Master Sourcing Japanese Food Vending Machines for B2B
Guide to Japanese Food Vending Machines
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for japanese food vending machines
- Understanding japanese food vending machines Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of japanese food vending machines
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for japanese food vending machines
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for japanese food vending machines
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for japanese food vending machines Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential japanese food vending machines Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for japanese food vending machines
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the japanese food vending machines Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of japanese food vending machines
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for japanese food vending machines
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for japanese food vending machines
In the dynamic landscape of global commerce, Japanese food vending machines have emerged as a pivotal solution for businesses looking to capitalize on consumer trends towards convenience and diverse culinary experiences. These machines not only cater to the growing demand for quick service dining but also introduce authentic Japanese cuisine to a wider audience, making them an attractive investment for B2B buyers across various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the multifaceted world of Japanese food vending machines, providing insights into different types available in the market, the materials used in their construction, and the manufacturing processes that ensure quality and reliability. We will explore key suppliers, discuss cost considerations, and analyze market trends that influence purchasing decisions.
Additionally, we will address frequently asked questions that often arise during the sourcing process, equipping international buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions. By understanding the intricate details of these vending machines, businesses can effectively integrate them into their operations, enhancing customer satisfaction and expanding their market reach. With this guide, you will be empowered to navigate the complexities of sourcing Japanese food vending machines and leverage their potential to drive growth and innovation in your markets.
Understanding japanese food vending machines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Food Vending Machines | Offers freshly cooked meals, often with heating elements | Restaurants, office buildings, hospitals | Pros: High customer satisfaction; Cons: Requires regular maintenance and power supply. |
| Cold Beverage Vending Machines | Dispenses chilled drinks; often includes a variety of brands | Convenience stores, schools, gyms | Pros: Low maintenance; Cons: Limited food options. |
| Snack Vending Machines | Provides packaged snacks and quick bites | Airports, train stations, retail outlets | Pros: Easy to restock; Cons: Less healthy options may deter health-conscious buyers. |
| Automated Sushi Machines | Specializes in sushi; often uses advanced technology for freshness | Japanese restaurants, food courts | Pros: Unique offering; Cons: Higher initial investment and operational complexity. |
| Specialty Dessert Machines | Focuses on desserts like mochi or soft serve | Cafes, dessert shops, event venues | Pros: Appeals to niche markets; Cons: Seasonal demand fluctuations. |
Hot Food Vending Machines
Hot food vending machines are designed to provide freshly cooked meals, often equipped with heating elements to ensure food remains warm. These machines are particularly suitable for locations with high foot traffic, such as office buildings, hospitals, and universities. B2B buyers should consider the machine’s capacity, ease of maintenance, and the variety of meals offered to cater to diverse dietary preferences. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure food safety and quality, which can be a significant factor in operational costs.
Cold Beverage Vending Machines
Cold beverage vending machines focus on dispensing chilled drinks, including soft drinks, juices, and bottled water. They are commonly found in convenience stores, schools, and gyms. For B2B buyers, the advantages include low maintenance and ease of restocking, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. However, the limited food options may not meet the needs of customers seeking more substantial meals, which could affect overall sales in some environments.
Snack Vending Machines
Snack vending machines offer a variety of packaged snacks and quick bites, making them a popular choice in airports, train stations, and retail outlets. These machines are easy to restock and maintain, providing a steady revenue stream. However, B2B buyers should be aware that the prevalence of less healthy options might deter health-conscious consumers, potentially limiting sales in certain demographics. Choosing a machine that allows for healthier snack options can enhance appeal.
Automated Sushi Machines
Automated sushi machines specialize in dispensing sushi and often utilize advanced technology to maintain freshness. They are particularly suited for Japanese restaurants and food courts looking to offer a unique dining experience. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and operational complexity, as these machines may require specialized training for staff. However, their ability to provide high-quality, fresh sushi can significantly enhance a venue’s reputation and customer satisfaction.
Specialty Dessert Machines
Specialty dessert machines focus on providing niche offerings like mochi or soft serve ice cream. They are ideal for cafes, dessert shops, and event venues that aim to attract dessert lovers. B2B buyers must consider the seasonal demand fluctuations and the potential need for promotional strategies to maintain sales throughout the year. The appeal to niche markets can create a loyal customer base, but understanding local preferences is essential for success.
