Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Can You Use Google Pay On
Guide to Can You Use Google Pay On Vending Machine
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for can you use google pay on vending machine
- Understanding can you use google pay on vending machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of can you use google pay on vending machine
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for can you use google pay on vending machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for can you use google pay on vending machine
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for can you use google pay on vending machine Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential can you use google pay on vending machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for can you use google pay on vending machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the can you use google pay on vending machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of can you use google pay on vending machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for can you use google pay on vending machine
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for can you use google pay on vending machine
In today’s fast-evolving landscape of cashless transactions, the integration of mobile payment systems like Google Pay into vending machines is reshaping consumer interactions across various markets. This innovation not only enhances user convenience but also presents a competitive edge for businesses seeking to engage with tech-savvy consumers. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the implications of this technology is crucial for staying ahead in the market.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of vending machines equipped with Google Pay functionality. It covers an array of topics, including the types of vending machines available, the materials used in their construction, and the manufacturing and quality control processes that ensure reliability. Additionally, it highlights key suppliers and offers insights into cost factors associated with implementing these systems.
By addressing common FAQs and providing a detailed market overview, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. Whether you are operating in Turkey, the UAE, or other regions, understanding how to leverage mobile payment technology can significantly enhance your operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Embrace the future of vending and unlock new revenue streams by integrating Google Pay into your offerings.
Understanding can you use google pay on vending machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contactless Payment Vending | Uses NFC technology for quick transactions | Retail, offices, universities | Pros: Fast transactions, increased convenience. Cons: May require regular software updates. |
| App-Integrated Vending | Requires a specific app for payment processing | Fitness centers, malls, corporate offices | Pros: Customizable user experience. Cons: User must download the app, which may limit usage. |
| Multi-Payment Method Vending | Accepts various payment methods, including Google Pay | Airports, public transport stations | Pros: Flexibility for users, increased sales opportunities. Cons: More complex setup and maintenance. |
| Smart Vending Machines | Equipped with IoT technology for remote management | Large organizations, tech hubs | Pros: Real-time inventory management, data analytics. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Eco-Friendly Vending Machines | Focus on sustainability, using renewable materials | Schools, eco-conscious businesses | Pros: Aligns with corporate social responsibility goals. Cons: May have higher operational costs. |
Contactless Payment Vending
These machines utilize Near Field Communication (NFC) technology to facilitate quick and secure transactions. They are ideal for high-traffic environments like retail stores, offices, and universities, where speed and convenience are paramount. B2B buyers should consider the machine’s compatibility with various payment systems and its ability to handle regular software updates to ensure seamless operation.
App-Integrated Vending
App-integrated vending machines require users to download a specific application to process payments, offering a tailored user experience. This type is particularly suitable for fitness centers, malls, and corporate offices where customer engagement and loyalty can be enhanced through app features. Buyers should evaluate the app’s functionality, ease of use, and potential impact on customer adoption.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Multi-Payment Method Vending
These vending machines accept a variety of payment methods, including Google Pay, credit cards, and cash. They are often found in airports and public transport stations, where diverse payment preferences are essential. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of increased sales against the complexities of setup and ongoing maintenance, as these systems can be more intricate to manage.
Smart Vending Machines
Equipped with Internet of Things (IoT) technology, smart vending machines allow for remote management and real-time inventory tracking. They cater to large organizations and tech hubs, providing insights into user behavior and stock levels. Buyers should consider the initial investment and the long-term benefits of data analytics, which can lead to optimized inventory and improved sales strategies.
Eco-Friendly Vending Machines
Focusing on sustainability, eco-friendly vending machines utilize renewable materials and energy-efficient technologies. They appeal to schools and businesses committed to corporate social responsibility. Buyers should assess the operational costs versus the potential marketing benefits of aligning with eco-friendly practices, as these machines may come with a higher price tag but can enhance brand reputation.
