Unlock Profitable Vending Machine Vacancies for Your B2B
Guide to Vending Machine Vacancies
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vending machine vacancies
- Understanding vending machine vacancies Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of vending machine vacancies
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vending machine vacancies
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vending machine vacancies
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vending machine vacancies Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential vending machine vacancies Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vending machine vacancies
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vending machine vacancies Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vending machine vacancies
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vending machine vacancies
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vending machine vacancies
In today’s fast-paced global economy, the vending machine industry has emerged as a vital component for businesses seeking innovative solutions to enhance customer engagement and streamline operations. As urbanization accelerates and consumer preferences evolve, vending machine vacancies present lucrative opportunities for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These vacancies not only reflect market demand but also signify a shift towards automated retail environments that cater to the convenience-driven consumer.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of vending machine vacancies, offering insights that empower informed sourcing decisions. Buyers will explore various types of vending machines, including traditional snack dispensers, cutting-edge smart machines, and specialty vendors that cater to niche markets. Additionally, the guide addresses essential considerations such as materials used in manufacturing, quality control measures, and the profiles of reputable suppliers.
Understanding the cost structures and market dynamics is crucial for buyers looking to optimize their investments. This guide includes a detailed analysis of pricing strategies and market trends to help B2B buyers navigate their purchasing decisions effectively. Furthermore, a dedicated FAQ section addresses common queries, ensuring that buyers have access to the information they need to make confident choices.
By leveraging this guide, international B2B buyers will be well-equipped to capitalize on the potential of vending machine vacancies, driving growth and innovation in their respective markets.
Understanding vending machine vacancies Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Snack Vending | Dispenses snacks, beverages, and quick meals | Offices, schools, hospitals | Pros: Easy to operate; Cons: Limited product variety |
| Healthy Vending Machines | Focus on nutritious snacks and beverages | Gyms, schools, health-focused locations | Pros: Aligns with health trends; Cons: Higher initial cost |
| Specialty Product Vending | Offers niche products like electronics or beauty | Airports, malls, tourist attractions | Pros: Unique offerings; Cons: Higher maintenance needs |
| Automated Retail Kiosks | Combines vending with retail space for various goods | Shopping centers, events, festivals | Pros: Versatile product range; Cons: Requires more space |
| Cashless Payment Vending | Accepts digital payments via mobile apps or cards | Modern retail environments | Pros: Convenient for users; Cons: Dependence on technology |
Traditional Snack Vending Machines
Traditional snack vending machines are ubiquitous in various settings, dispensing a range of snacks, beverages, and quick meals. They are particularly suitable for environments like offices, schools, and hospitals where quick access to food is essential. B2B buyers should consider the machine’s capacity, product selection, and ease of restocking. While these machines are easy to operate and maintain, they may offer limited product variety, which could deter health-conscious consumers.
Healthy Vending Machines
Healthy vending machines cater to the growing demand for nutritious food options. They typically stock items like granola bars, fruit, and low-calorie snacks and are commonly found in gyms, schools, and health-focused environments. Buyers should evaluate the nutritional value of the products offered and the machine’s ability to attract health-conscious customers. Although these machines align with current health trends, they often come with a higher initial cost, which may be a barrier for some businesses.
Specialty Product Vending Machines
Specialty product vending machines provide niche offerings such as electronics, beauty products, or gourmet foods. These machines are ideal for locations like airports, malls, and tourist attractions, where unique products can enhance the consumer experience. B2B buyers should assess the target market and the potential demand for such specialized items. While these machines can draw significant consumer interest, they may also require more frequent maintenance and restocking due to their unique inventory.
Automated Retail Kiosks
Automated retail kiosks take vending to the next level by combining traditional vending with retail space, allowing for a diverse range of products, from clothing to electronics. These kiosks are well-suited for high-traffic areas like shopping centers, events, and festivals. Buyers must consider the space requirements and the complexity of the inventory management system. While offering a versatile product range can attract a broader audience, these kiosks may require more space than standard vending machines.
