Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Hot Food Vending Machine
Guide to Hot Food Vending Machine For Sale
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hot food vending machine for sale
- Understanding hot food vending machine for sale Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of hot food vending machine for sale
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for hot food vending machine for sale
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hot food vending machine for sale
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hot food vending machine for sale Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential hot food vending machine for sale Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hot food vending machine for sale
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the hot food vending machine for sale Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hot food vending machine for sale
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hot food vending machine for sale
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hot food vending machine for sale
In today’s fast-paced world, the demand for convenient and accessible food options is on the rise, particularly in urban areas across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Hot food vending machines have emerged as a transformative solution, offering a diverse range of freshly prepared meals to meet the needs of busy consumers. These machines not only enhance customer satisfaction but also provide a lucrative opportunity for businesses looking to expand their service offerings.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international B2B buyers by providing critical insights into the hot food vending machine market. Covering essential aspects such as types of machines, materials used, manufacturing quality control, and supplier recommendations, this resource is tailored to facilitate informed sourcing decisions. Additionally, we will explore cost considerations, market trends, and a curated list of frequently asked questions to address common concerns and challenges faced by buyers.
By delving into these topics, buyers from regions like Colombia and Spain will gain a clearer understanding of the hot food vending machine landscape, enabling them to identify reliable suppliers and make strategic purchasing decisions. In an increasingly competitive market, leveraging this knowledge can lead to improved operational efficiency and enhanced customer engagement.
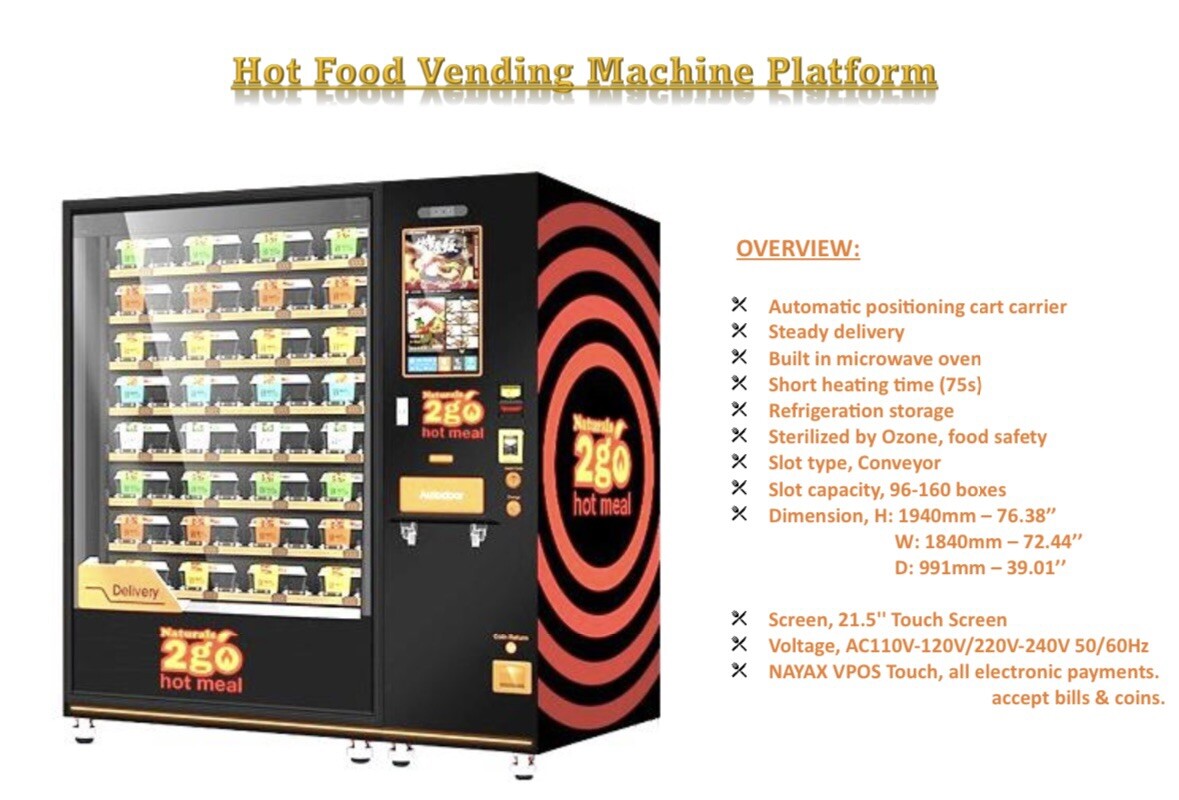
Understanding hot food vending machine for sale Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Hot Food Vending Machine | Offers a variety of hot meals, often with a microwave for heating | Offices, schools, hospitals | Pros: Easy to use, familiar technology; Cons: Limited menu options, potential for equipment failure. |
| Smart Hot Food Vending Machine | Equipped with touch screens, cashless payment options, and remote monitoring | Corporate campuses, public areas | Pros: Enhanced user experience, data analytics; Cons: Higher initial investment, requires internet connectivity. |
| Compact Hot Food Vending Machine | Smaller footprint, designed for tight spaces, often with fewer meal options | Small offices, break rooms | Pros: Space-saving, lower cost; Cons: Limited capacity, fewer menu choices. |
| Gourmet Hot Food Vending Machine | Offers premium meals, often from local restaurants, and features high-quality ingredients | Airports, upscale workplaces | Pros: Attracts health-conscious consumers, diverse menu; Cons: Higher operational costs, may require partnerships with local chefs. |
| Mobile Hot Food Vending Machine | Designed for mobility, often truck-mounted or trailer-based | Events, festivals, construction sites | Pros: Flexibility in location, ability to cater events; Cons: Dependent on location regulations, potential logistical challenges. |
Traditional Hot Food Vending Machine