Related Video: How to Use Google Pay to Spend Money More Wisely
Key Industrial Applications of can you use google pay on vending machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Google Pay on Vending Machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Contactless Payment Solutions for Vending Machines | Increased sales through convenience and speed | Compatibility with existing vending infrastructure |
| Hospitality | Guest Services in Hotels and Airports | Enhanced customer experience and operational efficiency | Integration with hotel management systems |
| Education | Campus Services for Universities | Streamlined payment process for students and staff | Security features and ease of use for diverse users |
| Transportation | Ticketing and Refreshment Vending in Transit Systems | Improved revenue and customer satisfaction | Compliance with local payment regulations |
| Health and Wellness | Vending Machines in Gyms and Hospitals | Access to healthy snacks and drinks with easy payment | Variety of product offerings and health compliance |
Retail Sector
In the retail sector, integrating Google Pay into vending machines facilitates a seamless, contactless payment process, appealing to tech-savvy consumers. This convenience can lead to increased sales, as customers are more likely to make impulse purchases when payment is quick and easy. International B2B buyers should consider compatibility with existing vending infrastructure and ensure that the vending machine’s software can support various payment options, including mobile wallets.
Hospitality Industry
In hospitality, particularly in hotels and airports, vending machines equipped with Google Pay enhance guest services by allowing quick access to snacks and beverages without cash. This integration not only improves customer satisfaction but also streamlines operations, as it reduces the need for cash handling. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the payment systems are compatible with hotel management systems and comply with any regional financial regulations.
Education Sector
In educational institutions, vending machines that accept Google Pay streamline transactions for students and staff, making it easier to purchase snacks and drinks on campus. This application solves the problem of cash shortages and enhances the overall campus experience. B2B buyers should focus on security features, ensuring that the payment systems are reliable and easy to use for a diverse user base, including younger students who may be less familiar with cash transactions.
Transportation Sector
In the transportation sector, vending machines equipped with Google Pay can be used for ticketing and refreshments in transit systems. This application not only improves revenue by making purchasing more accessible but also enhances customer satisfaction by minimizing wait times. Buyers should consider compliance with local payment regulations and the ability to integrate with existing ticketing systems to ensure a smooth transition.
Health and Wellness Sector
In gyms and hospitals, vending machines that accept Google Pay provide easy access to healthy snacks and beverages, catering to health-conscious consumers. This solution addresses the need for convenient food options while promoting wellness. When sourcing these machines, B2B buyers should prioritize a variety of product offerings and ensure compliance with health regulations, as well as the ease of use for customers who may have different levels of tech-savviness.
Related Video: How to Use Google Pay in a Store (Easy Step-by-Step)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for can you use google pay on vending machine
When selecting materials for vending machines that accept Google Pay, several factors come into play, including durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of such machines, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°F (427°C) and can handle pressures up to 150 psi, depending on the grade.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Highly durable, resistant to rust and staining, and easy to clean, making it ideal for food and beverage applications. Its aesthetic appeal also enhances the machine’s overall look.
– Cons: Higher initial cost compared to other materials like carbon steel. Manufacturing complexity can increase due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including food and beverages, making it suitable for vending machines that sell consumables.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel is essential. Buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe may prefer grades that meet specific food safety regulations.
2. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel offers good strength and toughness, with a temperature rating typically up to 400°F (204°C). Its pressure rating varies based on the specific grade and treatment.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Cost-effective and widely available, making it a popular choice for many industrial applications. It can be easily machined and fabricated.
– Cons: Susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated or coated, which can limit its lifespan in outdoor or humid environments.
Impact on Application: While suitable for structural components, carbon steel may not be ideal for areas exposed to moisture or food products unless adequately protected.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A36. In Africa and South America, local sourcing of carbon steel can reduce costs, but attention to corrosion resistance is critical.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C). It is also known for its excellent thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Lightweight, making it easier to transport and install. It is also cost-effective for certain applications and offers good aesthetic versatility.
– Cons: Lower strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. It can also be more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for non-structural components and decorative elements in vending machines, particularly in regions with less extreme weather conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B221 is important. In Europe, buyers may favor aluminum for its lightweight properties, especially in mobile vending solutions.