Cashless Payment Vending Machines
Cashless payment vending machines accept digital payments via mobile apps or credit cards, catering to the modern consumer’s preference for convenience. They are commonly found in retail environments where quick transactions are essential. B2B buyers should focus on the technology used and the machine’s integration with existing payment systems. Although these machines enhance convenience and streamline transactions, they are dependent on technology, which can lead to potential issues if systems fail or if connectivity is lost.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of vending machine vacancies
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vending machine vacancies | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Automated product dispensing | Increased sales through 24/7 availability | Reliability of machine, product variety, payment options |
| Education | Snack and beverage provision in schools | Improved student satisfaction and performance | Health regulations, product selection, machine maintenance |
| Hospitality | Guest convenience in hotels and resorts | Enhanced guest experience and loyalty | Space efficiency, energy consumption, service support |
| Healthcare | Medication and health product dispensing | Improved patient adherence to treatment | Compliance with health regulations, security features |
| Transportation & Logistics | On-the-go snacks and drinks at transit hubs | Capturing impulse purchases from travelers | Location analysis, product turnover, machine accessibility |
Retail: Automated Product Dispensing
In the retail sector, vending machine vacancies can be utilized for automated product dispensing, allowing businesses to offer a wide range of products without the need for additional staff. This application is particularly beneficial for high-traffic areas, as it enables 24/7 availability, thus driving sales and improving customer satisfaction. International buyers should consider the reliability and maintenance of machines, as well as the diversity of product offerings and payment options to cater to different customer preferences.
Education: Snack and Beverage Provision in Schools
Vending machine vacancies in educational institutions serve the essential function of providing snacks and beverages to students. This not only enhances student satisfaction but can also contribute to improved academic performance by ensuring students have access to nourishment throughout the day. Buyers in this sector must prioritize compliance with health regulations, ensuring that products are nutritious and appealing, while also considering the variety of options available and the machine’s maintenance needs.
Hospitality: Guest Convenience in Hotels and Resorts
In the hospitality industry, vending machines can be strategically placed in hotels and resorts to offer guests convenient access to snacks, beverages, and essential items. This application enhances the guest experience by providing quick solutions for hunger or last-minute needs, ultimately fostering customer loyalty. B2B buyers should focus on space efficiency, energy consumption, and the availability of service support when sourcing vending machines for this sector, ensuring they meet the unique demands of hospitality environments.
Healthcare: Medication and Health Product Dispensing
Vending machine vacancies in healthcare settings can be leveraged for the dispensing of medications and health-related products, addressing patient needs effectively. This application helps in improving patient adherence to prescribed treatments by providing easy access to medications outside of regular pharmacy hours. Buyers in this sector should ensure compliance with stringent health regulations and consider security features to protect sensitive items, alongside the need for reliable machine operation.
Transportation & Logistics: On-the-Go Snacks and Drinks
Vending machines positioned in transportation hubs such as airports, train stations, and bus terminals serve the vital role of offering on-the-go snacks and drinks to travelers. This application captures impulse purchases, significantly boosting revenue for businesses operating in these high-traffic areas. Key considerations for international buyers include conducting thorough location analysis to optimize machine placement, understanding product turnover rates, and ensuring machines are accessible to all travelers, including those with disabilities.
Related Video: How to Start a Vending Machine Business, Cost, Tips, How Much You Make
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vending machine vacancies
When selecting materials for vending machine vacancies, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to consider the unique properties and applications of various materials. Here, we analyze four common materials used in vending machine construction: stainless steel, aluminum, plastic, and glass. Each material has distinct advantages and limitations that can impact the overall performance and suitability of the vending machines in different environments.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. It typically withstands high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust and staining, which is essential in environments where hygiene is a concern. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, such as welding and polishing.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including food and beverages, and is often preferred in high-traffic areas due to its robust nature.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East where safety regulations are stringent. Buyers should also consider the availability of stainless steel grades that meet local regulations in Africa and South America.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It is also easily machinable, allowing for complex shapes and designs.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not withstand high-impact environments as well.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for use in vending machines that dispense lighter products or require frequent mobility. Its resistance to corrosion makes it a good choice for outdoor vending machines in humid climates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the aluminum used complies with local standards, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary greatly. Understanding the specific alloy grades that meet these standards is crucial.
Plastic
Key Properties: Plastic materials, such as polycarbonate and ABS, are lightweight, impact-resistant, and versatile. They can be molded into various shapes and sizes.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of plastic include low cost and ease of manufacturing. However, plastics may not offer the same level of durability as metals and can be susceptible to UV degradation and chemical exposure.