Related Video: How Japanese Food Vending Machines Work ★ ONLY in JAPAN
Key Industrial Applications of japanese food vending machines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Japanese Food Vending Machines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitality | In-room dining solutions for hotels | Enhances guest experience and reduces staff workload | Customization options for menu, payment systems, and service support |
| Corporate Offices | Employee snack and meal provision | Improves employee satisfaction and productivity | Variety of food options, nutritional information, and payment flexibility |
| Educational Institutions | Student dining solutions | Convenient access to meals, supports student health | Compliance with dietary requirements, machine durability, and ease of use |
| Transportation Hubs | Quick-service food options at airports and stations | Reduces wait times, increases passenger satisfaction | Space efficiency, energy consumption, and reliability in high traffic areas |
| Retail Environments | Point-of-sale for gourmet snacks and meals | Attracts foot traffic, increases impulse purchases | Location analysis, product variety, and integration with existing retail systems |
Hospitality Sector
In the hospitality industry, Japanese food vending machines serve as innovative in-room dining solutions, providing guests with a variety of meal options at their convenience. This application addresses the challenge of limited staff availability while enhancing the overall guest experience. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, it’s crucial to consider customization options that reflect local tastes and dietary preferences, alongside robust service support to ensure machine reliability.
Corporate Offices
Within corporate environments, these vending machines can significantly enhance employee satisfaction by providing quick access to healthy snacks and meals. This application is particularly beneficial in regions like South America and Europe, where work-life balance is increasingly valued. Buyers should focus on the variety of food options available, ensuring they meet nutritional standards, and consider flexible payment systems that align with employee preferences.
Educational Institutions
Japanese food vending machines are also increasingly utilized in educational institutions, offering students easy access to nutritious meals and snacks. This application addresses common challenges such as limited dining hours and overcrowded cafeterias. For international buyers, particularly in Europe and Africa, it is essential to ensure compliance with dietary requirements and to select machines that are durable and user-friendly for students.
Transportation Hubs
In transportation hubs like airports and train stations, Japanese food vending machines provide quick-service food options that cater to the fast-paced environment. This solution helps reduce wait times and enhances passenger satisfaction, particularly in the Middle East and Europe where travel is frequent. Buyers should prioritize space efficiency and energy consumption, ensuring that machines can withstand high traffic while remaining reliable.
Retail Environments
Retail environments benefit from Japanese food vending machines as they act as a point-of-sale for gourmet snacks and meals. This application attracts foot traffic and encourages impulse purchases, making it a valuable addition to any retail strategy. For B2B buyers in South America and Africa, conducting a thorough location analysis and ensuring a diverse product variety are critical to maximizing the impact of these machines in retail settings.
Related Video: 23 Must-See Unique Japanese Vending Machines in 2024
Strategic Material Selection Guide for japanese food vending machines
When selecting materials for Japanese food vending machines, it is crucial to consider various factors that impact the performance, durability, and compliance of the machines. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these vending machines, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C (1472°F) and can handle moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and staining, making it ideal for food applications. However, it tends to be more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to fabricate due to its toughness.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with various food media, ensuring hygiene and safety. Its non-reactive nature prevents contamination, making it suitable for vending machines dispensing perishable items.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international food safety standards, such as those set by the FDA or EU regulations. Common grades like AISI 304 and 316 are widely accepted, but buyers must verify local standards in regions like the UAE or Turkey.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized. It can handle temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and is generally not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easier to transport and install, reducing overall shipping costs. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can dent or scratch more easily, which may affect the aesthetic appeal of the vending machine.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for non-perishable food items and dry goods. Its lower melting point makes it less ideal for hot food applications unless specifically treated or alloyed.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific aluminum grades that comply with local standards. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental factors may vary, ensuring the right coating for corrosion resistance is essential.
Polycarbonate
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is a strong, lightweight thermoplastic with a temperature tolerance of up to 120°C (248°F). It offers good impact resistance and is inherently UV resistant.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of polycarbonate is its transparency and strength, making it ideal for display panels in vending machines. However, it is less resistant to scratches and may require protective coatings to maintain clarity over time.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is suitable for displaying food items and is often used in the front panels of vending machines. Its clarity allows customers to see products easily, enhancing user experience.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the polycarbonate used is food-grade and compliant with local regulations. In markets like the Middle East, where UV exposure is high, selecting UV-stabilized polycarbonate is advisable.