These machines typically offer a selection of pre-packaged hot meals that can be heated on-site, often utilizing microwave technology. They are widely used in environments such as offices, schools, and hospitals where convenience is paramount. When considering purchasing, businesses should evaluate the variety of meals available and the reliability of the machine, as equipment failures can lead to disruptions in service.
Smart Hot Food Vending Machine
Smart vending machines are equipped with advanced technologies, including touch screens for user interaction and cashless payment systems. They are particularly suitable for corporate campuses and public areas where user experience and data collection are valued. Buyers should consider the initial investment and ongoing maintenance, as these machines require reliable internet connectivity and may involve more complex servicing.
Compact Hot Food Vending Machine
Designed for spaces with limited room, compact machines provide a smaller selection of hot meals. They are ideal for small offices or break rooms where space is a premium. While these machines are generally more affordable and easier to install, buyers need to be aware of their limited meal capacity and variety, which may not meet the needs of larger teams.
Gourmet Hot Food Vending Machine
Offering high-quality meals often sourced from local restaurants, gourmet vending machines cater to health-conscious consumers and are commonly found in airports and upscale workplaces. These machines can enhance a company’s image by providing premium food options. However, businesses should consider the higher operational costs and the necessity of establishing partnerships with local food providers.
Mobile Hot Food Vending Machine
Mobile vending machines, typically mounted on trucks or trailers, provide flexibility for businesses looking to cater to events or operate in multiple locations. They are particularly useful at festivals and construction sites. However, buyers must navigate location regulations and potential logistical challenges, such as ensuring consistent food quality and managing inventory on the move.
Related Video: TCN hot food vending machine
Key Industrial Applications of hot food vending machine for sale
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hot food vending machine for sale | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Patient and staff meal provision | Quick access to nutritious meals, reduces wait times | Compliance with health regulations, temperature control features |
| Education | Campus dining options | Enhances student satisfaction, offers diverse food choices | Payment system integration, energy efficiency |
| Transportation | Train and bus stations | Provides convenience for travelers, increases revenue | Durability for outdoor use, adaptability to various food types |
| Corporate Offices | Employee break rooms | Boosts employee morale, encourages healthy eating | Compact design, easy maintenance |
| Retail | Shopping malls and supermarkets | Attracts customers, increases foot traffic | High turnover rate, variety of food options |
Healthcare
In healthcare settings, hot food vending machines serve as efficient meal providers for both patients and staff. These machines can offer a variety of nutritious meals, ensuring that individuals in hospitals or clinics have quick access to food without long wait times. For international buyers, compliance with local health regulations is crucial, as well as features that maintain proper temperature control to ensure food safety.
Education
In educational institutions, hot food vending machines are increasingly adopted to provide diverse dining options for students. These machines can cater to varying dietary needs, enhancing student satisfaction and promoting healthier eating habits. For buyers in regions like South America and Europe, integrating payment systems that accommodate digital transactions and ensuring energy efficiency are essential considerations.