4. Polycarbonate
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic with excellent impact resistance and a temperature rating of up to 240°F (116°C). It is also lightweight and transparent.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Highly resistant to impact and shattering, making it ideal for transparent panels in vending machines. It is also cost-effective compared to metals.
– Cons: Not suitable for high-temperature applications and can degrade under prolonged UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: Ideal for display panels and protective covers, polycarbonate can enhance user interaction with the vending machine.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with safety standards, especially in regions with strict regulations regarding materials used in consumer-facing products.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for can you use google pay on vending machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Structural components, exterior panels | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher initial cost | High |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components, internal frames | Cost-effective, widely available | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Aluminum | Decorative elements, non-structural components | Lightweight, good aesthetic versatility | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Display panels, protective covers | High impact resistance | Not suitable for high temperatures | Medium |
This guide provides insights into material selection for vending machines that accept Google Pay, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for can you use google pay on vending machine
Manufacturing Processes for Vending Machines with Google Pay Integration
1. Material Preparation
The manufacturing process for vending machines equipped with Google Pay begins with careful material selection. Common materials include:
- Metal (e.g., steel or aluminum): Provides structural integrity and durability.
- Plastic: Used for internal components and user interfaces due to its lightweight nature and moldability.
- Electronic components: Such as sensors, payment processors, and display screens are sourced from specialized suppliers.
Once materials are sourced, they undergo quality checks to ensure they meet predefined standards. This initial stage is critical, as the quality of the materials directly impacts the final product’s reliability and performance.
2. Forming
In this stage, raw materials are shaped into components using various techniques:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are used to precisely cut and shape metal parts.
- Injection Molding: This technique is employed for creating plastic components, allowing for intricate designs and rapid production.
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: Essential for crafting the outer casing and structural elements of the vending machine.
The choice of forming technique depends on the complexity of the parts and the volume of production. For example, CNC machining is preferred for high precision parts, while injection molding is ideal for larger quantities of uniform plastic components.
3. Assembly
The assembly process involves bringing together various components into a cohesive unit. Key steps include:
- Component Integration: Electronic systems (like the Google Pay module) are integrated with mechanical parts.
- Wiring and Connectivity: Ensuring all electronic components are correctly connected and functional.
- User Interface Installation: This includes touchscreens and card readers that facilitate payments.
This stage requires skilled labor to ensure precision and adherence to safety standards. Effective assembly lines are designed for efficiency, reducing the risk of errors that could compromise the machine’s functionality.
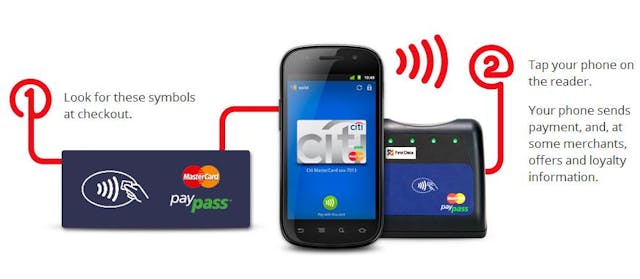
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Finishing
Once assembled, the vending machines undergo several finishing processes:
- Surface Treatment: Painting or coating protects against corrosion and enhances aesthetics.
- Quality Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to identify any defects or inconsistencies.
This finishing stage not only improves the vending machine’s appearance but also extends its lifespan, making it more appealing to B2B buyers.
Quality Assurance Processes
International Standards
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of vending machines, particularly those that process payments. Relevant international standards include:
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: For vending machines sold in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For machines that handle sensitive data (like payment information), adherence to API security standards is crucial.
These certifications not only enhance product credibility but also facilitate smoother market entry across different regions.
Quality Control Checkpoints
A structured quality control process incorporates multiple checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Evaluates the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors the manufacturing process to ensure adherence to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts a comprehensive inspection of the finished product to verify compliance with quality standards.
Each checkpoint plays a critical role in identifying potential issues early, thus minimizing costly rework or recalls.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods employed during quality assurance include:
- Functional Testing: Verifies that all features, including payment processing, are operational.
- Durability Testing: Assesses the machine’s resilience under various environmental conditions.