Impact on Application: Plastic is ideal for vending machines that require colorful designs or transparent sections to showcase products. However, it may not be suitable for hot or corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding the use of plastics, particularly concerning food safety. Buyers should verify that the plastic materials comply with local health regulations in their respective markets.
Glass
Key Properties: Glass is a rigid and transparent material that offers excellent aesthetic appeal. It is highly resistant to chemicals and does not react with food products.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of glass is its ability to provide visibility of the products inside the vending machine, enhancing consumer appeal. However, glass is heavy and fragile, which can lead to higher shipping costs and potential breakage.
Impact on Application: Glass is often used in vending machines that dispense premium products, as it conveys a sense of quality. However, its weight and fragility may limit its use in high-traffic or outdoor environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the local regulations regarding glass use in vending machines, especially in markets where safety and durability are paramount. Compliance with standards such as JIS in Japan or EN in Europe is also important.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for vending machine vacancies | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High-traffic areas, food and beverage dispensing | Excellent corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight machines, outdoor environments | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Less durable than stainless steel | Medium |
| Plastic | Colorful designs, transparent product displays | Low cost and versatile | Susceptible to UV degradation and chemicals | Low |
| Glass | Premium product displays in vending machines | Aesthetic appeal and chemical resistance | Heavy and fragile, higher shipping costs | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection considerations for vending machines, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific market needs and regulatory environments.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vending machine vacancies
Manufacturing Processes for Vending Machines
Understanding the manufacturing processes involved in producing vending machines is crucial for B2B buyers looking to secure quality products. The production typically involves several key stages, including material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
1. Material Preparation
The initial step in vending machine manufacturing is the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include:
- Steel and Aluminum: These metals are favored for their durability and strength, essential for the machine’s structural integrity.
- Plastics: Used for components like buttons and internal fittings, plastics are lightweight and can be molded into various shapes.
- Electronic Components: This includes payment systems, sensors, and displays, which are critical for functionality.
Before production begins, materials undergo inspections to ensure they meet specified standards. This includes checking for defects, dimensions, and quality certifications.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, they are shaped into components. Key techniques used in this stage include:
- Cutting: Sheets of metal are cut to size using lasers or water jets, ensuring precision.
- Bending: Metal parts are bent to form the outer casing and internal structures using CNC bending machines.
- Molding: Plastics are molded into specific shapes for various components, such as trays and covers.
This stage is crucial as it establishes the basic structure and design of the vending machine.
3. Assembly
The assembly process involves combining the various components into a complete unit. This is typically done in a systematic manner:
- Sub-assembly: Components like the payment system and storage trays are assembled separately before being integrated into the main machine.
- Main Assembly: The casing, electronic components, and internal mechanisms are assembled. This may involve manual labor as well as the use of automated systems.
Quality checks during assembly are vital. Manufacturers often implement real-time inspections to ensure that parts fit correctly and that the assembly meets design specifications.
4. Finishing
Finishing touches are applied to the vending machines to enhance aesthetics and durability. This includes:
- Coating: Machines are often coated with powder paint to prevent rust and improve appearance.
- Labeling: Branding and operational instructions are printed and applied.
- Final Assembly: Any remaining components are added, and the machine is prepared for testing.
Quality Assurance in Vending Machine Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing vending machines, ensuring that the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations.
International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of relevant international standards that manufacturers should adhere to, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Indicates that the product complies with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for specific electronic components, ensuring they meet industry-specific requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process ensure that any defects are caught early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed machine undergoes a thorough inspection and testing to ensure all specifications are met.
Common Testing Methods
To verify quality, manufacturers often employ various testing methods, including:
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that all mechanical and electronic components operate correctly.
- Durability Testing: Machines are subjected to stress tests to evaluate their resilience and longevity.
- Safety Testing: Checks for electrical safety, potential hazards, and compliance with safety standards.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality assurance practices of potential suppliers is essential. Here are several actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to evaluate their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. This can involve on-site visits and reviews of production practices.
-
Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for documentation detailing their quality control measures, including testing results and compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Consider hiring third-party inspection services to conduct independent evaluations of the manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This adds an extra layer of assurance.
-
Certifications Review: Verify the validity of certifications claimed by suppliers, such as ISO or CE markings, through official channels.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate specific nuances related to quality control and certification:
-
Regulatory Variances: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Understanding local regulations is essential for compliance.