Transportation
Hot food vending machines are strategically placed in train and bus stations to cater to travelers seeking convenient meal options. They help reduce congestion in dining areas and provide a steady revenue stream for transportation hubs. Buyers should consider the machine’s durability for outdoor exposure and its ability to handle a variety of food types, especially in diverse climates found in the Middle East and Africa.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Corporate Offices
In corporate environments, hot food vending machines can significantly improve employee satisfaction by offering quick meal solutions in break rooms. They encourage healthier eating habits and can boost productivity by minimizing downtime during lunch breaks. For international buyers, it is important to select machines with a compact design that can fit into limited spaces and are easy to maintain for continuous operation.
Retail
In retail environments, such as shopping malls and supermarkets, hot food vending machines can attract customers and increase foot traffic. They provide quick meal options for shoppers, enhancing their overall experience. Key considerations for buyers include ensuring a high turnover rate for the food offered and providing a variety of options that cater to different tastes and preferences, especially in culturally diverse regions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hot food vending machine for sale
When selecting materials for hot food vending machines, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Here’s a detailed analysis of common materials used in these machines, focusing on their properties, advantages, limitations, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength. It can withstand temperatures up to 800°C (1472°F) and is often used in environments where hygiene is paramount.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and staining, making it ideal for food applications. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes, increasing production complexity.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of food products, maintaining food safety and quality. Its non-reactive nature ensures that it does not alter the taste or quality of the food.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with food safety standards such as FDA (USA) or EU regulations is crucial. Buyers should also be aware of local standards like ASTM or DIN, which may dictate specific grades of stainless steel for food contact.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for heating applications. It generally withstands temperatures up to 600°C (1112°F) and is resistant to corrosion when anodized.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, often resulting in lower production costs. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can deform under high temperatures or heavy loads, which may limit its use in certain applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with various food types, but its lower strength may be a concern for heavy-duty machines. Anodized aluminum can enhance its durability and corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that the aluminum used meets local standards for food safety. In regions with high humidity, additional coatings may be necessary to prevent corrosion.
Polycarbonate
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is a high-performance plastic known for its impact resistance and clarity. It can withstand temperatures up to 135°C (275°F) and is often used in areas requiring visibility, such as display windows.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polycarbonate is its lightweight nature and high impact resistance, making it ideal for safety and visibility. However, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications and can be prone to scratching.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is suitable for non-contact surfaces and displays but should not be used for components that directly heat food. Its transparency allows customers to view food items, enhancing sales potential.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should ensure that polycarbonate complies with regulations regarding food safety and environmental impact, such as REACH in Europe. Understanding local recycling regulations is also important.
Glass
Key Properties:
Glass is non-porous and chemically resistant, making it an excellent choice for food applications. It can withstand high temperatures and is often used in heating elements.
Pros & Cons:
Glass offers aesthetic appeal and excellent thermal stability. However, it is fragile and can break easily, posing safety risks. Manufacturing glass components can also be more complex and costly.
Impact on Application:
Glass is suitable for food storage and display, ensuring that food remains uncontaminated. Its inert nature means it does not react with food, preserving flavor and quality.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the fragility of glass and ensure proper packaging and handling during shipping. Compliance with local safety standards is essential, especially in regions with strict regulations regarding food service equipment.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for hot food vending machine for sale | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Structural components, heating elements | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Body panels, structural supports | Lightweight, cost-effective | Lower strength, deformation risk | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Display windows, non-contact surfaces | High impact resistance, visibility | Not suitable for high temperatures, prone to scratches | Low |
| Glass | Food storage, heating elements | Non-reactive, aesthetic appeal | Fragile, complex manufacturing | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into material choices for hot food vending machines, helping them make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hot food vending machine for sale
In the competitive market for hot food vending machines, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section outlines the typical manufacturing stages, key techniques, relevant international standards, quality control checkpoints, and how buyers can effectively verify supplier quality assurance.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of hot food vending machines involves several critical stages, each requiring precision and attention to detail.
1. Material Preparation
This initial stage involves sourcing high-quality materials such as stainless steel, tempered glass, and high-grade electronics. Suppliers should focus on:
- Material Selection: Ensure that materials are resistant to corrosion and wear, suitable for food safety.
- Pre-Processing: Materials may undergo treatments like cutting, bending, or surface finishing to prepare them for the next stage.
2. Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the components of the vending machine.
- Techniques: Common techniques include stamping, molding, and laser cutting. Each technique should be chosen based on the component’s design and functional requirements.
- Automation: Utilizing CNC machines can enhance precision and reduce waste during the forming process.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the final product.
- Modular Design: Implementing a modular design allows for easier assembly and maintenance, which is beneficial for both manufacturers and end-users.
- Integration of Systems: This includes the installation of heating elements, refrigeration units, and electronic control systems. Proper alignment and integration are crucial to ensure functionality.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the machine’s aesthetic appeal and durability.
- Surface Treatments: Processes such as powder coating or anodizing can improve corrosion resistance and provide a visually appealing finish.
- Testing of Features: Ensure that all components function correctly, including heating, cooling, and payment systems.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process, especially in the context of international B2B sales.
International Standards
B2B buyers should ensure that manufacturers adhere to relevant international standards, which include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that products meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently.
- CE Marking: For machines sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Depending on the regions served, certain API standards may apply, especially concerning food safety and equipment reliability.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, random checks are conducted to monitor the quality of work and adherence to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, the completed machines undergo comprehensive testing to ensure all systems operate correctly and meet quality standards.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of the testing methods used to ensure product quality:
- Functional Testing: Each machine is tested to confirm that heating, cooling, and vending mechanisms work properly.
- Safety Testing: Compliance with electrical safety standards is verified, including overload protection and emergency shut-off systems.
- Durability Testing: Machines are subjected to stress tests to evaluate their performance under varying operational conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Assurance
For B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is vital.
Supplier Audits
Conducting supplier audits can provide insight into the manufacturing practices and quality control measures in place. Key aspects include:
- Facility Inspection: Evaluating the manufacturing environment for cleanliness and organization.
- Process Evaluation: Reviewing the steps taken to ensure quality at each stage of production.
Quality Reports
Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s adherence to standards:
- Production Reports: These should outline the number of units produced, defects found, and corrective actions taken.
- Certification Documents: Ensure that suppliers provide documentation of compliance with ISO and other relevant standards.
Third-Party Inspections
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance processes. These services typically involve:
- Pre-Shipment Inspections: Conducting inspections before products are shipped to ensure they meet the agreed-upon specifications.
- Random Sampling: Assessing a sample of units from a batch to verify overall quality.
Nuances for International B2B Buyers
Navigating the nuances of quality assurance for hot food vending machines is essential for international buyers. Factors such as regional regulations, cultural expectations, and logistical challenges can influence quality standards.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding regional preferences for machine design, functionality, and safety can enhance buyer-supplier relationships.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarizing oneself with local regulations and standards is crucial, as they can vary significantly between regions such as Europe and Africa.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing hot food vending machines, ensuring that they partner with reliable suppliers who meet international standards.
Related Video: Parle-G Biscuits Manufacturing process – Food Factory Tour- Modern Food factory, Mega Factory II
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hot food vending machine for sale Sourcing
When sourcing hot food vending machines, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will provide insights into the various cost components, pricing influencers, and actionable tips for negotiating better deals.
Cost Structure
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in manufacturing hot food vending machines includes high-quality materials such as stainless steel, plastics, and electronic components. The choice of materials directly impacts durability and functionality. Bulk purchasing can significantly reduce material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Western Europe, the manufacturing expenses will be higher compared to regions with lower labor costs, like parts of Africa and South America. Outsourcing production to low-cost countries can be a viable strategy for reducing overall labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and indirect labor costs associated with the production facility. Efficient management of manufacturing processes and overhead can lead to significant savings.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. This includes molds and dies used in the manufacturing process. For buyers requiring specific features or designs, it is essential to factor in these costs early in the sourcing process.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the machines meet safety and operational standards incurs costs. Implementing a robust QC process is essential, especially for machines intended for food service, where health and safety regulations are stringent.
-
Logistics: Transporting machines from the manufacturer to the buyer’s location can add significant costs, particularly for international shipments. Consideration of shipping methods, tariffs, and local logistics is essential to calculate the total cost accurately.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin on top of the production costs, which can range from 10% to 30% depending on the market and competition. Understanding the expected margin can help buyers negotiate better.
Pricing Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) often influence pricing. Higher volume purchases can lead to lower per-unit costs, making it essential for buyers to consider their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom machines with specific features or branding will generally incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly outline their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The choice of materials affects pricing. For example, opting for high-grade materials will increase costs, but may be necessary for durability and compliance with regulations.
