Unlock Profits with Solar Powered Vending Machines for B2B
Guide to Solar Powered Vending Machine
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solar powered vending machine
- Understanding solar powered vending machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of solar powered vending machine
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for solar powered vending machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solar powered vending machine
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solar powered vending machine Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential solar powered vending machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solar powered vending machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the solar powered vending machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solar powered vending machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solar powered vending machine
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solar powered vending machine
In an increasingly mobile world, solar-powered vending machines are revolutionizing how businesses engage with consumers. These innovative machines not only provide convenient access to products but also align with global sustainability goals by harnessing renewable energy. For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in solar-powered vending machines presents a unique opportunity to enhance operational efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of solar-powered vending machines, covering various types, materials, manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and sourcing suppliers. It also provides insights into cost considerations, market trends, and frequently asked questions to equip buyers with the knowledge needed for informed decision-making.
Understanding the nuances of solar-powered vending machines empowers businesses to make strategic investments that resonate with eco-conscious consumers and meet the demands of modern retail landscapes. As you navigate this guide, you will discover how these machines can serve diverse markets, offering flexibility and scalability that are crucial for success in today’s competitive environment. By leveraging this knowledge, B2B buyers can confidently pursue partnerships that foster innovation and sustainability, ultimately driving growth and profitability in their enterprises.
Understanding solar powered vending machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standalone Solar Vending Machine | Fully autonomous, equipped with solar panels and battery storage | Remote locations, outdoor events | Pros: Low maintenance, no electricity costs. Cons: Limited product capacity due to size. |
| Hybrid Solar Vending Machine | Combines solar power with grid electricity for reliability | Urban areas, high foot traffic sites | Pros: Reliable power supply, flexible operation. Cons: Higher initial investment costs. |
| Smart Solar Vending Machine | IoT-enabled for inventory tracking and customer interaction | Retail environments, smart cities | Pros: Enhanced customer engagement, data collection. Cons: Complexity in technology management. |
| Refrigerated Solar Vending Machine | Equipped with cooling systems powered by solar energy | Food and beverage sales, health products | Pros: Preserves perishable items, attracts health-conscious consumers. Cons: Higher energy consumption. |
| Customizable Solar Vending Machine | Tailored design and features to meet specific business needs | Niche markets, promotional events | Pros: Unique branding opportunities, tailored offerings. Cons: Longer lead times for production. |
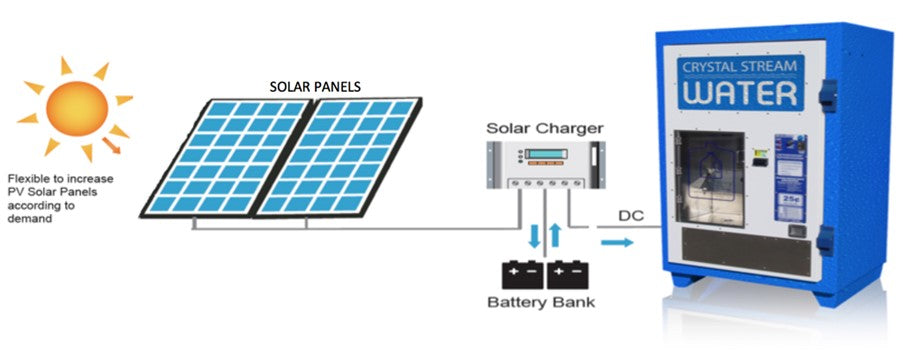
Standalone Solar Vending Machine
Standalone solar vending machines are self-sufficient units that operate entirely on solar energy. These machines are ideal for remote locations where traditional power sources are unavailable. They typically feature solar panels and battery storage to ensure continuous operation, even during cloudy days. B2B buyers should consider their product capacity and maintenance requirements, as these machines can be limited in size and may require periodic battery checks.
