Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Vending Machine Lock
Guide to Vending Machine Lock
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vending machine lock
- Understanding vending machine lock Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of vending machine lock
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vending machine lock
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vending machine lock
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vending machine lock Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential vending machine lock Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vending machine lock
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vending machine lock Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vending machine lock
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vending machine lock
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vending machine lock
In today’s dynamic global marketplace, the demand for secure and reliable vending machine locks has surged, driven by the increasing prevalence of unattended retail solutions across various regions. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, you are at the forefront of this transformation. Understanding the intricacies of vending machine locks is crucial not just for safeguarding assets but also for enhancing customer trust and operational efficiency.
This comprehensive guide serves as your go-to resource for navigating the complexities of the vending machine lock market. We will explore a wide array of lock types, including electronic, mechanical, and keyless solutions, and delve into the materials used in their construction, ensuring durability and resistance to tampering. Additionally, we will highlight key considerations in manufacturing and quality control, providing insights into the best practices that suppliers employ to deliver high-quality products.
Cost analysis and market trends will be examined to help you make informed financial decisions, while a curated list of reputable suppliers will streamline your sourcing process. We also address common FAQs, ensuring that you have all the information needed to navigate procurement challenges confidently.
Empowering you with actionable insights, this guide will enhance your sourcing strategies and help you secure the best vending machine lock solutions tailored to your specific market needs.
Understanding vending machine lock Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Key Lock | Traditional lock mechanism using physical keys | General vending operations | Pros: Simple to use, widely available. Cons: Vulnerable to unauthorized duplication. |
| Electronic Lock | Keypad or card access, often programmable | High-security environments | Pros: Enhanced security, customizable access. Cons: Requires power, may be costlier. |
| Smart Lock | Connects to mobile apps or IoT systems | Remote management, tech-savvy users | Pros: Remote control, real-time monitoring. Cons: Dependency on technology, potential for hacking. |
| Combination Lock | Uses a numerical code for access | Budget-friendly vending solutions | Pros: No keys required, cost-effective. Cons: Codes can be forgotten or shared. |
| Cam Lock | Simple mechanism often used in smaller units | Low-security vending applications | Pros: Easy installation, low cost. Cons: Limited security, easily bypassed. |
Mechanical Key Lock
Mechanical key locks are one of the oldest and most straightforward types of vending machine locks. They operate using a physical key, which is easy to replace and manufacture. These locks are suitable for general vending operations and are widely used across various industries. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider the availability of replacement keys and the potential risks of unauthorized duplication, which can compromise security.
Electronic Lock
Electronic locks offer enhanced security features compared to their mechanical counterparts. They often utilize keypads or card access systems, allowing for programmable access codes. This type of lock is particularly advantageous in high-security environments where the risk of theft is elevated. Buyers should evaluate the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs, as these locks require power and may be more expensive than mechanical options.
Smart Lock
Smart locks represent the next evolution in vending machine security, integrating with mobile applications and IoT systems. These locks allow for remote management, enabling operators to monitor access and usage in real-time. This is particularly appealing for tech-savvy businesses looking to streamline operations. However, buyers must consider the potential risks associated with technology dependence, such as hacking vulnerabilities and the need for a reliable power source.
Combination Lock
Combination locks provide a cost-effective solution for businesses that prefer not to deal with physical keys. They operate using a numerical code, which can be easily changed to enhance security. This type of lock is suitable for budget-friendly vending solutions where moderate security is acceptable. B2B buyers should be aware that while these locks eliminate key management issues, there is a risk of codes being forgotten or inadvertently shared.
Cam Lock
Cam locks are simple locking mechanisms commonly used in smaller vending units. They are easy to install and are typically low-cost, making them an attractive option for businesses on a tight budget. However, their limited security features make them more suitable for low-security applications. Buyers should carefully assess the security needs of their vending operations before opting for cam locks, as they can be easily bypassed.
Related Video: How to pick a vending machine lock
Key Industrial Applications of vending machine lock
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vending machine lock | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Secure vending machines in shopping centers | Prevents theft, increases customer trust | Lock durability, compatibility with existing machines |
| Hospitality | Mini-bar locks in hotels | Enhances guest experience, reduces inventory loss | Aesthetic design, ease of use for staff |
| Education | Locking vending machines in schools | Ensures safety, controls access to products | Compliance with safety standards, ease of operation |
| Transportation | Vending machines in airports and train stations | Streamlines operations, increases revenue potential | Weather resistance, high-security features |
| Healthcare | Vending machines in hospitals | Provides quick access to supplies, reduces waste | Hygiene standards, robust locking mechanisms |
Retail
In the retail sector, vending machines are commonly placed in shopping centers and malls to provide convenience to shoppers. Vending machine locks play a crucial role in securing these machines against theft and vandalism. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, the emphasis should be on acquiring locks that are durable and can withstand various environmental conditions. Additionally, compatibility with existing vending machines is vital to ensure seamless installation and operation.
Hospitality
In the hospitality industry, mini-bars in hotels utilize vending machine locks to secure high-value items. These locks not only enhance the guest experience by providing convenience but also help in reducing inventory loss through theft or misuse. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider the aesthetic design of locks, ensuring they match the hotel’s décor while also being user-friendly for staff. Ensuring that locks can withstand frequent use without compromising security is essential.