-
Cultural Considerations: Engaging with suppliers who understand local customs and business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and quality assessments.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain: Ensure that quality control measures are maintained throughout the supply chain, especially if components are sourced from multiple countries.
Conclusion
Investing in a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for vending machines is critical for B2B buyers. By ensuring that suppliers adhere to international standards and implementing robust quality control measures, buyers can mitigate risks and secure high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vending machine vacancies Sourcing
When sourcing vending machine vacancies, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will break down the cost components, identify key price influencers, and provide actionable buyer tips to facilitate effective negotiations and procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in vending machine vacancies is the materials used for the machines themselves. This includes the housing, internal mechanisms, and electronic components. Sourcing high-quality materials is vital, as it directly influences the machine’s durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect expenses related to manufacturing. This includes wages for assembly workers, engineers, and quality control personnel. In regions with varying labor rates, understanding local labor costs can significantly impact the overall pricing strategy.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and other operational costs incurred during production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, thereby allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Investment in tooling is necessary for production efficiency. Custom tooling may be required for specialized machine designs, which can add to the initial investment but may lead to cost savings in the long run through reduced production times.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality involves additional costs associated with testing and inspection. Buyers should seek suppliers that prioritize QC to avoid future costs related to product failures or recalls.
-
Logistics: The transportation of machines from the manufacturer to the buyer’s location can incur significant costs, especially for international shipments. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and customs duties will influence overall logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will incorporate a profit margin into their pricing. Understanding the market rate for similar products can help buyers gauge whether the proposed margin is reasonable.
Price Influencers
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer discounts for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing and manage inventory effectively.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized vending machines tailored to specific market needs may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications (such as ISO) can impact both cost and pricing. Machines with higher certifications may command a premium but could offer better reliability and lower total ownership costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a strong track record may charge more but often provide better support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential for cost management. These terms dictate who bears the costs and risks associated with shipping, which can significantly affect total expenses.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Buyers should be prepared to negotiate prices based on volume, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Leveraging multiple supplier quotes can provide a stronger negotiating position.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, operational costs, maintenance, and potential resale value. A cheaper initial price may lead to higher long-term costs if quality is compromised.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations that may affect pricing. It’s advisable to conduct market research specific to the region to understand these dynamics fully.
Disclaimer
Prices and costs mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and other variables. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence and obtain updated quotes from suppliers to ensure accurate budgeting and planning.
Spotlight on Potential vending machine vacancies Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘vending machine vacancies’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vending machine vacancies
Key Technical Properties for Vending Machine Vacancies
Understanding the essential technical properties of vending machines is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used in the construction of vending machines, such as stainless steel or high-grade plastic. High-quality materials enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, which is especially important in high-traffic areas or outdoor settings. For buyers, selecting machines made from superior materials can reduce maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of the equipment. -
Capacity
Capacity indicates the number of items a vending machine can hold, typically measured in terms of product slots or total volume. Understanding capacity is essential for aligning machine offerings with the target market’s demand. For instance, a high-capacity machine may be necessary in busy locations like airports or shopping malls, while smaller machines may suffice for office buildings. -
Power Consumption
This specification measures the energy efficiency of the vending machine, usually expressed in watts. As energy costs continue to rise, selecting energy-efficient models can lead to significant cost savings over time. Additionally, machines with lower power consumption may have a smaller environmental footprint, appealing to businesses focused on sustainability.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the acceptable variations in the dimensions of machine components. In vending machines, precise tolerances ensure that parts fit together correctly, contributing to operational reliability. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance specifications can help ensure compatibility with existing systems or replacement parts, reducing the risk of operational disruptions. -
User Interface Features
The user interface includes screens, buttons, and payment systems that facilitate customer interactions. Advanced user interfaces with touchscreens and cashless payment options can enhance the user experience, leading to increased sales. Buyers should assess these features to determine how they align with customer preferences in their specific markets.
