Mastering the Art of Investing in Vending Machines for B2B
Guide to Investing In Vending Machines
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for investing in vending machines
- Understanding investing in vending machines Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of investing in vending machines
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for investing in vending machines
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for investing in vending machines
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for investing in vending machines Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential investing in vending machines Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for investing in vending machines
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the investing in vending machines Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of investing in vending machines
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for investing in vending machines
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for investing in vending machines
Investing in vending machines represents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in dynamic regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As consumer habits evolve and the demand for convenient, on-the-go solutions increases, vending machines have emerged as a lucrative avenue for generating revenue. This guide is designed to empower you with the knowledge necessary to navigate this expanding market effectively.
In the following sections, we will delve into various types of vending machines, including traditional, smart, and specialized units tailored for specific markets. You’ll gain insights into the essential materials and manufacturing processes, ensuring you understand what contributes to quality and durability. Additionally, we will explore the landscape of suppliers, providing a comprehensive overview of key players in the industry, alongside considerations for evaluating their offerings.
Understanding the cost implications and market trends is crucial for making informed decisions. This guide addresses frequently asked questions, equipping you with the answers needed to mitigate risks and maximize returns on your investment. By leveraging this information, you will be better positioned to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with your business objectives, whether you’re looking to penetrate new markets or enhance existing operations. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your business through smart investments in vending machines.
Understanding investing in vending machines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Snack Vending | Dispenses packaged snacks and beverages | Offices, schools, gyms | Pros: Low maintenance, wide product variety. Cons: Limited health options, may require regular restocking. |
| Fresh Food Vending | Offers perishable items like sandwiches and salads | Hospitals, universities, corporate cafes | Pros: Attracts health-conscious consumers. Cons: Higher spoilage risk and maintenance needs. |
| Specialty Vending | Focuses on niche products (e.g., electronics, beauty) | Airports, tech hubs, malls | Pros: Unique offerings can drive higher sales. Cons: Limited customer base and potential for high inventory costs. |
| Automated Retail Kiosks | Combines vending with e-commerce features | Retail stores, event venues | Pros: Advanced technology, real-time inventory tracking. Cons: High initial investment and tech maintenance. |
| Micro Market Systems | Self-service kiosks with open product displays | Workplaces, factories, residential complexes | Pros: Flexible product selection, enhances user experience. Cons: Requires space and can be costly to set up. |
Traditional Snack Vending
Traditional snack vending machines are the most common type, offering a variety of packaged snacks and beverages. They are particularly suitable for environments like offices, schools, and gyms, where quick access to snacks is valued. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the product mix and machine reliability. While these machines require less maintenance and offer a wide variety, they often lack healthier options, which could limit appeal in health-conscious markets.
Fresh Food Vending
Fresh food vending machines provide perishable items such as sandwiches, salads, and fruit. They cater to sectors like hospitals, universities, and corporate cafes, where fresh meal options are in demand. Buyers should consider the freshness and sourcing of products, as well as the machine’s refrigeration capabilities. Although these machines can attract health-conscious consumers, they also face challenges like higher spoilage rates and more frequent maintenance needs.
Specialty Vending
Specialty vending machines focus on niche markets by offering unique products such as electronics, beauty items, or artisanal foods. They are often found in high-traffic areas like airports, tech hubs, and malls. B2B buyers should assess the target audience and product demand before investing. While these machines can command higher prices and attract specific customer segments, they may also face limited customer bases and higher inventory costs.
Automated Retail Kiosks
Automated retail kiosks blend traditional vending with e-commerce, allowing for a more interactive shopping experience. They are suitable for retail environments and event venues, where technology-savvy consumers seek convenience. Buyers should consider the initial investment and ongoing tech support when evaluating these machines. Although they offer advanced features like real-time inventory tracking, the higher setup costs and maintenance can be a barrier for some businesses.