Mild Steel
Key Properties:
Mild steel has a good strength-to-weight ratio and is suitable for structural applications. It typically has a temperature rating of around 250°C (482°F) but is prone to corrosion without protective coatings.
Pros & Cons:
Mild steel is cost-effective and easy to fabricate, making it a popular choice for structural components. However, its susceptibility to rust can lead to increased maintenance costs and reduced lifespan if not properly treated.
Impact on Application:
Mild steel is generally used for the frame and structural parts of vending machines. It is not suitable for direct food contact unless adequately coated or treated.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must consider the need for protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid or coastal environments. Compliance with local standards is essential to ensure safety and durability.
| Material | Typical Use Case for japanese food vending machines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Structural components and food contact surfaces | Excellent corrosion resistance, durable | Higher cost, manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Non-perishable food compartments and frames | Lightweight, cost-effective shipping | Less durable, prone to dents | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Display panels for food visibility | Strong, transparent, UV resistant | Scratches easily, requires coatings | Medium |
| Mild Steel | Structural framework | Cost-effective, easy to fabricate | Prone to corrosion, requires treatment | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in Japanese food vending machines, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific markets and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for japanese food vending machines
The manufacturing of Japanese food vending machines is a complex process that combines advanced technology with meticulous quality assurance measures. Understanding these processes is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to invest in reliable and innovative vending solutions. Here’s an in-depth look at the typical manufacturing stages, quality control measures, and how buyers can ensure they are partnering with reputable suppliers.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process involves selecting high-quality materials that meet both aesthetic and functional requirements. Common materials include stainless steel for the machine body, tempered glass for display panels, and durable plastics for internal components. Material preparation includes:
- Sourcing: Suppliers should provide documentation verifying the quality and origin of materials, which is especially important for buyers from regions with stringent import regulations.
- Testing: Materials undergo initial quality checks to ensure they meet specifications. For example, stainless steel components must be resistant to corrosion and easy to clean.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves shaping the materials into the necessary components of the vending machine. Key techniques include:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are used to precisely cut and shape metal parts. This method ensures high precision and repeatability.
- Injection Molding: For plastic components, injection molding is employed to produce complex shapes efficiently and with minimal waste.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage is where all components come together to form the final product. This stage includes:
- Sub-assembly: Components such as the refrigeration unit, payment systems, and control panels are assembled separately before being integrated into the main structure.
- Integration: The final assembly involves combining all sub-assemblies, ensuring that wiring, plumbing, and mechanical systems work seamlessly together.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic appeal and functionality of the vending machine. Key processes include:
- Painting and Coating: Machines often receive protective coatings or paint to improve durability and visual appeal. Buyers should inquire about the types of coatings used, as these can affect longevity and maintenance.
- Quality Checks: After finishing, machines undergo a final quality inspection to ensure that all components are correctly installed and functioning.
Quality Assurance
Quality control (QC) is critical in the manufacturing of vending machines, especially considering the diverse regulations across international markets. Here’s how the QC process typically unfolds:
International Standards
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards to ensure product reliability and safety. Relevant standards include:
- ISO 9001: This quality management system standard ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes.
- CE Marking: For machines sold within Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be relevant for machines that include heating elements or other energy-related components.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Before production begins, raw materials are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous checks are conducted during the manufacturing process to identify defects early. This might include monitoring machine calibration and part fitment.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product is subjected to rigorous testing, including operational tests to ensure all functions perform correctly.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods vary, but some common practices include:
- Functional Testing: Machines are powered on to test all operational features, including vending mechanisms, payment systems, and user interfaces.
- Durability Testing: Machines may undergo stress tests to simulate long-term usage and ensure that all components withstand wear and tear.
Verifying Supplier QC
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance practices is vital. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers allows buyers to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand. This is particularly important when sourcing from regions with different regulatory standards.
- Requesting Documentation: Buyers should ask for certificates of compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, CE) and detailed reports of quality inspections performed during manufacturing.
- Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s QC processes. This is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets your specific requirements.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
When dealing with international suppliers, buyers must be aware of potential quality control nuances:
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality management. Understanding these cultural differences can aid in negotiations and quality expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that products meet local regulations in their target markets. For example, the UAE may have specific requirements for food safety and vending operations that differ from those in Europe.