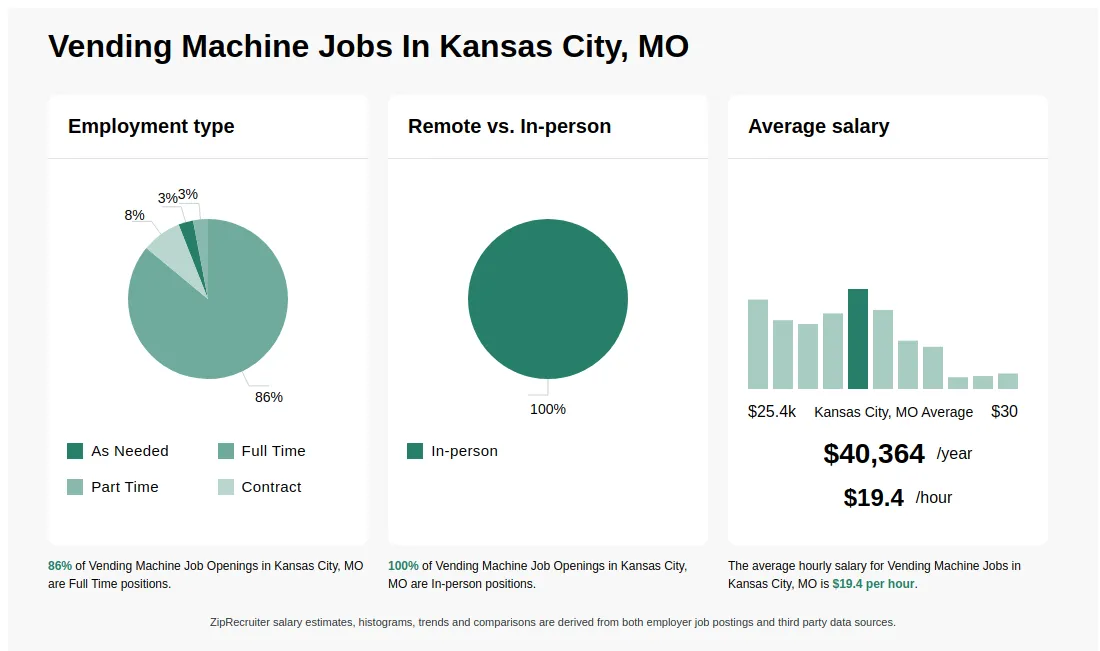
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication in the vending machine sector. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of vending machines, OEMs provide high-quality components that are essential for machine functionality. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing reliable parts for maintenance or upgrades. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers to understand, as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their sales projections to avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is vital for comparing supplier offerings and ensuring competitive pricing. For international buyers, clear RFQs can streamline communication and facilitate better pricing negotiations. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for buyers to avoid misunderstandings regarding shipping, insurance, and risk transfer. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between the initiation of an order and the completion of the product delivery. This term is crucial for planning and inventory management. Buyers should consider lead times when placing orders, especially if they operate in markets with fluctuating demand.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing vending machines, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and market competitiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vending machine vacancies Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global vending machine market has been experiencing significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for convenience and automation continues to rise. Notably, smart vending solutions that incorporate IoT technology are becoming increasingly prevalent. These systems allow operators to monitor inventory in real-time, optimize routes for restocking, and enhance customer engagement through personalized promotions.
Another key trend is the shift towards cashless transactions. With the growing penetration of mobile payment systems and contactless options, international B2B buyers should consider vending machines that accommodate these payment methods to attract a broader customer base. Additionally, the focus on product diversity is essential, as consumers now expect healthier options alongside traditional snacks and beverages. This is particularly relevant for markets like Europe, where there is a strong inclination towards organic and locally sourced products.
Furthermore, the impact of sustainability on purchasing decisions cannot be overlooked. Buyers are increasingly seeking vending machines that utilize eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies. Understanding local regulations regarding health and safety standards, as well as environmental impact, is crucial for successful market entry and operation.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has emerged as a core consideration for businesses in the vending machine sector. The environmental impact of vending operations, from energy consumption to waste generation, necessitates a commitment to ethical sourcing. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through the use of recyclable materials and energy-efficient designs.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to ethical practices. Additionally, sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce carbon footprints and promote local economies. Implementing closed-loop systems for packaging and waste can also enhance sustainability efforts, making the vending machine operation more appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
Investing in green technologies, such as solar-powered machines or those that minimize energy consumption, can not only reduce operational costs but also improve brand reputation among environmentally aware customers. By aligning with sustainability goals, B2B buyers can create a competitive advantage and foster long-term relationships with consumers who value corporate responsibility.
