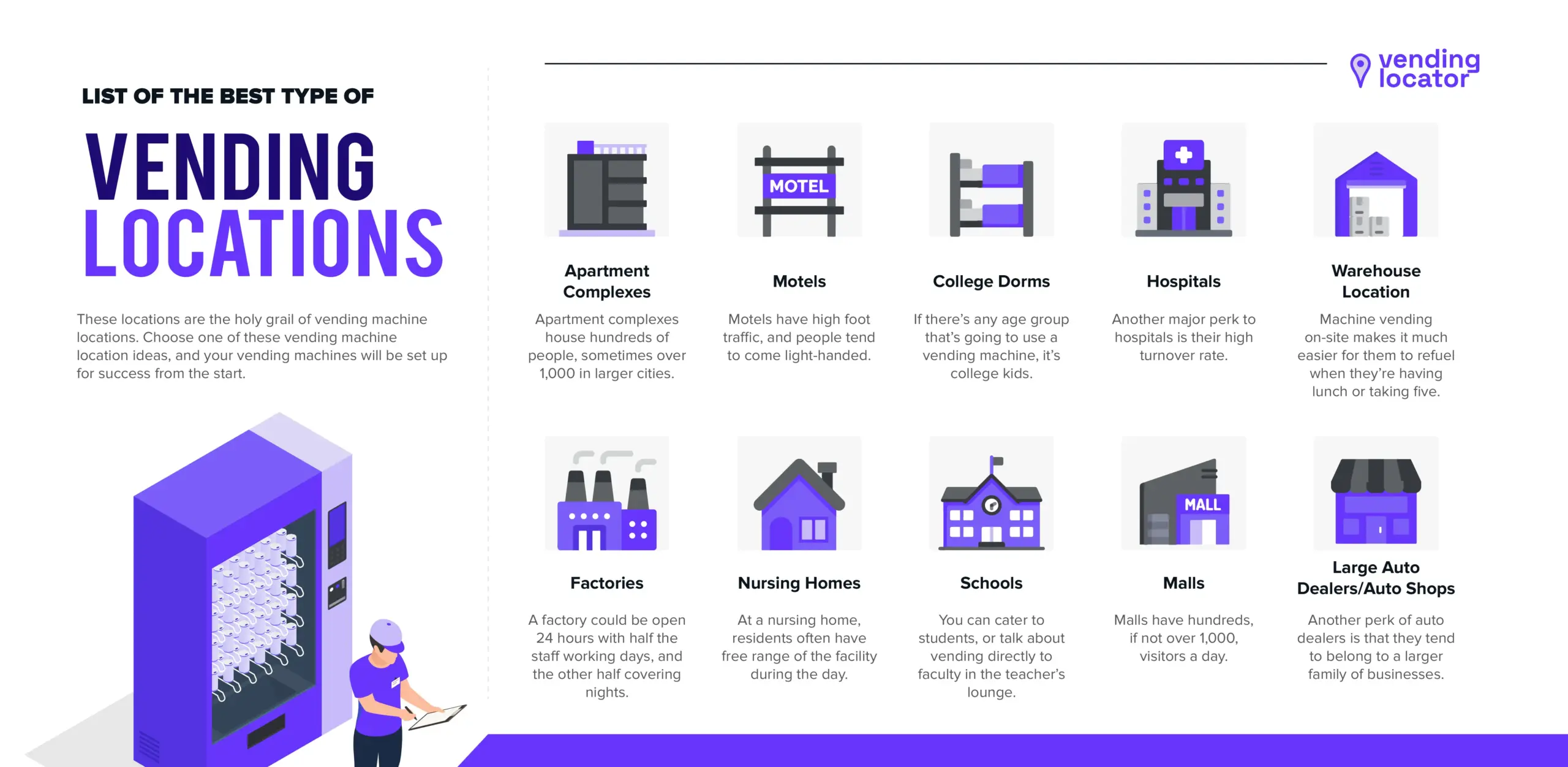
Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Places With Vending Machines
Guide to Places With Vending Machines
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for places with vending machines
- Understanding places with vending machines Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of places with vending machines
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for places with vending machines
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for places with vending machines
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for places with vending machines Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential places with vending machines Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for places with vending machines
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the places with vending machines Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of places with vending machines
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for places with vending machines
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for places with vending machines
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the demand for convenience and accessibility has driven the proliferation of vending machines across various sectors globally. For B2B buyers, understanding the strategic placement and functionality of vending machines can unlock significant opportunities. These machines are not merely points of sale; they represent a powerful channel for enhancing customer engagement, improving service delivery, and optimizing operational efficiency.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse landscape of vending machine placements, providing critical insights tailored for international buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Mexico and Colombia. It covers a wide array of topics, including the types of vending machines available, the materials used in their construction, and the manufacturing and quality control processes that ensure reliability and longevity. Furthermore, the guide offers a detailed examination of suppliers across different regions, insights into cost considerations, and an overview of the current market trends.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers will be empowered to make informed sourcing decisions, ensuring they select the right vending solutions that meet their specific needs and those of their customers. Whether you are looking to enhance your product offerings or streamline your operations, understanding the global market for vending machines is essential to staying competitive and responsive in an evolving landscape.
Understanding places with vending machines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Snack Vending | Dispenses snacks and beverages | Offices, schools, public spaces | Pros: Low maintenance, familiar to users. Cons: Limited variety, potential for stock issues. |