-
Quality/Certifications: Machines with certifications (e.g., CE marking in Europe) may come at a premium. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications are essential for their market.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can significantly influence pricing. Establishing a relationship with reputable suppliers may yield better terms and pricing.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for determining responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This can affect total costs and should be clearly defined in contracts.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms and prices. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but maintenance, operational costs, and longevity of the machine. This approach can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. Factors such as local demand, competition, and economic conditions can lead to significant variations in pricing.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research and compare multiple suppliers to identify the best value for your requirements.
Disclaimer
Prices for hot food vending machines can vary widely based on specifications, supplier location, and market conditions. The information provided here is indicative, and buyers are encouraged to conduct their own due diligence before making purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential hot food vending machine for sale Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘hot food vending machine for sale’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hot food vending machine for sale
Understanding the essential technical properties and terminology associated with hot food vending machines is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section provides insights into the critical specifications that buyers should consider and the trade terms commonly used in the industry.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
The material used in hot food vending machines typically includes stainless steel for its durability and resistance to corrosion. Buyers should ensure that the materials meet local health and safety standards, which can vary by region. High-quality materials reduce the likelihood of breakdowns and ensure longevity, making it a vital consideration for B2B buyers. -
Temperature Control Range
The ability of a vending machine to maintain a specific temperature range is essential for food safety and quality. Machines should have a temperature control range that complies with food safety regulations. For instance, maintaining temperatures above 60°C (140°F) is crucial for hot food. This specification is particularly important for buyers in regions where food safety standards are stringent. -
Power Consumption
Energy efficiency is a significant factor for operational costs. Vending machines should be evaluated based on their power consumption, often measured in watts. Machines with lower power consumption not only reduce electricity bills but also contribute to sustainability goals, which can be a selling point for businesses focusing on eco-friendly practices. -
Capacity and Size
The dimensions and storage capacity of the vending machine directly impact its usability. Buyers should consider the volume of food items they plan to offer and the physical space available for installation. Understanding the capacity can help in optimizing inventory management and ensuring that the machine meets the demands of the intended market. -
User Interface and Payment Options
A user-friendly interface enhances customer experience and can influence sales. Additionally, the availability of various payment options, including cash, card, and mobile payments, is increasingly important. Buyers should look for machines that offer flexible payment solutions to cater to diverse customer preferences.
- Warranty and Support
Warranty terms and the availability of technical support are crucial for long-term investment. A robust warranty indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in their product and provides peace of mind for the buyer. Understanding the terms of service and support options is essential for minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, understanding OEM relationships can help in sourcing high-quality components and ensuring compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for buyers to consider when planning inventory purchases, as it affects cost and storage. Negotiating lower MOQs can be beneficial for smaller businesses or those testing new products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific quantities of goods. It’s an essential tool for buyers to gather competitive pricing and assess supplier capabilities before making purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding Incoterms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for buyers to clarify shipping costs and risks involved in the transaction. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving it. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is critical for inventory planning and ensuring timely availability of products, especially in competitive markets. -
Customization
This term refers to the ability to modify products according to specific buyer requirements. For businesses looking to differentiate themselves in the market, understanding customization options can enhance the product offering and meet unique customer needs.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing hot food vending machines, ensuring they meet both operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the hot food vending machine for sale Sector
In the competitive landscape of the hot food vending machine market, international B2B buyers must navigate a variety of market dynamics and emerging trends. The global push towards convenience and on-the-go dining has intensified demand for hot food vending solutions. Key drivers include urbanization, busy lifestyles, and the increasing need for contactless services, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. This shift has led to the integration of technology, such as cashless payment systems and IoT capabilities, allowing vendors to monitor inventory and sales in real-time.
Emerging trends highlight a focus on personalization and diverse menu options. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America are increasingly seeking machines that can cater to local tastes and preferences, integrating traditional foods into their offerings. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on health-conscious options, with machines featuring fresh, organic, and nutritious meals. This trend is particularly resonant in European markets, where consumers prioritize sustainability and healthy eating.