Brief Evolution/History
The vending machine sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially designed for simple transactions like dispensing candy and cigarettes, modern vending machines have transformed into high-tech solutions offering a wide variety of products, including healthy snacks and beverages. The introduction of cashless payment systems in the 2000s marked a pivotal shift, enhancing convenience and accessibility.
Over the last decade, the focus has shifted towards smart vending technology, integrating IoT capabilities for real-time data analytics and inventory management. This evolution reflects broader trends in consumer behavior towards automation and personalization, positioning vending machines as a vital component in the retail landscape for international B2B buyers. As the sector continues to innovate, understanding these historical shifts will aid buyers in making informed decisions that align with current market dynamics.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vending machine vacancies
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for vending machine vacancies?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, reputation, and customer reviews. Ensure they have a robust track record in your region, particularly focusing on compliance with local regulations. Request references from previous clients, and conduct background checks to verify their legitimacy. Additionally, inquire about their production capabilities and whether they can meet your specific requirements. Engaging suppliers with a transparent business model fosters trust and minimizes risks. -
Can I customize vending machines to fit my business needs?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization options for vending machines. This can include branding, selection of products, and machine features such as payment methods or energy efficiency. Discuss your specific requirements early in the negotiation process to ensure the supplier can accommodate your needs. Customization may impact lead times and costs, so be clear about your budget and timeline to avoid misunderstandings. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for vending machines?
Minimum order quantities vary significantly by supplier and can depend on the type of vending machines ordered. Generally, MOQs may range from a few units to several dozen. Lead times also differ based on customization levels and supplier capacity, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. Always clarify these details upfront to align your procurement schedule with your operational needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing vending machines?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common arrangements include upfront payments, deposits, or installment payments. International buyers should be aware of currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide security for both parties, such as letters of credit or escrow services, particularly for larger orders. Ensure that payment terms are clearly documented in the contract to avoid future disputes. -
How can I ensure the quality of the vending machines I purchase?
To ensure quality, request detailed specifications and certifications from suppliers, including ISO certifications and compliance with international safety standards. Conduct thorough inspections upon delivery, and consider third-party quality assurance services for additional scrutiny. Implement a trial period to assess the machines’ performance in real-world conditions, which can help identify any issues before fully committing to the supplier. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing vending machines?
Logistics is critical in the vending machine supply chain. Consider shipping methods, potential tariffs, and customs clearance processes in your target market. Collaborate with reliable freight forwarders who have experience in handling large equipment. Additionally, factor in local transportation and installation services, as well as after-sales support, to ensure a smooth transition from supplier to your operational site. -
How can I handle disputes with vending machine suppliers?
Establish a clear dispute resolution process in your contract, including steps for mediation and arbitration. Maintain open communication with your supplier to address issues promptly. Document all interactions and agreements to provide evidence if disputes arise. If necessary, consider involving legal counsel familiar with international trade laws to navigate complex situations, particularly when dealing with cross-border contracts. -
What certifications should I look for when sourcing vending machines?
Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with safety and operational standards, such as CE marking in Europe, UL certification in the US, or ISO standards relevant to manufacturing and quality management. These certifications can indicate the machine’s reliability and adherence to safety protocols. Additionally, inquire about any environmental certifications if sustainability is a priority for your business strategy.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vending machine vacancies
The landscape of vending machine vacancies presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers to capitalize on emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As urbanization and consumer habits evolve, strategic sourcing becomes paramount. By aligning with local suppliers who understand regional preferences, businesses can enhance their product offerings and improve customer engagement.
Key Takeaways:
– Local Insights: Leverage local market knowledge to tailor vending machine selections that resonate with diverse consumer bases.
– Sustainable Practices: Embrace eco-friendly sourcing to meet increasing consumer demand for sustainability.
– Technology Integration: Invest in smart vending solutions that enhance user experience and operational efficiency.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers must remain agile and responsive to changing market dynamics. The future of vending machines lies in adaptability and innovation. By forging strategic partnerships and embracing new technologies, businesses can secure a competitive edge.
Call to Action: Engage with local distributors, explore partnerships with tech firms, and invest in market research to position your business for success in this burgeoning sector. The time to act is now—capitalize on these opportunities to lead in the vending machine market.