Micro Market Systems
Micro market systems are self-service kiosks that provide open product displays, allowing customers to choose from a wide range of items. These are ideal for workplaces, factories, and residential complexes where flexibility and variety are essential. B2B buyers must consider the space requirements and initial setup costs. While they enhance the user experience and can adapt to changing consumer preferences, the investment needed for installation can be significant.
Key Industrial Applications of investing in vending machines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of investing in vending machines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Medicine and health supplies dispensing | Improved patient care, reduced wait times | Compliance with health regulations, secure payment systems |
| Education | Snack and beverage vending for students | Enhanced student satisfaction, increased revenue | Supplier reliability, nutritional content of offerings |
| Corporate Offices | Coffee and snack vending for employees | Boosted employee morale, increased productivity | Variety of products, maintenance services |
| Transportation Hubs | Travel essentials vending (snacks, drinks, toiletries) | Convenience for travelers, reduced operational costs | Location analysis, product turnover rates |
| Retail | Automated retail for high-demand products | 24/7 sales capability, reduced labor costs | Product selection, technology integration |
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, investing in vending machines for dispensing medicine and health supplies addresses the need for quick access to essential items. These machines can significantly improve patient care by providing medications, first-aid supplies, or personal protective equipment (PPE) outside of regular pharmacy hours. For B2B buyers, it is crucial to ensure compliance with local health regulations and to incorporate secure payment systems to protect sensitive patient information.
Education
In educational institutions, vending machines offering snacks and beverages cater to the needs of students and staff. This not only enhances student satisfaction by providing convenient access to food but also generates additional revenue for the institution. Buyers should consider the reliability of suppliers and the nutritional content of the offerings, ensuring that they align with health guidelines and support student well-being.
Corporate Offices
Corporate offices benefit from vending machines that provide coffee and snacks for employees. This investment can lead to improved employee morale and increased productivity, as it offers convenient access to refreshments throughout the workday. B2B buyers should focus on the variety of products offered and the availability of maintenance services to ensure that machines remain stocked and functional.
Transportation Hubs
Vending machines in transportation hubs, such as airports and train stations, provide travelers with essential items like snacks, drinks, and toiletries. This application meets the demand for convenience, allowing travelers to purchase items quickly without the need for extensive staff involvement. When sourcing these machines, it’s essential to conduct a location analysis to determine high-traffic areas and assess product turnover rates to maximize profitability.
Retail
Automated retail solutions through vending machines allow businesses to offer high-demand products, such as electronics or personal care items, in a 24/7 format. This not only increases sales potential but also reduces labor costs associated with traditional retail environments. Buyers should evaluate product selection and technology integration capabilities to ensure that the machines can effectively meet consumer demands and enhance the shopping experience.
Related Video: Kooler Ice Vending Machines – IM600XL vs. IM1000
Strategic Material Selection Guide for investing in vending machines
When investing in vending machines, selecting the right materials is crucial for ensuring durability, functionality, and compliance with local regulations. Here, we analyze four common materials used in vending machine construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°F (427°C) and is resistant to rust and staining.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its durability and low maintenance requirements, making it ideal for high-traffic environments. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process can be complex, which may lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of media, including food and beverages, making it a preferred choice for vending machines. Its resistance to corrosion ensures that it maintains hygiene standards, which is crucial in food service.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local health and safety regulations. In Europe, for instance, materials must meet standards such as EN 10088 for stainless steel. In Africa and South America, buyers should consider local sourcing to reduce costs and ensure compliance with regional standards.
Plastic (Polycarbonate)
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a lightweight, impact-resistant plastic with a temperature rating of around 240°F (115°C). It offers good clarity and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of polycarbonate is its cost-effectiveness and versatility in design. However, it can be less durable than metals and may become brittle over time, especially under UV exposure.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is suitable for non-structural components, such as windows or display panels in vending machines. Its transparency allows for visibility of products, enhancing customer engagement.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying quality of polycarbonate in different regions. Compliance with standards such as ASTM D635 for flammability and ISO 179 for impact resistance is essential, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and has a good strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°F (316°C) and is often treated with anodization for enhanced durability.