| Bulk Vending Machines | Dispenses larger quantities of single items | Warehouses, factories, events | Pros: Cost-effective for bulk purchases. Cons: Requires more space, potential waste if items are not popular. |
| Automated Retail Kiosks | Combines vending with retail experience | Airports, shopping malls, events | Pros: Enhanced customer experience, diverse offerings. Cons: Higher initial investment, requires tech support. |
| Health-Conscious Vending | Focuses on healthier snack options | Gyms, schools, corporate offices | Pros: Aligns with wellness trends, attracts health-conscious consumers. Cons: Potentially higher prices, limited audience. |
| Specialty Vending Machines | Offers niche products (e.g., tech gadgets) | Universities, tech hubs, events | Pros: Unique offerings attract specific demographics. Cons: Risk of limited demand, requires market research. |
Traditional Snack Vending
Traditional snack vending machines are ubiquitous in various environments, including offices, schools, and public spaces. These machines typically offer a range of snacks and beverages, catering to the general population’s preferences. For B2B buyers, the key considerations include maintenance costs and the need for regular restocking. While these machines are low-maintenance and familiar to users, they may suffer from limited variety, which can lead to stock issues if demand fluctuates.
Bulk Vending Machines
Bulk vending machines dispense larger quantities of single items, making them ideal for environments such as warehouses, factories, and events. These machines often focus on candy, toys, or other low-cost items, providing a cost-effective solution for bulk purchases. B2B buyers should consider the space requirements and potential for waste if items do not sell well. While bulk vending can lead to significant savings, it necessitates careful inventory management to avoid overstocking.
Automated Retail Kiosks
Automated retail kiosks represent a modern twist on traditional vending, integrating advanced technology to enhance the customer experience. Common in airports, shopping malls, and events, these kiosks offer a diverse range of products, from snacks to electronics. For B2B buyers, the initial investment can be higher, but the potential for increased customer engagement and sales is significant. Ongoing tech support is essential to ensure smooth operations and address any technical issues that may arise.
Health-Conscious Vending
Health-conscious vending machines cater to the growing demand for healthier snack options. Typically found in gyms, schools, and corporate offices, these machines focus on offering nutritious snacks and beverages. For B2B buyers, aligning with wellness trends can attract a health-conscious consumer base, making these machines a strategic investment. However, buyers should be aware of potentially higher prices and a limited audience, necessitating market research to ensure viability.