- Communication: Clear communication about quality expectations and standards is essential. Establishing a mutual understanding of quality metrics can prevent future disputes.
By focusing on these manufacturing and quality assurance processes, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing Japanese food vending machines, ensuring they select partners that align with their quality expectations and operational needs.
Related Video: Parle-G Biscuits Manufacturing process – Food Factory Tour- Modern Food factory, Mega Factory II
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for japanese food vending machines Sourcing
When sourcing Japanese food vending machines, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will cover various cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable buyer tips tailored for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including specific considerations for countries like the UAE and Turkey.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials significantly influences the final price of vending machines. High-quality components, such as stainless steel or specialized electronic parts, may elevate costs but are essential for durability and performance. Buyers should evaluate material specifications to ensure they align with their operational needs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can affect the overall manufacturing price. In countries with higher labor costs, expect to see higher prices for machines. Understanding the labor market in the supplier’s location is essential for anticipating these costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Suppliers with efficient manufacturing processes can offer more competitive pricing. Buyers should inquire about the production environment to gauge potential overhead impacts.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for unique designs or specifications, adding to initial costs. For standard models, tooling expenses are typically spread across larger production runs, making them more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures that machines meet international standards, which can prevent costly returns or repairs. Buyers should inquire about the QC measures in place and how they affect pricing.
-
Logistics: Transport costs can vary based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer’s location. Factors such as shipping method, packaging, and any customs duties or tariffs must be considered. Buyers should explore different logistics options to find the most cost-effective solution.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary widely based on market conditions, competition, and brand reputation. Understanding these margins can provide insight into pricing flexibility during negotiations.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs to determine if they can meet MOQs for better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or enhanced specifications will typically increase costs. Buyers must balance the desire for customization with budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Machines that comply with international quality standards may carry a premium price but can reduce long-term maintenance costs and enhance reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better warranties and support, justifying higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in the contract can significantly impact overall costs. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate responsibilities for shipping and insurance, which can affect pricing.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage your knowledge of the cost components and price influencers during negotiations. Be prepared to discuss specifics, such as volume discounts or payment terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the initial purchase price and consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances: For international buyers, currency fluctuations can impact pricing. Establish a clear understanding of payment terms and currency risks when negotiating contracts.
-
Local Regulations: Be aware of local regulations in your market concerning vending machine operations, as compliance can influence machine specifications and pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and geopolitical factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence and obtain multiple quotations to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential japanese food vending machines Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for japanese food vending machines.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for japanese food vending machines
Key Technical Properties of Japanese Food Vending Machines
When evaluating Japanese food vending machines for international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding critical specifications is vital. Here are essential technical properties that buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
The construction material of vending machines significantly influences durability and maintenance. Common materials include stainless steel, which offers corrosion resistance, and high-grade plastics, known for their lightweight and flexibility. For B2B buyers, selecting machines with appropriate material grades ensures longevity and reduces replacement costs, particularly in diverse climates. -
Temperature Control Range
Japanese food vending machines often require precise temperature control to maintain food quality. A typical range might be between -5°C to 70°C, depending on the type of food dispensed. Understanding the temperature control specifications helps buyers ensure that the machines can handle local environmental conditions and comply with food safety regulations. -
Capacity and Size
Vending machines come in various sizes and capacities, measured by the number of food items they can hold. A standard machine may accommodate 100-200 items. B2B buyers should assess the expected foot traffic and demand in their target locations to choose machines that optimize space and maximize profitability.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Payment Systems
Modern vending machines are equipped with diverse payment options, including cash, credit/debit cards, and mobile payments. The ability to accept various payment methods is crucial for attracting a broader customer base. Buyers should verify that the machines are compatible with local payment systems and currencies to facilitate seamless transactions. -
Energy Efficiency Rating
Energy consumption is a significant operational cost for vending machine operators. Machines with high energy efficiency ratings not only reduce costs but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Understanding energy ratings helps B2B buyers align their purchasing decisions with sustainability goals and regulatory requirements. -
User Interface and Accessibility Features
An intuitive user interface enhances customer experience and increases sales. Features such as touch screens, multiple language options, and accessibility for people with disabilities are vital. B2B buyers should prioritize machines that offer user-friendly designs to cater to diverse customer needs and maximize usability.