Pros & Cons: The benefits of aluminum include its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, making it easy to handle and install. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may require additional coatings for enhanced durability.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in the structural components of vending machines, such as frames and panels. Its lightweight properties contribute to easier transportation and installation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum used meets local standards, such as ASTM B221 for extruded aluminum and EN 573 for aluminum alloys. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing locally can help mitigate costs and support local economies.
Glass
Key Properties: Glass is a rigid material with excellent clarity and aesthetic appeal. It can withstand moderate temperatures but is more fragile than other materials, with a typical temperature rating of around 200°F (93°C).
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of glass is its visual appeal, providing an upscale look to vending machines. However, its fragility can be a significant drawback, requiring careful handling and installation.
Impact on Application: Glass is commonly used for display panels in vending machines, allowing customers to see products clearly. Its non-porous surface also aids in maintaining hygiene.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of safety standards regarding glass, such as ANSI Z97.1 in the U.S. and EN 12150 in Europe. In regions prone to vandalism, tempered or laminated glass may be a preferred option to enhance security.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for investing in vending machines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Structural components, food contact surfaces | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic (Polycarbonate) | Display panels, non-structural components | Cost-effective, versatile design | Less durable, may become brittle over time | Medium |
| Aluminum | Frames, panels | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than steel, requires coatings | Medium |
| Glass | Display panels | Aesthetic appeal, good visibility | Fragility, requires careful handling | Medium |
Selecting the appropriate materials for vending machines is essential for ensuring product longevity and compliance with local standards. By understanding the properties and implications of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for investing in vending machines
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance systems in the vending machine industry are critical for ensuring product reliability, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. For international B2B buyers, understanding these processes can significantly impact investment decisions. This section delves into the typical manufacturing stages, key quality control measures, and actionable insights for verifying supplier quality.
Manufacturing Processes
Investing in vending machines involves a complex manufacturing process that can be broken down into several key stages:
-
Material Preparation
– Sourcing Materials: High-quality materials such as stainless steel, plastics, and electronic components are sourced from reliable suppliers. This stage is crucial, as the durability and functionality of the vending machines depend heavily on material quality.
– Material Testing: Before production begins, materials undergo rigorous testing for strength, durability, and compliance with international standards. -
Forming
– Fabrication Techniques: Common techniques used include laser cutting, stamping, and CNC machining. These methods allow for precise shaping of components, ensuring that all parts fit together seamlessly.
– Component Manufacturing: Individual parts such as the chassis, doors, and dispensing mechanisms are created during this stage. Advanced robotics may be employed to enhance precision and efficiency. -
Assembly
– Sub-assembly: Components are first assembled into sub-units, such as the control panel and product dispensing systems. This modular approach facilitates easier troubleshooting and maintenance.
– Final Assembly: All sub-units are then combined into the final vending machine. This stage often includes the installation of software and testing of electronic systems to ensure functionality. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: This may include painting, powder coating, or applying anti-corrosion treatments to enhance aesthetics and longevity.
– Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to check for defects and ensure that the vending machine meets design specifications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is essential in the vending machine manufacturing process to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. Here are some key aspects:
-
International Standards
– ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is crucial for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
– CE Marking: For machines sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. -
Industry-Specific Certifications
– API (American Petroleum Institute): Relevant for vending machines that dispense fuel or other petroleum products, ensuring they meet specific safety and operational standards.
– RoHS Compliance: Ensures that electrical and electronic equipment does not contain hazardous substances. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors manufacturing processes to detect defects early, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts a comprehensive review of the completed machines, including functionality tests and visual inspections. -
Common Testing Methods
– Functional Testing: Verifies that all mechanical and electronic components operate correctly.
– Durability Testing: Simulates long-term use to assess the machine’s performance under stress.