- Security Testing: Ensures that payment systems are secure against hacking or fraud.
These testing methods help build trust with B2B buyers by assuring them of the product’s reliability and safety.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers must be diligent in verifying supplier quality control processes. Key methods include:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers to assess their quality management systems and adherence to standards.
- Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline inspection results and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the manufacturing process and quality assurance measures.
These steps are particularly crucial for buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where varying standards and practices may exist.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers must navigate several nuances when dealing with international suppliers:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local practices and expectations can aid in effective communication and negotiation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarity with regional regulations (such as GDPR in Europe) is essential, especially for products handling personal data.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Buyers should consider the implications of shipping times, tariffs, and potential delays in the supply chain.
Navigating these complexities requires a proactive approach, ensuring that quality and compliance are maintained throughout the procurement process.
By understanding the manufacturing and quality assurance processes for vending machines that accept Google Pay, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their quality expectations.
Related Video: What is Google Pay and how does it work (2025) | Quick & Easy Tutorial
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for can you use google pay on vending machine Sourcing
Cost Components for Google Pay-Enabled Vending Machines
When sourcing vending machines compatible with Google Pay, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. Here are the primary cost components:
-
Materials: The quality of materials used in manufacturing vending machines significantly impacts costs. High-grade steel for the frame, reinforced glass for the display, and electronic components for payment systems can elevate the price. Opting for sustainable or locally sourced materials may also influence overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. For instance, countries in Europe may have higher labor costs compared to those in Africa or South America. It’s essential to consider both direct labor for assembly and indirect labor costs related to management and quality assurance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Overhead costs can fluctuate based on the manufacturing location. Facilities in regions with high operational costs, such as Western Europe, may pass these expenses onto buyers.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling may be required for customizing vending machines for Google Pay integration. This can include specialized machinery for electronic components or design alterations to accommodate user interfaces.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures the machines are reliable and meet international standards. The costs associated with QC can be significant, particularly when sourcing from manufacturers with stringent certification requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs should not be overlooked. Factors such as distance, mode of transport (air vs. sea), and customs duties can greatly affect total costs. Buyers should assess Incoterms to understand who bears responsibility for shipping and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and risks. Understanding the expected margins within different regions can help in negotiating better pricing.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of Google Pay-enabled vending machines:
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, which is advantageous for buyers planning to deploy multiple machines.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features, such as branding or specific payment integrations, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. High-quality, durable materials may cost more initially but can lead to lower maintenance and replacement costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Machines with higher certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and reliability. Buyers should evaluate the importance of these certifications for their markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence prices. Established suppliers may charge more for their proven track record, while newer companies might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can help buyers manage costs effectively. Incoterms determine who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties, directly impacting the total cost of ownership.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better deals over time.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of just the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. A slightly higher upfront cost may lead to significant savings in the long run.
-
Research Local Market Conditions: Understanding local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and supplier landscapes can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Consider Regional Suppliers: Sourcing from regional suppliers may reduce shipping costs and lead times, enhancing overall efficiency.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Nuances: Keep abreast of industry trends, such as changes in material costs or technological advancements, which can impact pricing strategies.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on specific supplier conditions, market fluctuations, and contract negotiations. Always conduct thorough research and engage in direct discussions with suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to your needs.
Spotlight on Potential can you use google pay on vending machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘can you use google pay on vending machine’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for can you use google pay on vending machine
Understanding the technical specifications and terminology relevant to the integration of Google Pay in vending machines is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge ensures informed decision-making when sourcing and negotiating with suppliers in different regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Technical Properties
-
Payment Processing Speed
– Definition: The time taken for a transaction to be completed from the moment a user initiates it until confirmation.
– Importance: Faster processing speeds improve customer satisfaction and increase the turnover rate of vending machines, which is essential in high-traffic areas. -
Compatibility with Payment Gateways
– Definition: The ability of vending machines to connect and communicate with various payment gateways that process digital transactions.