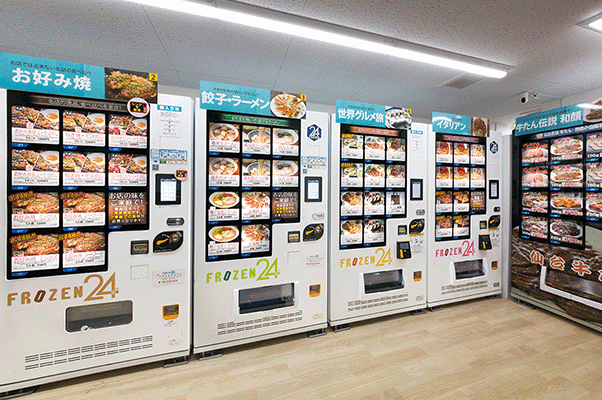
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the vending machine market. Here are key terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components or products that are then marketed by another company under its brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reputable suppliers and negotiate better pricing based on brand value and quality assurance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, being aware of MOQ helps in budget planning and inventory management. Understanding this term is crucial for negotiating favorable terms and avoiding excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price offers from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications and requirements. B2B buyers should prepare comprehensive RFQs to receive accurate quotes, ensuring that all potential suppliers understand their needs clearly. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, insurance, and risks involved in the delivery process, enabling them to negotiate better terms. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory management and planning. Buyers should inquire about lead times to ensure that they can meet market demands without delay. -
Warranty and Service Agreements
Warranties provide assurance regarding the quality and reliability of the machines. Service agreements outline the maintenance and repair responsibilities of the manufacturer or supplier. B2B buyers should thoroughly review these documents to ensure they are protected against potential defects and have access to necessary support.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing Japanese food vending machines, ensuring they align with their operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the japanese food vending machines Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The Japanese food vending machines sector is experiencing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and the growing demand for convenience. Globally, the rise of urbanization and fast-paced lifestyles has heightened the appeal of vending solutions that offer quick access to diverse food options. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for successful market entry and sourcing strategies.
Key trends influencing the market include:
-
Integration of Technology: Smart vending machines equipped with AI and IoT capabilities are emerging, offering features such as cashless payments, real-time inventory tracking, and personalized customer experiences. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in tech-savvy markets like the UAE and Turkey.
-
Diverse Product Offerings: There is a growing demand for healthy and ethnic food options, which includes traditional Japanese foods such as sushi, ramen, and mochi. International buyers should consider sourcing machines that cater to local tastes while maintaining authenticity.
-
Customization and Branding: Vending machine suppliers are increasingly offering customizable solutions, allowing businesses to brand their machines and curate unique product selections. This presents an opportunity for B2B buyers to enhance their market presence and customer engagement.
-
Focus on Automation: The push for contactless solutions post-pandemic has accelerated the adoption of automated vending systems, minimizing human interaction and improving hygiene standards. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in markets where health and safety are paramount.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As global awareness of environmental issues rises, sustainability has become a cornerstone of business strategy in the vending machine sector. For B2B buyers, aligning with sustainable practices is not only a moral obligation but also a competitive advantage.
Key considerations include:
-
Environmental Impact: Vending machines contribute to waste generation, particularly through single-use packaging. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer eco-friendly packaging solutions and promote recycling initiatives.
-
Ethical Supply Chains: Transparency in sourcing ingredients is vital. Buyers should seek vendors that adhere to ethical sourcing practices, ensuring fair labor conditions and sustainable agricultural methods. This is particularly important for markets in Africa and South America, where agricultural practices can significantly impact local communities.
-
Green Certifications: Look for machines and suppliers that hold recognized environmental certifications, such as ISO 14001 or similar standards. These certifications can serve as indicators of a commitment to sustainability and can enhance your brand’s reputation in eco-conscious markets.
-
Sustainable Materials: The use of biodegradable or recyclable materials in vending machines is gaining traction. Buyers should evaluate vendors based on their commitment to using sustainable materials in machine construction and packaging.