Specialty Vending Machines
Specialty vending machines provide niche products, such as tech gadgets or gourmet food items, targeting specific demographics like university students or tech enthusiasts. These machines can differentiate a business in competitive environments. B2B buyers should conduct thorough market research to understand demand and ensure that the offerings resonate with the target audience. While specialty vending can attract unique customers, it also carries the risk of limited demand, making careful selection and placement crucial for success.
Related Video: Business Model Canvas Explained with Examples
Key Industrial Applications of places with vending machines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of places with vending machines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Dispensing medications and health supplies | Improved patient compliance, reduced wait times | Regulatory compliance, temperature control for products |
| Education | Providing snacks and beverages in schools | Enhanced student satisfaction, reduced cafeteria costs | Variety of offerings, payment system compatibility |
| Manufacturing | Supplying tools and parts on-demand | Increased operational efficiency, reduced downtime | Inventory management, real-time tracking capabilities |
| Corporate Offices | Offering refreshments and snacks to employees | Boosted employee morale, increased productivity | Healthy options, automated inventory replenishment |
| Transportation Hubs | Delivering travel essentials and quick meals | Enhanced passenger experience, additional revenue | Location optimization, high-traffic product selection |
Healthcare Applications
In healthcare facilities, vending machines serve a critical role by dispensing medications and essential health supplies. This application addresses the challenge of patient compliance, as it allows for easy access to medications outside of regular pharmacy hours. Buyers in this sector must consider regulatory compliance to ensure that machines meet health standards, as well as the need for temperature control to preserve medication efficacy. Additionally, the integration of user-friendly interfaces can enhance patient interaction and streamline the dispensing process.
Education Applications
In educational institutions, vending machines provide snacks and beverages, catering to the needs of students throughout the day. This application not only enhances student satisfaction but also helps schools manage cafeteria costs effectively. For international buyers in this sector, it is crucial to focus on the variety of offerings to meet diverse dietary preferences and restrictions. Furthermore, payment system compatibility, including cashless options, can significantly influence purchasing decisions, especially in regions with varying technological adoption rates.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Applications
Manufacturing facilities leverage vending machines to supply tools, parts, and other necessary items on-demand. This application is particularly valuable for reducing operational downtime and increasing efficiency, as workers can quickly access what they need without lengthy delays. Buyers in the manufacturing sector should prioritize inventory management capabilities, ensuring that machines can track usage and automatically reorder supplies. Real-time tracking features can also provide insights into consumption patterns, enabling better resource allocation.
Corporate Office Applications
In corporate environments, vending machines offering refreshments and snacks can significantly boost employee morale and productivity. This application addresses the need for convenient access to food and beverages during busy work hours. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on providing healthy options to cater to growing health-conscious trends among employees. Additionally, automated inventory replenishment systems can help maintain stock levels, ensuring that popular items are always available without manual oversight.
Transportation Hub Applications
Vending machines in transportation hubs, such as airports and train stations, deliver travel essentials and quick meals to passengers on the go. This application enhances the overall passenger experience while generating additional revenue for operators. Buyers in this sector must consider location optimization to maximize foot traffic and ensure that product selections align with traveler preferences. High-traffic product offerings, such as bottled water and ready-to-eat meals, can drive sales and improve customer satisfaction in these fast-paced environments.
Related Video: Kooler Ice Vending Machines – IM600XL vs. IM1000
Strategic Material Selection Guide for places with vending machines
When selecting materials for vending machines, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the environment in which the machines will operate, the types of products they will dispense, and compliance with local standards. Below is an analysis of several common materials used in vending machine construction, along with actionable insights for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°F (427°C) and can handle moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and longevity, making it ideal for outdoor or high-traffic locations. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of media, including beverages and snacks, and is easy to clean, which is essential for maintaining hygiene in vending machines.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local food safety standards and certifications, such as ASTM or DIN. In regions like Europe, EN standards may also apply, while in Africa and South America, local regulations should be reviewed.