Hybrid Solar Vending Machine
Hybrid solar vending machines utilize both solar energy and grid electricity, providing a reliable power source for urban environments and high-traffic areas. This type allows businesses to operate during peak hours without interruptions, ensuring product availability. For B2B buyers, the key considerations include the initial investment cost and the potential for lower operational costs over time due to reduced energy bills.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Smart Solar Vending Machine
Smart solar vending machines are equipped with Internet of Things (IoT) technology, enabling features like inventory tracking, real-time sales data, and customer interaction. These machines are particularly suited for retail environments and smart cities. B2B buyers must evaluate the complexity of the technology and the potential need for ongoing technical support, as these systems can require more sophisticated management than traditional vending machines.
Refrigerated Solar Vending Machine
Refrigerated solar vending machines are designed to sell perishable items, such as food and beverages, utilizing solar power for their cooling systems. This type is perfect for outdoor events and locations where fresh products are in demand. B2B buyers should assess the energy consumption of these machines, as they may require more solar capacity to maintain optimal temperatures, which could impact initial investment and operational costs.
Customizable Solar Vending Machine
Customizable solar vending machines offer tailored designs and features to meet specific business needs, making them suitable for niche markets and promotional events. These machines can be branded and equipped with unique offerings that resonate with target audiences. For B2B buyers, the main considerations include the longer lead times for production and the need for a clear understanding of their specific requirements to ensure the final product meets their expectations.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of solar powered vending machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Solar Powered Vending Machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Automated retail for snacks and beverages in remote areas | Increases sales in underserved markets, reduces operating costs | Energy efficiency, payment systems integration, product variety |
| Education | Campus vending for students and staff | Enhances convenience, promotes healthy eating choices | Durability, user-friendly interface, security features |
| Hospitality | Mini bars and snack stations in hotels | Improves guest experience, reduces staff workload | Temperature control, aesthetic design, serviceability |
| Transportation | Vending machines at bus and train stations | Provides quick access to food and drinks, increases foot traffic | Location analysis, size and capacity, payment options |
| Construction & Events | Temporary vending solutions at construction sites or events | Meets on-site demands, reduces downtime for workers | Portability, rugged design, stock management capabilities |
Retail
In the retail sector, solar-powered vending machines can serve as automated retail points for snacks and beverages, especially in remote or underserved areas. They offer a sustainable solution that reduces operating costs by relying on renewable energy. International buyers should consider energy efficiency and the ability to integrate payment systems to facilitate cashless transactions, which are increasingly preferred in modern retail environments.
Education
Schools and universities can utilize solar-powered vending machines to provide students and staff with quick access to snacks and beverages. This application not only enhances convenience but also promotes healthier eating choices by allowing institutions to curate product selections. Buyers in the education sector must prioritize durability and user-friendly interfaces, ensuring that machines can withstand high usage while being easy to operate for students of all ages.
Hospitality
In the hospitality industry, solar-powered vending machines can be installed in hotel lobbies or guest rooms as mini bars or snack stations. This innovation enhances the guest experience by offering a variety of food and drink options while simultaneously reducing the workload for hotel staff. When sourcing, businesses should focus on temperature control features to ensure product freshness, as well as aesthetic design elements that align with the hotel’s branding.
Transportation
Transportation hubs, such as bus and train stations, can benefit significantly from solar-powered vending machines. These machines provide travelers with quick access to food and drinks, improving overall customer satisfaction and increasing foot traffic. Key considerations for international buyers include conducting location analysis to determine optimal placement, ensuring the machines are appropriately sized for high-traffic areas, and offering diverse payment options to cater to a wide range of travelers.
Construction & Events
Solar-powered vending machines can serve as temporary solutions at construction sites or large events, meeting the on-site demands of workers and attendees. By providing easy access to refreshments, these machines help reduce downtime and keep personnel energized. Buyers in this sector should look for machines that are portable and rugged, capable of withstanding outdoor conditions, and equipped with stock management capabilities to monitor inventory levels efficiently.
Related Video: DIY Vending Machine – Arduino based Mechatronics Project
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solar powered vending machine
When selecting materials for solar-powered vending machines, international B2B buyers must carefully consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these machines, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity. It can withstand a range of temperatures, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its high strength-to-weight ratio, which enhances mobility and ease of installation. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may require additional coatings for enhanced corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including food and beverages, making it ideal for vending machines. Its lightweight nature allows for easy transportation and installation.