– Importance: Ensuring compatibility with multiple payment gateways allows businesses to cater to a broader customer base, accommodating various payment methods, including Google Pay. -
Security Features
– Definition: Measures implemented to protect transaction data, including encryption and compliance with PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
– Importance: Enhanced security features are critical for building trust with customers, especially in markets where digital payments are still gaining traction. -
User Interface Design
– Definition: The layout and functionality of the machine’s interface that customers interact with during the payment process.
– Importance: A user-friendly interface is vital for reducing transaction errors and enhancing the overall user experience, leading to higher sales. -
Durability and Material Grade
– Definition: The quality of materials used in the vending machine’s construction, affecting its resistance to wear and environmental factors.
– Importance: Durable machines reduce maintenance costs and downtime, which is particularly important in regions with harsh climates or high operational demands. -
Connectivity Options
– Definition: The methods through which the vending machine connects to the internet or payment networks (e.g., Wi-Fi, Ethernet, cellular).
– Importance: Reliable connectivity is crucial for real-time transaction processing and inventory management, ensuring that machines are always ready to accept payments.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers and negotiate terms effectively. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for international buyers managing logistics and supply chain dynamics. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ helps buyers compare prices and terms from different suppliers, facilitating better purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for understanding shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations, crucial for international trade. -
POS (Point of Sale)
– Definition: The place where a retail transaction is completed, which can include vending machines equipped with payment technology.
– Relevance: Recognizing the role of POS systems aids buyers in evaluating the technological capabilities of vending machines. -
KYC (Know Your Customer)
– Definition: A process of verifying the identity of clients to prevent fraud and ensure compliance with regulations.
– Relevance: KYC practices are increasingly important in digital payment systems, impacting the selection of vending machines that support secure transactions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding the integration of Google Pay into vending machines, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the can you use google pay on vending machine Sector
In the evolving landscape of payment technologies, the ability to use Google Pay on vending machines is becoming increasingly significant for international B2B buyers. The growth of contactless payments is largely driven by consumer demand for convenience and speed. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, mobile payment solutions are gaining traction, with Google Pay leading the charge. This trend is not only enhancing customer experience but also streamlining operational efficiencies for vending machine operators.
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for vending machines is experiencing a notable transformation, with an emphasis on integrating advanced payment solutions. Key drivers include:
- Consumer Preferences: Today’s consumers, particularly millennials and Gen Z, prefer cashless transactions. This shift is pushing vending machine operators to adopt mobile payment solutions like Google Pay to meet customer expectations.
- Technology Integration: The rise of IoT (Internet of Things) is enabling vending machines to connect with mobile payment systems seamlessly. This integration allows for real-time inventory management and enhanced user experiences.
- Geographic Expansion: While established markets in Europe and North America are leading the way, emerging markets in Africa and South America are rapidly adopting these technologies, driven by increasing smartphone penetration and mobile internet access.
For B2B buyers, the implications are clear: investing in smart vending machines that support Google Pay can provide a competitive edge. Furthermore, understanding local regulations and consumer behavior in these diverse markets is crucial to successfully navigating this landscape.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As businesses increasingly focus on sustainability, the vending machine sector is not left behind. The environmental impact of manufacturing and operating vending machines can be significant, thus ethical sourcing and sustainability are becoming paramount. Key considerations include:
- Sustainable Materials: B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that utilize eco-friendly materials in vending machine production. This includes recyclable plastics and energy-efficient components.
- Green Certifications: Look for vendors who hold certifications such as ISO 14001, which signifies a commitment to environmental management. This can enhance the brand’s reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Ethical supply chains are becoming essential. B2B buyers must ensure that their partners adhere to ethical labor practices and environmentally friendly operations.
By aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, businesses can not only reduce their ecological footprint but also attract a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.
Brief Evolution/History
The use of mobile payments in vending machines has evolved significantly over the past decade. Initially dominated by cash and coins, the sector began integrating card readers in the early 2000s. The advent of smartphones and mobile wallets in the 2010s marked a pivotal shift, allowing for contactless payments. Google Pay emerged as a leader in this space, enhancing security and convenience. Today, vending machines equipped with Google Pay represent a modern solution that caters to the needs of a tech-savvy consumer base, reflecting broader trends in digital payment adoption across various sectors.