Polycarbonate
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and transparency. It can withstand temperatures up to 250°F (121°C) and has good UV resistance.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of polycarbonate is its lightweight nature, making it easier to transport and install. However, it is less durable than metals and can be prone to scratching, which may affect the aesthetic appeal over time.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is often used for the front panels of vending machines, allowing visibility of products. Its impact resistance makes it suitable for high-traffic areas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local safety and environmental regulations, especially regarding the recyclability of polycarbonate. Standards like JIS in Japan or ISO may also influence material selection in different regions.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a good strength-to-weight ratio. It can handle temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) and is suitable for moderate pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive and easy to fabricate, making it a popular choice for vending machine structures. However, it may not be as strong as stainless steel and can be more susceptible to dents and scratches.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in the frames and structural components of vending machines. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for various environments, including coastal areas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the various aluminum grades and their specific properties. Compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or EN, is crucial, particularly in regions with strict manufacturing regulations.
Glass
Key Properties: Glass is a rigid material that offers excellent visibility and aesthetic appeal. It can withstand moderate temperatures but is not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of glass is its transparency, which enhances product visibility and can attract customers. However, it is fragile and can break easily, requiring careful handling and installation.
Impact on Application: Glass is commonly used in vending machine doors and display cases. Its aesthetic appeal can enhance the overall customer experience but may require additional safety measures to prevent breakage.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the safety standards applicable to glass in vending machines, such as tempered or laminated glass requirements. Compliance with local regulations, particularly in Europe, where safety standards are stringent, is essential.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for places with vending machines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Structural components, exterior panels | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing process | High |
| Polycarbonate | Front panels, product displays | Lightweight, impact-resistant | Prone to scratching, less durable | Medium |
| Aluminum | Frames, structural components | Cost-effective, easy to fabricate | Less strong than stainless steel, dents easily | Low |
| Glass | Doors, display cases | Aesthetic appeal, excellent visibility | Fragile, requires careful handling | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for vending machines, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for places with vending machines
Understanding the Manufacturing Processes for Vending Machines
When it comes to vending machines, the manufacturing process is critical for ensuring durability, reliability, and efficiency. The process typically involves several key stages:
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process involves selecting high-quality materials that meet both functional and aesthetic requirements. Common materials used include:
- Metal Alloys: For structural components, ensuring strength and longevity.
- Plastics: Used in components like buttons and displays for lightweight and design flexibility.
- Glass: Often used for front panels to display products attractively.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who utilize materials that comply with international quality standards, ensuring safety and sustainability.
2. Forming
This stage includes shaping the raw materials into specific components. Key techniques employed in this phase are:
- Stamping: Commonly used for metal parts, allowing for precise shapes.
- Injection Molding: Essential for producing plastic components with complex designs.
- CNC Machining: Used for high-precision parts that require tight tolerances.
Buyers should inquire about the technologies used by suppliers to ensure they are leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques that enhance product quality.
3. Assembly
After forming, the components are assembled into the final product. This step often involves:
- Automated Assembly Lines: Utilizing robotics for speed and accuracy.
- Manual Assembly: Necessary for complex tasks that require human dexterity.
- Quality Checks During Assembly: Frequent inspections ensure that components fit correctly and function as intended.
B2B buyers should assess the efficiency of the assembly processes and the training of personnel to maintain high standards.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves applying finishes that enhance both functionality and appearance. Techniques include:
- Painting and Coating: Protects against corrosion and wear, while also providing an appealing look.
- Screen Printing: Used for branding and user interface elements on the machine.
A strong finishing process not only improves aesthetics but also extends the machine’s lifespan, which is crucial for buyers looking for durability.
Quality Assurance Measures
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of vending machines. B2B buyers should be aware of various international standards and industry-specific certifications that ensure the quality of products.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard ensures that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Indicates that a product conforms to European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
These certifications provide buyers with confidence in the reliability of their suppliers.