Specific Considerations: Buyers must ensure that the aluminum grades used comply with international standards like ASTM or DIN. In regions with high humidity or saline environments, additional protective coatings may be necessary to prevent corrosion.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons: The durability and aesthetic appeal of stainless steel make it a popular choice for vending machines. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be more costly, which may impact the overall budget for manufacturers.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is highly compatible with food-grade applications, ensuring safety and hygiene. Its robustness makes it suitable for high-traffic areas.
Specific Considerations: Compliance with food safety standards is crucial, especially in regions with stringent regulations. Buyers should consider the specific grade of stainless steel (e.g., 304 or 316) based on environmental conditions.
Polycarbonate
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and transparency. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and is lightweight.
Pros & Cons: The transparency of polycarbonate allows for easy visibility of products within the vending machine, enhancing customer experience. However, it may not be as durable as metals in extreme conditions and can be susceptible to scratching.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is suitable for protective covers and displays in vending machines, allowing for product visibility while protecting against environmental elements.
Specific Considerations: Buyers should ensure that polycarbonate materials meet relevant safety and environmental standards. In regions with high UV exposure, UV-resistant grades should be considered to prevent degradation.
Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composites often combine materials like fiberglass and resin, offering lightweight and high-strength characteristics with good weather resistance.
Pros & Cons: Composites can be tailored for specific applications, providing flexibility in design and aesthetics. However, they may have higher manufacturing complexities and costs compared to traditional materials.
Impact on Application: Composites can be used in various components of the vending machine, including structural parts and outer casings, providing excellent insulation and protection.
Specific Considerations: International buyers should verify that the composites used comply with local and international standards. The manufacturing process should also be assessed for sustainability, especially in regions focused on environmental impact.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for solar powered vending machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Structural components and outer casing | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Structural components, food-grade surfaces | High durability, aesthetic appeal | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Polycarbonate | Protective covers and product displays | High impact resistance, visibility | Susceptible to scratching | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Structural parts and insulation | Lightweight, customizable | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solar powered vending machine
The manufacturing of solar-powered vending machines involves a systematic approach that ensures high-quality outputs suited for various markets, including those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section outlines the key manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures essential for international B2B buyers.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing process involves sourcing and preparing materials. Common materials include:
– Metal Components: Typically aluminum or stainless steel for durability and resistance to corrosion.
– Plastic Parts: High-grade polymers are used for housing and internal mechanisms.
– Solar Panels: Photovoltaic cells are sourced from certified manufacturers, ensuring efficiency and longevity.
– Electronic Components: Includes microcontrollers, sensors, and payment processing units.
Key Techniques:
– Supplier Verification: It is crucial for buyers to verify suppliers through audits or certifications to ensure material quality.
– Inventory Management: Efficient stock management systems are employed to avoid delays and ensure timely production.
2. Forming
This stage involves shaping the prepared materials into usable components through various techniques:
– CNC Machining: Used for precision cutting of metal parts.
– Injection Molding: Commonly used for plastic parts, ensuring high-volume production and uniformity.
– Bending and Welding: Metal parts are bent and welded to form the structure of the vending machine.
Key Techniques:
– 3D Modeling: Advanced CAD software is used to design components, allowing for simulations and modifications before production begins.
3. Assembly
Once components are formed, they proceed to assembly. This stage includes:
– Component Integration: Solar panels, electronic systems, and vending mechanisms are assembled.
– Electrical Wiring: Ensuring that all components are correctly wired and connected to the power source.
Key Techniques:
– Automated Assembly Lines: Employing robotics to enhance speed and accuracy during assembly.
– Modular Design: Facilitates easier upgrades and maintenance, appealing to buyers looking for long-term solutions.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves surface treatments and quality checks before the product is packaged. This includes:
– Coating and Painting: To protect against environmental elements and enhance aesthetics.
– Labeling: Ensures compliance with local regulations and provides necessary product information.
Key Techniques:
– Quality Control Systems: Integration of automated systems to ensure consistency in the finishing process.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is critical in manufacturing solar-powered vending machines to meet international standards and customer expectations.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA).