Brief Evolution/History
The concept of vending machines dates back to ancient Greece, but the modern iteration as we know it began in Japan during the 1960s. Initially offering simple products like beverages and snacks, Japanese vending machines quickly evolved to include a wide array of items, including hot meals and specialty foods. The sector’s growth was fueled by Japan’s dense urban environments and a culture that values convenience and efficiency.
Over the decades, technological innovations have transformed vending machines into sophisticated retail solutions, incorporating features like digital displays and interactive interfaces. Today, as the global market expands, international B2B buyers are presented with opportunities to tap into Japan’s rich heritage of vending technology while adapting to local demands and sustainability expectations.
Related Video: Japan’s Biggest Retro Vending Machine Wonderland – Over 100 Machines 🍔 🍭 🍜 🥤
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of japanese food vending machines
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of Japanese food vending machines?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their experience and reputation in the industry. Look for certifications that validate their quality standards, such as ISO or CE markings. Assess their previous projects and customer reviews, especially from international clients. Establish direct communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to provide references. Additionally, inquire about their after-sales support, warranty policies, and service capabilities in your region to ensure long-term satisfaction. -
Can Japanese food vending machines be customized for local tastes?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options to tailor vending machines to local preferences. Discuss your specific needs, such as menu items, packaging, and machine aesthetics, during the procurement process. Ensure that the supplier has experience in adapting products for various markets. Customization can also extend to payment options, such as mobile payments or multi-currency support, which may be crucial for attracting a diverse customer base. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for these machines?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the machines. Generally, expect MOQs to range from 5 to 20 units. Lead times are influenced by customization requirements and shipping logistics, typically ranging from 8 to 16 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss these details upfront and explore options for bulk orders that may offer cost savings or faster delivery times. Always factor in additional time for potential customs delays in your planning. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing Japanese food vending machines?
Payment terms can differ among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit (usually 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipping. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment plans, particularly for larger orders. Be sure to clarify any additional costs, such as shipping or customs duties, upfront. Always use secure payment methods and consider drafting a contract that outlines payment terms to protect your interests. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should have established quality assurance (QA) protocols that include rigorous testing of machines before shipment. Inquire about their QA certifications and processes, such as random inspections and compliance with international safety standards. Request documentation that proves adherence to these standards, including test reports or quality control checklists. Understanding the QA processes helps ensure that you receive reliable, high-quality machines that meet your operational needs. -
How should I handle logistics and shipping for international orders?
Logistics planning is crucial when ordering Japanese food vending machines. Coordinate with your supplier to determine the best shipping method—air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Understand the customs regulations in your country to avoid unexpected delays or fees. Consider partnering with a logistics company experienced in international shipping to streamline the process. Tracking shipments and maintaining communication with the supplier can help mitigate potential issues during transit. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with a supplier?
In case of a dispute, maintain clear communication with the supplier to address the issue directly. Document all interactions and keep records of agreements and transactions. If the matter cannot be resolved amicably, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution. Engaging a mediator or legal advisor experienced in international trade can also provide guidance. Always prioritize maintaining a professional relationship, as long-term partnerships can be valuable. -
Are there specific certifications I should look for in Japanese food vending machines?
When sourcing vending machines, look for certifications that indicate compliance with international safety and quality standards. Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management systems, CE marking for compliance with European health and safety regulations, and local health department certifications. These certifications not only ensure product reliability but also enhance your credibility in the market. Request documentation to verify these certifications before finalizing your purchase.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for japanese food vending machines
As international B2B buyers consider the integration of Japanese food vending machines into their operations, it is essential to recognize the strategic advantages these machines offer. Key takeaways include the ability to tap into the growing demand for convenience and diverse cuisine, especially in urban areas where traditional dining options may be limited. By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can secure high-quality machines that not only meet consumer preferences but also align with local regulations and cultural expectations.
The value of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated; it enables buyers to identify reliable suppliers, negotiate favorable terms, and ensure the procurement of innovative technologies that enhance customer experience. Additionally, understanding regional market dynamics in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe is crucial for optimizing placement and maximizing ROI.
Looking ahead, the potential for Japanese food vending machines is significant as trends toward automation and convenience continue to rise. International B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers and distributors to stay ahead of market demands. Engaging in this niche market now positions your business for future growth. Embrace the opportunity to diversify your offerings and cater to evolving consumer tastes—take the next step in your strategic sourcing journey today.