Industry-Specific Standards
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for vending machines that dispense food or beverages, ensuring hygiene and safety in production processes.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is often segmented into various checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the production process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive checks on the finished product before it is shipped.
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers have robust QA processes in place at each of these checkpoints.
Common Testing Methods
To validate the quality of vending machines, several testing methods are employed:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that all mechanical and electronic components operate correctly.
- Durability Testing: Simulates long-term use to assess how machines withstand wear and tear.
- Safety Testing: Verifies that machines meet safety regulations, especially for electrical components.
Buyers should request details on the testing protocols used by suppliers to gauge the thoroughness of their quality assurance processes.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following verification methods:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular on-site audits to assess manufacturing practices and quality controls.
- Quality Reports: Request documentation that details the QA processes, inspection results, and compliance with standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies to conduct assessments and validate supplier claims.
These steps are essential for mitigating risks and ensuring that the products meet the required specifications.
Navigating QC Nuances for International Buyers
For B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control can be crucial:
- Cultural Differences: Recognize that quality expectations may vary by region. Engage with suppliers to establish a common understanding.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers understand and comply with local regulations in the buyer’s region, which may differ significantly from their own.
- Language Barriers: Effective communication is vital. Consider using bilingual representatives or translators during negotiations and audits to avoid misunderstandings.
By taking these factors into account, international buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and build strong, quality-driven partnerships with suppliers in the vending machine industry.
Related Video: Most Satisfying Factory Production Processes And Heavy-Duty Factory Machines!
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for places with vending machines Sourcing
When sourcing vending machines, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis will delve into the key cost components and pricing influencers that affect sourcing decisions, while also providing actionable buyer tips tailored for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The materials used in manufacturing vending machines significantly impact costs. Common materials include steel for the frame, plastic for components, and electronic parts for payment systems. Sourcing quality materials may increase initial costs but can lead to better durability and lower maintenance expenses over time.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing; however, it is crucial to assess the skill level and experience of the workforce to ensure quality craftsmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, rent, and administrative costs that a manufacturer incurs. Understanding these costs can help buyers identify suppliers that maintain efficient operations, which can translate to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom designs can be substantial. Buyers should consider whether they require bespoke solutions or can work with standard models. Standard machines typically come with lower tooling costs and faster lead times.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality control measures can raise initial costs but is essential for ensuring reliability and compliance with international standards. Buyers should inquire about the QC processes of potential suppliers to assess the risk of defects and associated costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can significantly affect the total price. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties play a role. Buyers should evaluate logistics options early in the sourcing process to manage costs effectively.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on the market and competition. Buyers should be aware of the typical margins in their region to negotiate better prices.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing can lead to discounts. Understanding the minimum order quantity (MOQ) that suppliers require can help buyers negotiate more favorable terms.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized machines often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the additional costs involved.
-
Materials Quality/Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can influence pricing. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their market to avoid paying for unnecessary features.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices but can offer peace of mind regarding product performance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is critical for international transactions. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always be prepared to negotiate. Suppliers may have flexibility in pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Building a good relationship with suppliers can also lead to better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. A lower upfront cost may not always equate to better value in the long run.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, suppliers in Europe may have higher base prices due to labor and regulatory costs compared to those in South America or Africa. Understanding these nuances can help in making informed sourcing decisions.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to benchmark prices and quality. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help them select the best suppliers.
Disclaimer
Prices and costs mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market fluctuations, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct due diligence when assessing potential suppliers and pricing structures.
Spotlight on Potential places with vending machines Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for places with vending machines.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for places with vending machines
When engaging in international trade for vending machines, understanding the essential technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This section will outline critical specifications and common jargon that can facilitate smoother transactions and better product quality.
Essential Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of materials used in the construction of vending machines, including metals (stainless steel, aluminum) and plastics (polycarbonate).