– Safety Testing: Ensures that the machine complies with safety regulations, minimizing risks to users.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Verifying Supplier Quality
For B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits
– Schedule on-site audits to evaluate manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. This allows buyers to gain firsthand insight into the supplier’s operations. -
Request Quality Reports
– Ask suppliers for their quality assurance reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These documents should provide a clear picture of the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
Third-Party Inspections
– Engage third-party inspection services to independently assess the manufacturing processes and final products. This adds an extra layer of assurance regarding quality and compliance. -
Understand Certification Nuances
– Different regions may have varying certification requirements. For example, while CE marking is crucial in Europe, other regions may focus on local certifications. Understanding these nuances can help buyers ensure compliance with local regulations. -
Evaluate Post-Sale Support
– A reliable supplier should provide robust post-sale support, including maintenance, spare parts availability, and warranty terms. This is essential for the long-term success of the vending machine investment.
Conclusion
Investing in vending machines requires a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved. By focusing on key manufacturing stages, international standards, and effective verification methods, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure the reliability and longevity of their investments. This approach not only mitigates risks but also enhances overall operational efficiency and customer satisfaction in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Related Video: Most Satisfying Factory Production Processes And Heavy-Duty Factory Machines!
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for investing in vending machines Sourcing
In the realm of vending machine investment, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis is pivotal for international B2B buyers. This segment offers insights into cost components, price influencers, and practical tips for navigating the complexities of sourcing vending machines, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in vending machines—such as metal casings, electronic components, and glass fronts—significantly influence costs. Buyers should prioritize durable materials that can withstand varying climates, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. For instance, labor costs in South America may be lower than in Europe, but this must be weighed against potential quality differences. Ensuring that labor practices comply with international standards can also affect overall expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Understanding the overhead structure of suppliers can help buyers gauge the pricing rationale.
-
Tooling: Customization often requires specific tooling, which can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should discuss tooling costs upfront, particularly if they require unique specifications for their machines.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investment in quality control processes ensures reliability and compliance with safety standards. While this may add to initial costs, it can prevent future expenses related to defects or recalls.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors such as freight charges, insurance, and customs duties can add substantial expenses. Utilizing local suppliers or those with efficient logistics can mitigate these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the standard margins in different regions can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Price Influencers
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to discounts. Understanding the MOQ policies of suppliers can enable buyers to optimize their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom vending machines tailored to specific markets or consumer preferences can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether the added investment aligns with potential revenue gains.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., CE, ISO) can elevate costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better guarantees and service levels.
-
Incoterms: International Commercial Terms dictate responsibilities for shipping and delivery. Familiarizing oneself with these terms can prevent unexpected costs and liabilities.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Cultivate strong relationships with suppliers. Effective negotiation can lead to more favorable terms, especially for long-term contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs. Opt for machines designed for energy efficiency to reduce operational expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, costs in Italy may reflect higher labor and material standards compared to South Africa, which could influence total investment.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to identify the most competitive suppliers and pricing structures in your target region.
-
Trial Runs: If feasible, request prototypes or trial periods to evaluate the performance and reliability of vending machines before committing to large orders.
Disclaimer
Pricing for vending machines can vary significantly based on numerous factors including specifications, supplier location, and market conditions. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential investing in vending machines Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for investing in vending machines.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for investing in vending machines
Investing in vending machines requires a solid understanding of various technical properties and industry jargon that can influence decision-making. Below is an overview of essential specifications and trade terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the quality and type of materials used in manufacturing vending machines, such as stainless steel, plastic, or tempered glass.
– Importance: The material grade impacts durability, maintenance requirements, and resistance to environmental factors. High-quality materials can reduce long-term operational costs and enhance the machine’s lifespan. -
Dimensions and Capacity
– Definition: Dimensions refer to the physical size of the vending machine, while capacity indicates the number of items it can hold.
– Importance: Understanding the space available for installation and the expected volume of sales is crucial. Buyers must ensure that the machine fits in the designated area and meets consumer demand without frequent restocking. -
Power Consumption
– Definition: The amount of electricity the vending machine requires to operate, usually measured in watts.