For international buyers, understanding these market dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions. Collaborating with manufacturers who are responsive to these trends can enhance competitiveness. Networking with suppliers who offer customizable machines and can adapt to regional demands will be a significant advantage.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies within the hot food vending machine sector. The environmental impact of traditional vending machines, particularly concerning energy consumption and waste generation, cannot be overlooked. Buyers are encouraged to seek machines that utilize energy-efficient technologies and sustainable materials. For instance, selecting equipment with high energy ratings can significantly reduce operational costs and carbon footprints.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction. Ensuring that the components of vending machines are sourced from suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations is not only a moral imperative but also a market differentiator. Certifications such as Fair Trade and ISO 14001 can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers.
Buyers should also consider the lifecycle impact of the machines they procure, opting for models that facilitate recycling and waste reduction. This approach not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices.
Brief Evolution/History
The hot food vending machine sector has undergone significant transformations since its inception. Initially, vending machines primarily dispensed snacks and beverages. However, advancements in technology have led to the introduction of machines capable of cooking and serving hot meals on demand. The integration of refrigeration and microwaving capabilities has expanded the variety of food options available.
In recent years, the focus has shifted toward enhancing user experience through digital interfaces and contactless payment systems. This evolution reflects broader trends in consumer behavior, where convenience and speed are paramount. As the market continues to evolve, B2B buyers must stay informed about technological advancements and consumer preferences to remain competitive in the dynamic vending landscape.
Related Video: What global trade deals are really about (hint: it’s not trade) | Haley Edwards | TEDxMidAtlantic
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hot food vending machine for sale
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for hot food vending machines?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, customer reviews, and their ability to provide after-sales support. Check for certifications that demonstrate quality and compliance with local regulations. It’s also beneficial to request references from previous clients, and assess their production capacity to ensure they can meet your demands consistently. -
Can I customize the hot food vending machines to suit my market?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options such as branding, size, and food selection tailored to your target market’s preferences. Discuss your specific requirements during initial communications to ensure that the supplier can accommodate your needs. This may include adjusting the machine’s design, payment systems, or product offerings. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
MOQs for hot food vending machines can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from 5 to 50 units. Lead times generally depend on the complexity of customization and the supplier’s production capacity, averaging between 4 to 12 weeks. Always confirm these details upfront to align your purchasing strategy with your business goals. -
What payment options are available for purchasing vending machines internationally?
Payment options can include wire transfers, letters of credit, or escrow services, depending on the supplier’s policy and your location. It’s advisable to negotiate favorable terms, such as partial payments upfront and the balance upon delivery. Ensure that all payment methods are secure and that you have clear agreements to prevent disputes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and necessary certifications for the machines?
Request documentation proving that the vending machines comply with international safety and quality standards, such as CE, UL, or ISO certifications. Establish a quality assurance protocol with the supplier, which may include pre-shipment inspections or third-party audits. This will mitigate risks associated with defective products and ensure compliance with local regulations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing vending machines?
Logistics can be complex; consider factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Engage a freight forwarder experienced in international trade to streamline the process. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs, taxes, and insurance for the shipment to avoid unexpected costs. -
What steps should I take if I encounter disputes with the supplier?
Establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in writing to minimize misunderstandings. If disputes arise, try to resolve them amicably through direct negotiation. If necessary, escalate the issue to mediation or arbitration, and refer to the terms outlined in your contract for dispute resolution processes. -
Are there warranty or service agreements available for hot food vending machines?
Most reputable suppliers offer warranty and service agreements covering parts and labor for a specified period, typically one to three years. Review the warranty terms carefully, including what is covered and the process for claiming repairs. Consider negotiating extended service agreements for ongoing support, which can enhance your operational efficiency.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hot food vending machine for sale
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of hot food vending machines presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging insights from market trends, local consumer preferences, and technological advancements, businesses can enhance their offerings and meet rising demand for convenient food options.
Key Takeaways:
– Market Understanding: Recognizing regional preferences and regulatory environments is crucial. Tailoring your product offerings to local tastes can significantly enhance market penetration.
– Supplier Relationships: Building strong partnerships with reliable suppliers is essential for ensuring quality and consistency in product delivery. Consider suppliers that offer competitive pricing and robust after-sales support.
– Technological Integration: Embrace innovations such as cashless payment systems and smart vending solutions, which can enhance user experience and operational efficiency.
As the market for hot food vending machines continues to evolve, now is the time to act. Engage with suppliers, explore new technologies, and adapt to consumer needs to position your business for success. The future of vending solutions is bright, and your proactive approach can lead to substantial growth opportunities.