– B2B Importance: Higher material grades often correlate with increased durability and resistance to environmental factors, which is vital for machines placed in varied climates. Buyers should prioritize machines made from high-grade materials to ensure longevity and lower maintenance costs. -
Dimensions and Weight
– Definition: The physical size (height, width, depth) and weight of the vending machine.
– B2B Importance: Understanding these specifications is critical for ensuring that machines fit in designated spaces and comply with local regulations. Additionally, weight affects shipping costs and installation logistics, making it essential for buyers to consider these factors during procurement. -
Power Requirements
– Definition: The voltage and amperage needed to operate the vending machine.
– B2B Importance: Different regions have varying electrical standards. Ensuring that the machine meets local power specifications can prevent operational failures and reduce the risk of damage. This is especially significant for buyers in regions with less reliable power sources. -
Capacity and Configuration
– Definition: The number of items the vending machine can hold and the layout of the product slots.
– B2B Importance: Capacity directly impacts revenue potential. Buyers should assess the expected customer volume and product types to select a machine that maximizes sales opportunities. Configurations should also allow for easy replenishment and product rotation. -
User Interface and Technology
– Definition: Features like touchscreen displays, cashless payment options, and software for inventory management.
– B2B Importance: A user-friendly interface enhances customer experience, increasing the likelihood of repeat purchases. Advanced technology can also provide real-time data on sales and inventory, aiding in effective stock management.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: For B2B buyers, partnering with OEMs can ensure high-quality components that meet specific standards, which is essential for the reliability of vending machines. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is critical for budgeting and inventory planning. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their sales forecasts to avoid excess stock or missed sales opportunities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other relevant information for a specific product.
– Importance: An RFQ helps buyers gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better decision-making and cost management. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms is essential for defining shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation. This can significantly influence the total landed cost of vending machines. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time between the initiation of an order and its delivery.
– Importance: Buyers must consider lead times when planning for inventory and sales strategies. Longer lead times can affect cash flow and operational efficiency, making it vital to communicate these timelines clearly with suppliers.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make more informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and ultimately enhance their business operations in the vending machine market.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the places with vending machines Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The vending machine sector is experiencing a significant transformation driven by various global factors. As urbanization increases in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for convenient, on-the-go solutions is surging. This shift is supported by the rise of e-commerce and digital payment systems, allowing for a seamless purchasing experience. Notably, the integration of smart technology is revolutionizing the sector, with IoT-enabled machines providing real-time inventory management, customer analytics, and personalized marketing.
Emerging trends include a growing preference for healthy and locally sourced products. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking partnerships with suppliers who offer organic snacks and beverages that cater to health-conscious consumers. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in purchasing decisions, with many businesses prioritizing eco-friendly packaging and energy-efficient machines. The market is also witnessing a diversification of vending offerings, from traditional snacks to fresh food, beverages, and even electronics, broadening the appeal to various consumer segments.
For international buyers, understanding local market dynamics is essential. Each region presents unique challenges and opportunities, influenced by cultural preferences, economic conditions, and regulatory environments. For instance, in countries like Mexico and Colombia, local tastes can significantly affect product selection. Buyers should leverage market research and local partnerships to navigate these complexities effectively.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer an option but a necessity in the vending machine industry. The environmental impact of traditional vending practices, from excessive plastic waste to energy consumption, has prompted a shift towards greener alternatives. B2B buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing products and services that minimize ecological footprints. This includes selecting machines that are energy-efficient and equipped with solar panels, as well as opting for biodegradable or recyclable packaging materials.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are vital for building a reputable brand. Buyers should evaluate their suppliers based on their commitment to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing. Certifications such as Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, and organic labels can help buyers identify and partner with ethical suppliers. By aligning with these values, businesses not only meet consumer expectations but also enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles, which can be a significant competitive advantage.
Investing in sustainability and ethical sourcing not only contributes to environmental conservation but also caters to the growing consumer demand for responsible business practices. This alignment can ultimately lead to increased customer loyalty and brand strength in an increasingly competitive market.