- API Certification: Relevant for electronic components, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To ensure quality throughout the manufacturing process, several checkpoints are established:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verifies the quality of materials upon arrival.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive checks before packaging to ensure the product meets all specifications.
Common Testing Methods
- Functional Testing: Ensures that all electronic components function as intended.
- Environmental Testing: Assesses durability under various weather conditions, crucial for outdoor installations.
- Safety Testing: Checks for electrical safety and compliance with local regulations.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must implement strategies to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
- Conduct Audits: Regular supplier audits can help assess compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes.
- Request Documentation: Buyers should ask for quality assurance reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC data.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
Understanding the nuances of quality control is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have specific regulations; understanding these can mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
- Cultural Differences: Awareness of local business practices and expectations can enhance negotiations and partnerships.
- Supply Chain Considerations: Buyers should consider the reliability of logistics and supply chains in their regions, which can impact the overall quality and availability of products.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for solar-powered vending machines are multifaceted and essential for ensuring product reliability and customer satisfaction. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough verification methods, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs and market demands. This comprehensive approach not only enhances product quality but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers across various regions.
Related Video: solar cell manufacturing and solar panel production by suntech
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solar powered vending machine Sourcing
When sourcing solar-powered vending machines, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only aids in budget planning but also enhances negotiation strategies and ensures informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the materials used in the construction of the vending machine. High-quality components, such as solar panels, batteries, and structural materials, can significantly impact overall costs. Buyers should consider sourcing from reputable suppliers to ensure durability and efficiency.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location and complexity of assembly. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes compromise quality. Understanding local wage rates and labor practices is essential for accurate cost projections.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help minimize these expenses, but buyers should inquire about the supplier’s operational efficiencies to gauge potential savings.
-
Tooling: Customization often requires specialized tooling, which can increase initial costs. However, investing in the right tooling can lead to better quality and lower production costs in the long run. Discussing tooling options with suppliers can help in planning for both short-term and long-term expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures is vital for ensuring product reliability. While this may add to the cost, it protects against long-term losses from faulty products. Buyers should seek suppliers with robust QC protocols to mitigate risks.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary dramatically based on distance, mode of transport, and destination regulations. Understanding Incoterms and selecting the appropriate shipping options can optimize logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin based on their operational costs and market conditions. Buyers should be aware of typical margins in the industry to evaluate the fairness of quoted prices.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can heavily influence pricing. Larger orders often lead to volume discounts. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features can increase costs, particularly if they require unique materials or designs. Discussing the specific needs upfront can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can raise costs but also enhance product performance and marketability. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certifications against the associated costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can significantly affect pricing. Engaging with established suppliers can provide assurance of quality but may come at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms on shipping responsibilities and costs is critical. Buyers should select terms that align with their logistical capabilities and budget.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term partnerships. Building a rapport can facilitate better deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational expenses, rather than just the upfront price. This approach ensures long-term value from the investment.
-
Pricing Nuances: Buyers from different regions may encounter varying price structures due to local economic conditions. For instance, buyers in Africa and South America may face higher logistics costs compared to European counterparts. Understanding these nuances can aid in better budgeting.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Prices for solar-powered vending machines can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier changes, and geopolitical factors. Always request up-to-date quotes before making purchasing decisions.
By comprehensively analyzing these cost components and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals and budgetary constraints.
Spotlight on Potential solar powered vending machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘solar powered vending machine’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solar powered vending machine
Key Technical Properties of Solar-Powered Vending Machines
When considering the procurement of solar-powered vending machines, international B2B buyers should focus on several critical technical properties that can significantly impact performance and reliability. Here are the essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality of materials used in the construction of the vending machine, often specified by standards such as stainless steel or aluminum alloys.
– Importance: High-grade materials enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors, which is crucial for machines operating in diverse climates, especially in Africa and South America. -
Solar Panel Efficiency
– Definition: The percentage of sunlight that can be converted into usable electricity by the solar panels installed on the vending machine.