– Importance: This property is vital for budgeting operational costs. Machines with lower power consumption can significantly reduce electricity bills, making them more cost-effective in the long run. -
Payment Systems
– Definition: Refers to the methods of payment accepted by the vending machine, such as cash, credit/debit cards, or mobile payments.
– Importance: A diverse range of payment options can increase sales by catering to different consumer preferences. Understanding the integration of payment systems is essential for ensuring a seamless transaction process. -
Temperature Control
– Definition: The ability of the vending machine to maintain specific temperatures for perishable items, often measured in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit.
– Importance: For machines selling food and beverages, precise temperature control is crucial for compliance with health regulations and ensuring product quality. Buyers should assess the machine’s cooling or heating capabilities based on the intended product range.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality and reliability in components. Choosing machines from reputable OEMs can lead to better service and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers must evaluate whether the MOQ aligns with their market demand and financial capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to invite suppliers to bid on a specific product or service.
– Importance: An RFQ helps streamline the procurement process by providing a structured way to gather pricing and specifications from multiple vendors, ensuring competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities. This knowledge can prevent misunderstandings during the import/export process, especially for international buyers.
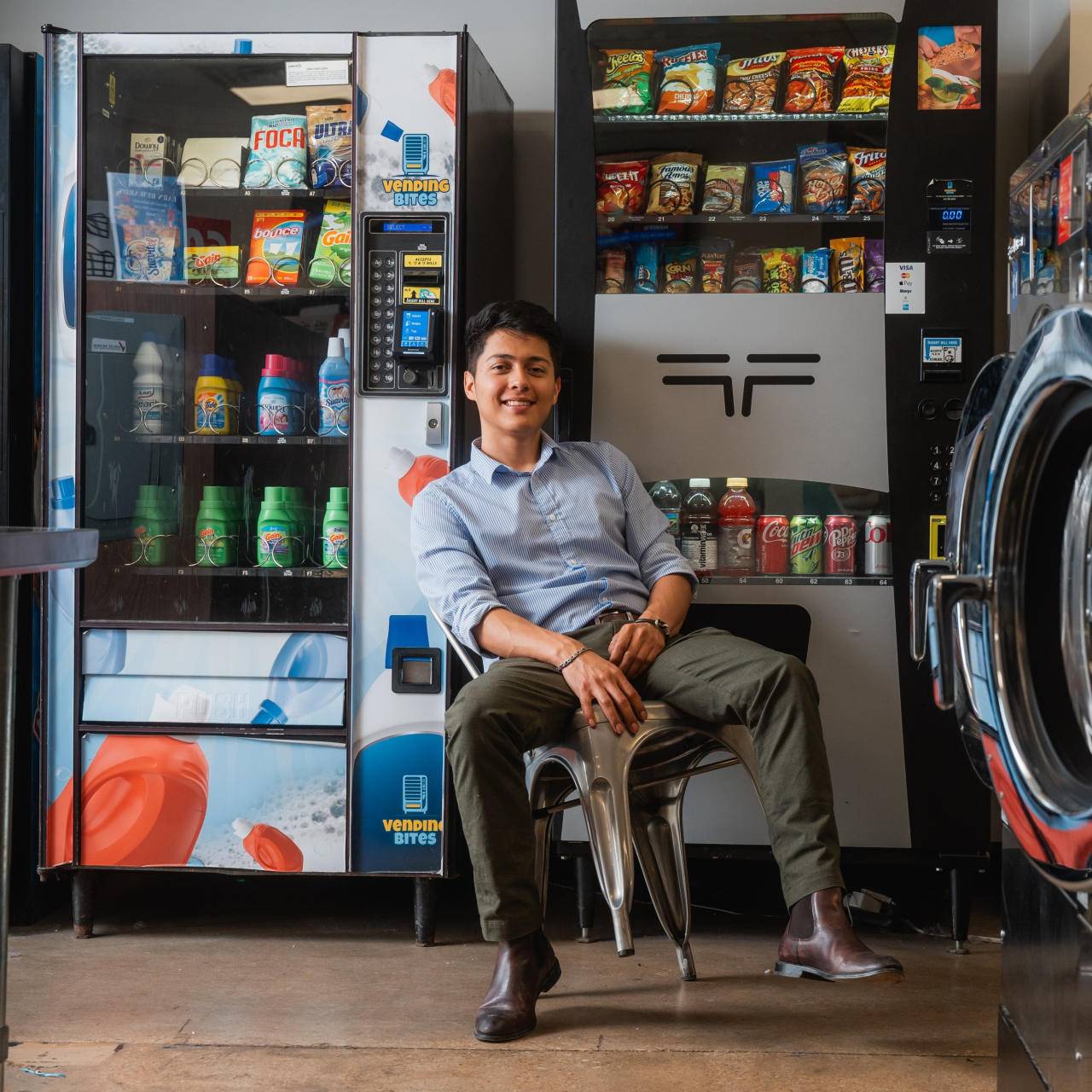

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times helps in planning inventory and managing customer expectations. Longer lead times can impact sales, particularly in markets with rapid consumer demand.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their investment in vending machines, ultimately leading to increased profitability and market competitiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the investing in vending machines Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global vending machine market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for convenience and automation in consumer interactions. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the current and emerging trends is crucial for making informed investment decisions. One of the primary drivers is the rising trend of cashless transactions, which is transforming how vending machines operate. Buyers should prioritize vendors that offer machines equipped with advanced payment options, including mobile wallets and contactless cards.
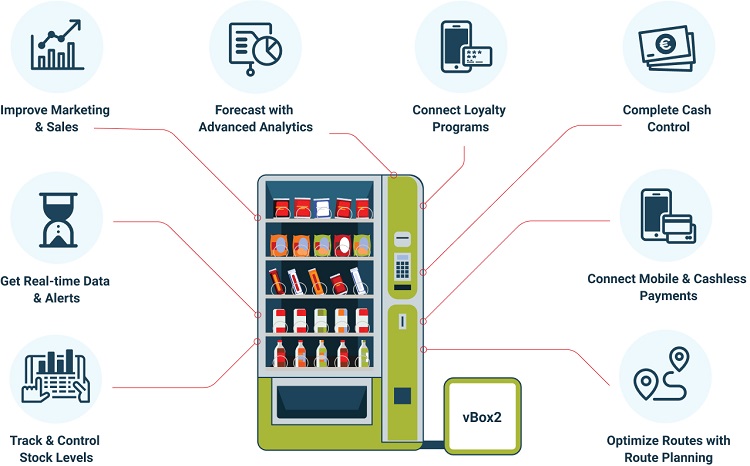
Moreover, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology is reshaping the vending landscape. Smart vending machines equipped with sensors and real-time data analytics provide operators with insights on inventory management and consumer behavior. This technology not only enhances operational efficiency but also improves the customer experience, a vital factor in driving sales. Buyers should seek suppliers that offer IoT-enabled machines to leverage these benefits.
Sustainability is another critical market dynamic. Consumers are increasingly conscious of their environmental impact, prompting vending machine operators to focus on sustainable practices. This includes sourcing eco-friendly products and utilizing energy-efficient machines. For international buyers, aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of vending machines extends beyond their operation; it encompasses the entire supply chain, from sourcing materials to product disposal. As B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe consider investments in this sector, it is essential to emphasize ethical sourcing practices. This includes selecting suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and environmentally responsible manufacturing processes.
Buyers should actively seek out vendors who utilize green certifications such as Energy Star or LEED, which indicate a commitment to sustainability. Additionally, sourcing materials like recycled plastics or biodegradable components can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of vending machines. By prioritizing these practices, buyers not only contribute to environmental preservation but also position themselves as leaders in sustainability within their markets.
Furthermore, transparency in the supply chain is vital. Buyers should establish partnerships with suppliers who provide clear information regarding their sourcing practices and environmental policies. This transparency fosters trust and aligns with the growing consumer demand for ethical business practices.