Brief Evolution/History
The vending machine industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 19th century, transitioning from simple coin-operated machines dispensing postcards and chewing gum to the sophisticated, tech-driven solutions available today. Initially popular in Europe and the United States, vending machines have expanded globally, adapting to local markets and consumer preferences.
In recent decades, the introduction of electronic payment systems and advanced inventory management technologies has transformed vending operations. Today’s machines are equipped with touch screens, cashless payment options, and even mobile app integrations, enhancing user experience and operational efficiency. This evolution is not just about convenience; it reflects a broader trend towards automation and digitalization in the B2B sector, providing valuable insights for international buyers looking to invest in the future of vending solutions.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of places with vending machines
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of vending machines?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, product quality, and customer reviews. Verify their certifications and compliance with local regulations in your target markets. It’s also crucial to assess their financial stability and after-sales support capabilities. Engage in direct conversations with potential suppliers to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to customize products to meet your specific needs. -
Can I customize vending machines to fit my brand or product offerings?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for vending machines, including branding elements like logos and colors. You can also request modifications to accommodate specific product sizes or types, such as healthy snacks or beverages. Ensure to communicate your requirements clearly and verify the supplier’s ability to deliver these customizations within your desired timeframe. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for vending machines?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the machine type. Generally, you might encounter MOQs ranging from 5 to 50 units. Lead times often depend on customization requests and production schedules, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss these details upfront and include them in your purchasing agreement to avoid surprises. -
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for vending machines?
Common payment terms include a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipping. Some suppliers may offer payment through letters of credit or escrow services for added security. It’s essential to clarify payment methods, currencies, and timelines in your contract to ensure smooth financial transactions and to mitigate risks associated with currency fluctuations. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from vending machine suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should provide documented quality assurance processes, including inspections and testing protocols for their products. Request information on certifications such as ISO 9001 or relevant safety standards applicable in your region. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and the supplier’s approach to handling defective units or product recalls. -
How do logistics and shipping work for international orders of vending machines?
Logistics for international orders typically involve freight forwarding services that handle shipping and customs clearance. Ensure your supplier has a reliable logistics partner and can provide tracking information. Discuss shipping options—air vs. sea freight—and associated costs. Additionally, clarify who bears responsibility for insurance and potential customs duties upon arrival. -
What steps should I take to resolve disputes with vending machine suppliers?
Establish clear communication channels and document all interactions with suppliers. In the event of a dispute, attempt to resolve issues amicably through direct negotiation. If necessary, refer to the dispute resolution clause in your contract, which may suggest mediation or arbitration. Having a legal advisor familiar with international trade can also be beneficial for navigating complex disputes. -
What certifications should I look for when sourcing vending machines?
Look for certifications that ensure product safety and compliance with international standards, such as CE marking for the European market or UL certification in the United States. Additionally, check for local certifications relevant to your target market, as these can enhance your credibility and ensure that the machines meet local regulatory requirements. Always ask suppliers for copies of these certifications before finalizing your purchase.