– Importance: Higher efficiency rates mean better performance in low-light conditions, which is vital for regions with inconsistent sunlight. Buyers should look for panels with an efficiency rating of at least 18-20%. -
Battery Capacity
– Definition: The total energy storage capacity of the onboard batteries, typically measured in ampere-hours (Ah).
– Importance: A larger battery capacity ensures that the vending machine can operate during the night or on cloudy days. This is particularly relevant in regions where solar availability is sporadic. -
Weather Resistance Rating
– Definition: A measure of the machine’s ability to withstand various environmental conditions, often classified by an Ingress Protection (IP) rating.
– Importance: An IP rating of at least IP65 is recommended for outdoor machines, indicating protection against dust and water, which is essential for machines in rainy or humid climates.
-
Temperature Tolerance
– Definition: The operational temperature range within which the vending machine can function effectively.
– Importance: Machines should be able to operate in extreme temperatures, from high heat in the Middle East to colder climates in Europe. This ensures reliability and reduces maintenance costs. -
User Interface Technology
– Definition: The type of technology used for customer interaction, such as touch screens, QR code scanners, or mobile payment systems.
– Importance: Advanced interfaces can improve user experience and increase sales. Buyers should consider the compatibility with local payment systems, which can vary significantly across regions.
Common Trade Terminology in Solar-Powered Vending Machines
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms frequently used in the solar-powered vending machine sector:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Usage: Buyers often work with OEMs to customize machines to meet specific needs or branding requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Usage: Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for businesses looking to enter new markets. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Usage: An RFQ allows buyers to compare costs and negotiate better terms with suppliers. -
Incoterms
– Definition: International commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Usage: Familiarity with Incoterms is critical for understanding shipping costs, risk, and delivery obligations, particularly in cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Usage: Buyers should inquire about lead times to effectively plan their operations and inventory levels. -
Warranty Period
– Definition: The duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the performance of the vending machine.
– Usage: A longer warranty period can be indicative of the product’s reliability and the manufacturer’s confidence in their equipment.
By focusing on these technical properties and familiarizing themselves with trade terminology, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing solar-powered vending machines, ensuring they choose products that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the solar powered vending machine Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The solar-powered vending machine sector is witnessing significant growth fueled by global sustainability initiatives and advancements in renewable energy technology. Key drivers include the increasing demand for eco-friendly solutions, urbanization in developing regions, and the rising cost of traditional energy sources. International B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should note that government incentives and subsidies for green technology are becoming more prevalent, making solar-powered options financially attractive.
Emerging trends within this market include smart vending technology, which integrates IoT capabilities for real-time inventory management and enhanced customer engagement. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers looking to optimize operations and reduce overhead costs. Additionally, the use of mobile payment systems is rising, catering to the preferences of tech-savvy consumers. For B2B buyers, aligning with suppliers who offer these advanced features can provide a competitive edge.
Furthermore, the global supply chain is evolving, emphasizing local sourcing to reduce transportation emissions and costs. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that have robust local operations, ensuring a stable supply chain that is responsive to market dynamics. As competition increases, buyers will benefit from staying informed about technological advancements and market shifts that can impact sourcing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is at the forefront of the solar-powered vending machine sector. The environmental impact of traditional vending machines, often reliant on non-renewable energy, is prompting a shift toward solar solutions. These machines not only reduce carbon footprints but also lower operational costs through energy savings. For B2B buyers, this translates to a dual benefit of cost efficiency and enhanced corporate social responsibility.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers should seek suppliers who prioritize sustainable materials, such as recycled metals and biodegradable components, in their vending machine designs. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for energy efficiency can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices. Implementing a rigorous vetting process for suppliers that includes these certifications can help ensure that the supply chain remains environmentally responsible.
Additionally, transparency in the supply chain is crucial. Buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers that provide clear information about their sourcing practices, including labor conditions and environmental impact. This not only fosters trust but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for ethical products.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Brief Evolution/History
The concept of vending machines dates back to ancient times, but the integration of solar technology is relatively recent. Initially, vending machines operated solely on electrical power, making them less sustainable. The introduction of solar-powered vending machines began in the early 2000s, driven by advancements in solar panel efficiency and battery storage technology. Over the past decade, as global awareness of climate change and sustainability has increased, these machines have evolved to incorporate smart technology, allowing for a more interactive and environmentally friendly consumer experience.