Brief Evolution/History
The vending machine industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, machines dispensed simple items like candy and cigarettes. However, advancements in technology have transformed vending into a sophisticated sector capable of offering a wide range of products, including fresh food and beverages.
As the market expanded, so did the need for enhanced consumer engagement. Modern vending machines now incorporate touchscreens, interactive interfaces, and IoT capabilities, allowing for a more personalized shopping experience. This evolution reflects the changing consumer landscape and highlights the importance of innovation for B2B buyers aiming to invest in the future of vending machines. Understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into current trends and future opportunities in the market.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of investing in vending machines
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for vending machines?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and customer reviews. Investigate their compliance with international quality standards and certifications relevant to your region, such as ISO or CE markings. Engage in direct communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to customize products according to your market needs. Additionally, assess their financial stability and the availability of after-sales support, as these can significantly impact your long-term investment. -
Can vending machines be customized to suit local preferences?
Yes, customization is crucial for vending machines to appeal to local markets. Suppliers often offer options for machine design, product selection, and payment methods tailored to specific consumer preferences. Discuss your target audience’s habits with potential suppliers to ensure the machines can accommodate local tastes and payment systems, such as mobile payments popular in many African and South American countries. This approach can enhance customer satisfaction and boost sales. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for vending machines?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the machines. Generally, MOQs range from a few units to several dozen, depending on customization options. Lead times can also differ, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss these details upfront with potential suppliers to align your business timeline and avoid unexpected delays, especially when planning for seasonal peaks in demand. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing vending machines internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common practices include partial upfront payments (30-50%) with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letters of credit for larger orders. It’s essential to clarify payment methods, currency, and any associated fees upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using secure payment platforms to protect your transactions, especially when dealing with international suppliers. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in vending machine suppliers?
Quality assurance is vital for ensuring the reliability and longevity of vending machines. Look for suppliers that implement rigorous testing protocols during production and provide certifications that verify compliance with international quality standards. Request documentation on their QA processes, such as inspections and performance testing. Additionally, inquire about warranties and service agreements to ensure support in case of defects or operational issues. -
How should I approach logistics and shipping for international vending machine purchases?
Logistics is a crucial component of your investment strategy. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including modes of transport (air, sea, or land) and associated costs. Understand the customs regulations in your country, as these can affect delivery timelines and import duties. Collaborating with a reputable logistics partner can streamline the shipping process and ensure that your machines arrive safely and on time, minimizing potential disruptions to your operations. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with vending machine suppliers?
To effectively manage disputes, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in writing. If issues arise, first attempt to resolve them directly with the supplier through discussions. If that fails, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Additionally, consider involving a legal advisor familiar with international trade laws to navigate complex situations and protect your interests. -
What certifications should I verify when sourcing vending machines?
When sourcing vending machines, verify that they have relevant certifications such as CE marking for compliance with European safety standards or other regional certifications applicable in Africa or South America. These certifications ensure that the machines meet safety, health, and environmental regulations. Request proof of compliance from suppliers and check if they adhere to local regulations in your target market, as this can impact your ability to operate legally and efficiently.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for investing in vending machines
Investing in vending machines presents a lucrative opportunity for B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in maximizing ROI by ensuring that businesses select the right equipment, suppliers, and locations to meet consumer demand effectively.
Key takeaways include understanding local market preferences, leveraging technology for operational efficiency, and considering the impact of regulations on supply chains. By sourcing high-quality machines that align with regional tastes and preferences, buyers can enhance customer satisfaction and drive sales.
As the vending industry evolves, embracing innovative solutions such as cashless payments and healthy product offerings will be crucial. International buyers should remain vigilant about emerging trends and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Looking ahead, the potential for growth in this sector is significant. By investing in the right partnerships and technologies, businesses can not only meet current consumer needs but also anticipate future demands. Now is the time for B2B buyers to take decisive action and explore the opportunities that vending machine investments can offer in their respective markets.