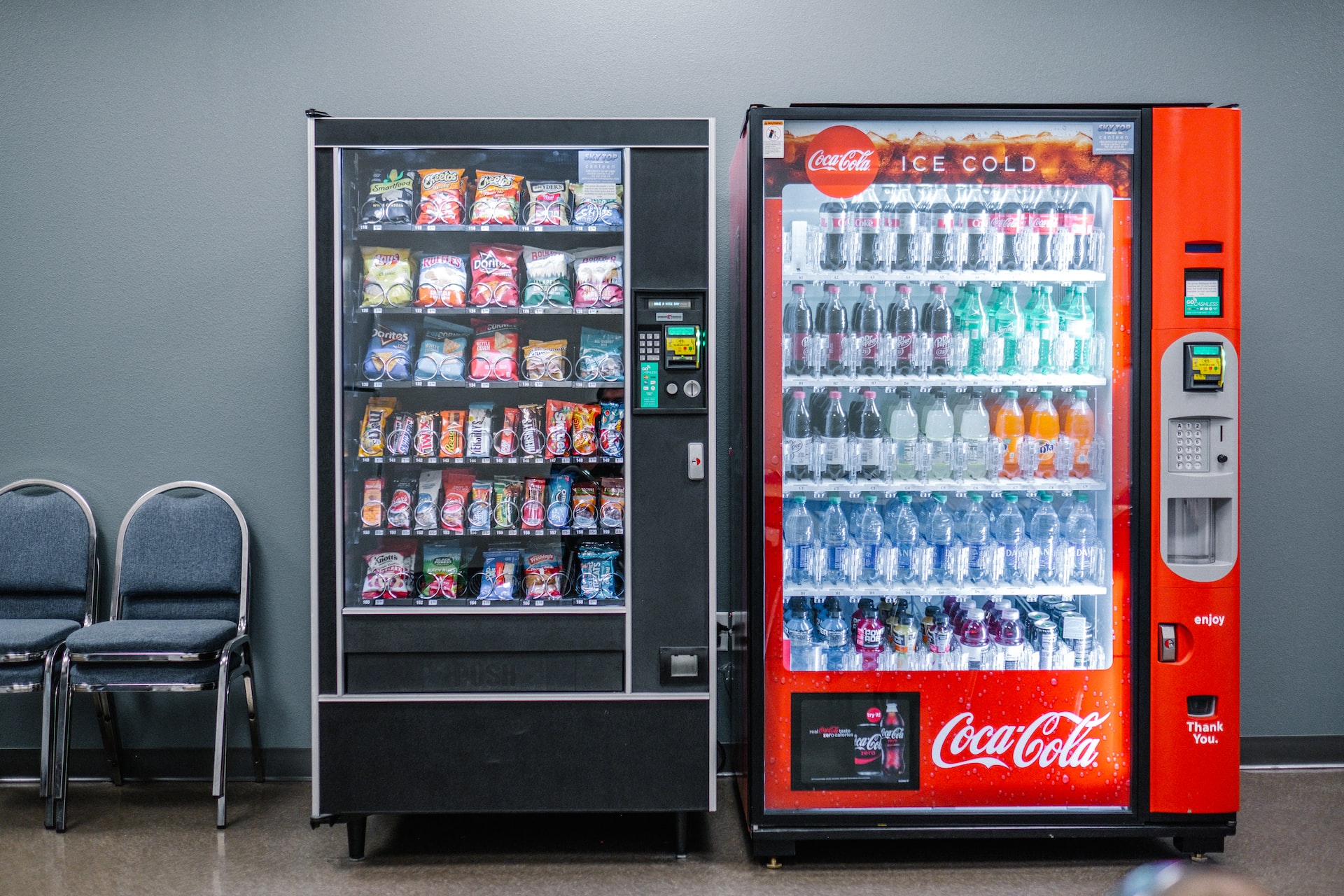
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for places with vending machines
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of vending machines offers significant opportunities for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing quality suppliers who can meet the diverse needs of local markets, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and improve operational efficiency.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key takeaways include:
- Market Understanding: Thoroughly research local preferences and trends to select products that resonate with consumers in your target region.
- Supplier Relationships: Foster strong partnerships with reliable vendors to ensure consistent product quality and timely delivery.
- Cost Management: Leverage bulk purchasing and negotiate terms that allow for competitive pricing without compromising on quality.
- Sustainability: Consider eco-friendly options to align with global sustainability trends, which can also serve as a unique selling point in marketing efforts.
As we look forward, the landscape of vending machine placements is poised for transformation. Embracing innovative technologies and adaptable business models will be crucial in capturing emerging market trends. International B2B buyers are encouraged to seize these opportunities, optimize their sourcing strategies, and position themselves for success in a competitive environment. The future of vending machines is bright—align your sourcing strategies today to reap the benefits tomorrow.