In conclusion, understanding market dynamics, embracing sustainability, and staying abreast of technological advancements are essential for B2B buyers in the vending machine sector. Leveraging these insights can lead to strategic advantages in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of can you use google pay on vending machine
-
Can I use Google Pay on vending machines worldwide?
Yes, you can use Google Pay on vending machines that support contactless payment systems. However, the availability of this feature may vary by region. In regions like Africa and South America, where contactless payment adoption is growing, more vending machines are being equipped with NFC technology. Always check with the vending machine operator or supplier to confirm compatibility with Google Pay in your specific area. -
What should I consider when sourcing vending machines that accept Google Pay?
When sourcing vending machines, ensure they are equipped with NFC technology to support contactless payments like Google Pay. Verify the machine’s software compatibility with various payment platforms and inquire about the machine’s operating system updates. Additionally, consider the machine’s ability to accept multiple currencies if you’re targeting international markets, which can enhance user experience. -
How can I vet suppliers of vending machines that support Google Pay?
Vetting suppliers involves checking their industry reputation, customer reviews, and certifications. Request references from other businesses that have purchased similar machines. Additionally, inquire about their experience in international trade, especially in your target regions, such as Europe or the Middle East, to ensure they understand local regulations and standards for electronic payments. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering vending machines that accept Google Pay?
Lead times can vary based on the supplier and the customization options chosen. Generally, expect lead times of 4 to 12 weeks for standard machines, while custom orders may take longer. Always confirm with the supplier about production timelines and shipping options to ensure timely delivery, especially if you are coordinating for a specific launch or event. -
What payment terms should I negotiate when sourcing vending machines?
When negotiating payment terms, consider discussing options such as partial upfront payments and the balance upon delivery. This can mitigate risks for both parties. Also, inquire about payment methods accepted by the supplier, as using secure platforms can protect your transaction. Be sure to clarify any additional costs related to shipping, installation, and maintenance in the total payment structure. -
What quality assurance certifications should I look for in vending machines?
Look for machines that hold relevant certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for Europe, ISO 9001 for quality management, and other local compliance marks. These certifications indicate that the machines meet safety and quality standards. Additionally, inquire about the warranty and support services provided by the supplier to address any potential issues post-purchase. -
How can I handle disputes with vending machine suppliers?
To handle disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in writing. Ensure that your purchase agreements include terms related to warranties, returns, and support. If a dispute arises, try to resolve it amicably through negotiation first. If that fails, consider mediation or arbitration as a means of resolution, especially if international trade laws apply. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing vending machines?
Logistics for importing vending machines include understanding shipping regulations, customs duties, and taxes applicable in your target country. Work with a logistics provider experienced in handling electronic equipment to navigate these complexities. Additionally, consider the machine’s dimensions and weight for shipping costs and ensure that the delivery service can accommodate installation requirements upon arrival.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for can you use google pay on vending machine
In conclusion, the integration of Google Pay into vending machines represents a significant evolution in payment methods, particularly for international B2B buyers looking to enhance customer convenience and operational efficiency. Adopting this technology not only aligns with the growing trend towards cashless transactions but also meets the increasing consumer demand for seamless payment experiences.
Key Takeaways:
– Consumer Preference: Acknowledge the shift towards digital wallets among consumers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, emphasizing the need for businesses to adapt.
– Strategic Sourcing: By sourcing vending machines equipped with Google Pay capabilities, businesses can improve transaction efficiency and reduce cash handling costs.
– Market Differentiation: Implementing innovative payment solutions can help businesses stand out in competitive markets, attracting tech-savvy customers.
As we look to the future, it is essential for international B2B buyers to prioritize partnerships with suppliers who are forward-thinking and capable of integrating advanced payment solutions. Embrace this opportunity to lead in your market by investing in smart vending solutions that cater to the evolving needs of consumers. The time to act is now—transform your vending operations and stay ahead of the curve in an increasingly digital marketplace.