For international B2B buyers, understanding the evolution of this sector is essential. It highlights the trajectory of innovation and the increasing importance of sustainability in product offerings. Buyers who stay informed about these developments can make strategic decisions that align with both market demands and ethical considerations.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solar powered vending machine
-
How do I vet suppliers for solar-powered vending machines?
Vetting suppliers is crucial in international trade. Start by checking their business licenses and certifications relevant to solar technology and vending machines. Request references from previous clients, and consider their experience in your target market. Online platforms, such as Alibaba or Global Sources, can provide insights through ratings and reviews. Additionally, look for suppliers who participate in international trade shows or industry-specific exhibitions, as this often indicates credibility and commitment to quality. -
Can I customize the solar-powered vending machines to fit my brand?
Most manufacturers offer customization options, including branding, color schemes, and machine features. When discussing your needs, clearly outline your requirements regarding size, technology, and additional functionalities like payment systems or product selection. Ensure that customization aligns with local regulations, especially regarding electrical and safety standards. Establishing a good relationship with the supplier can facilitate a smoother customization process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for these machines?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the level of customization. Standard orders might start from 10 to 50 units, while customized machines may require larger orders. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on production capacity and shipping logistics. To avoid delays, discuss your timeline upfront and consider placing orders well in advance of peak seasons or promotional events. -
What payment methods are commonly accepted in international transactions?
Payment methods can include bank transfers, credit cards, and online payment platforms like PayPal or Escrow services. For larger orders, letters of credit (LC) are often used to protect both parties. It is advisable to negotiate payment terms that include a deposit upfront and the balance upon delivery or inspection of the goods. Always be cautious of suppliers asking for full payment upfront, especially if they lack a solid reputation. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
A reputable supplier should have a robust quality assurance (QA) process in place, including inspections at various stages of production. Request copies of their QA certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, consider conducting third-party inspections before shipment to ensure the products meet your specifications and standards. Establishing a clear return policy for defective units is also advisable. -
What certifications should the solar-powered vending machines have?
Look for certifications that confirm compliance with local and international standards, such as CE, UL, or ISO certifications. These certifications ensure that the machines are safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly. In some regions, specific solar energy certifications may also be required. Always ask the supplier for documentation that proves these certifications are valid and up-to-date, especially when importing into your country. -
How should I handle logistics and shipping for these machines?
Logistics can be complex due to the size and weight of vending machines. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide detailed shipping options, including freight forwarding and customs clearance. Determine whether you will use FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) terms based on your risk tolerance. Ensure that the supplier provides tracking information and that you understand the estimated delivery timelines to manage expectations effectively. -
What should I do in case of disputes with suppliers?
Disputes can arise from various issues, including product quality, delivery delays, or contract misunderstandings. To minimize conflicts, maintain clear and open communication throughout the transaction. If a dispute occurs, first attempt to resolve it amicably through negotiation. If that fails, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Consider involving legal counsel familiar with international trade laws if necessary.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solar powered vending machine
The integration of solar-powered vending machines represents a pivotal shift in sustainable retail solutions, especially for international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As these regions increasingly prioritize renewable energy, sourcing these innovative machines can enhance brand reputation while addressing environmental concerns. Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating suppliers based on their sustainability practices, technological reliability, and after-sales support.
Strategic sourcing not only ensures that businesses secure high-quality products but also fosters partnerships that can lead to future innovations. By prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, buyers can align their purchasing decisions with broader corporate social responsibility goals.
Looking ahead, the demand for solar-powered vending machines is expected to rise as urbanization and energy costs increase. B2B buyers are encouraged to act now by exploring partnerships with manufacturers who offer cutting-edge technology and robust support systems. Investing in solar-powered solutions today positions companies to thrive in a competitive marketplace while contributing to a greener future. Embrace this opportunity to lead the charge towards sustainable retailing and meet the evolving expectations of your customers.