Education
Schools and universities often incorporate vending machines to provide snacks and beverages to students. The use of vending machine locks in these environments helps to ensure safety and control access to products, preventing unauthorized usage. Buyers in the education sector must prioritize compliance with safety standards, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where security can be a concern. Ease of operation is also crucial, as staff should be able to access the machines quickly and efficiently.
Transportation
Vending machines located in airports and train stations require robust security measures due to the high volume of travelers. Vending machine locks in this sector help streamline operations and increase revenue potential by preventing unauthorized access and theft. International buyers should focus on weather-resistant locks that can endure varying climates, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East. High-security features are also important to protect against sophisticated theft attempts.
Healthcare
In healthcare settings, vending machines provide essential supplies and snacks to staff and visitors. The implementation of vending machine locks ensures quick access to these items while minimizing waste and potential theft. Buyers in the healthcare sector must ensure that the locks meet hygiene standards and are easy to clean. Additionally, robust locking mechanisms are necessary to secure valuable medical supplies and prevent unauthorized access, especially in sensitive areas of hospitals.
Related Video: How to Start a Vending Machine Business, Cost, Tips, How Much You Make
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vending machine lock
When selecting materials for vending machine locks, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and the specific needs of international markets. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in vending machine locks, focusing on their performance characteristics and implications for B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and durability. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to rust and corrosion, which is critical in humid or coastal areas. However, it tends to be more expensive than other materials and may require more complex manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of media, including water and oils, making it ideal for vending machines that dispense beverages or snacks. Its resilience ensures a long service life, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel grades. In regions like Europe, certifications for food safety and environmental impact may also be necessary.
2. Zinc Alloy
Key Properties:
Zinc alloy offers good strength and corrosion resistance, though it is less robust than stainless steel. Its lower melting point allows for easier casting and molding.
Pros & Cons:
Zinc alloy is cost-effective and can be manufactured with intricate designs, making it suitable for locks with complex mechanisms. However, it may not perform well in extreme temperatures or highly corrosive environments, limiting its application.
Impact on Application:
This material is often used in vending machines that are not exposed to harsh conditions, such as indoor environments. It is suitable for locks that do not require heavy-duty performance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that the zinc alloy meets relevant standards, such as ISO 4042 for corrosion resistance. In regions like South America, local regulations may dictate specific alloy compositions.
3. Plastic Composites
Key Properties:
Plastic composites are lightweight and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They can be manufactured in various colors and finishes, providing aesthetic flexibility.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of plastic composites is their low cost and ease of manufacturing. However, they may lack the durability and strength of metal options, making them less suitable for high-security applications.
Impact on Application:
Plastic composites are ideal for vending machines in low-risk environments, such as schools or offices, where the risk of tampering is minimal. They are also suitable for machines that dispense non-perishable items.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with environmental regulations, particularly regarding the recyclability of plastics. In regions like Africa, where sustainability is increasingly prioritized, selecting eco-friendly materials can enhance brand reputation.
4. Brass
Key Properties:
Brass is known for its excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. It performs well in various temperatures and is relatively stable under pressure.
Pros & Cons:
Brass offers a good balance between cost and performance, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, it can be prone to dezincification in certain environments, which may compromise its integrity over time.
Impact on Application:
Brass is suitable for vending machines that require a combination of durability and aesthetic appeal, such as high-end or luxury models. Its resistance to corrosion makes it a viable option for outdoor or humid locations.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with standards like ASTM B36 for brass materials. In the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, ensuring that the brass used can withstand such conditions is crucial.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for vending machine lock | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High-security locks in outdoor machines | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Zinc Alloy | Indoor vending machines | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Limited performance in extreme conditions | Med |
| Plastic Composites | Low-risk environments (schools, offices) | Lightweight and low cost | Less durable and secure | Low |
| Brass | High-end vending machines | Good aesthetic appeal and machinability | Prone to dezincification in some environments | Med |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vending machine lock
The manufacturing process of vending machine locks involves several critical stages, each essential for producing a reliable and secure product. Understanding these processes is vital for B2B buyers to ensure they procure high-quality locks that meet their operational needs.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing vending machine locks is selecting the appropriate materials. Common materials include zinc alloy, stainless steel, and brass, chosen for their durability and resistance to wear and corrosion.
- Material Sourcing: Buyers should prioritize suppliers that source materials from reputable providers, ensuring compliance with international standards and environmental regulations.
- Material Testing: Before production, materials undergo testing for quality assurance. This includes checking for hardness, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves shaping the raw materials into the necessary components of the lock.
- Techniques Used:
- Die Casting: Often used for zinc alloys, this technique allows for intricate designs and high production rates.
- CNC Machining: For precision parts, CNC machines are utilized to create components that require exact specifications.
-
Stamping: Used for creating flat components, stamping can produce high volumes quickly.
-
Considerations for Buyers: It’s crucial to understand the forming techniques used, as this impacts the lock’s strength and longevity. Buyers should inquire about the technology and machinery used by potential suppliers.
3. Assembly
After forming, the components are assembled. This step typically involves:
- Manual and Automated Assembly: Depending on the complexity of the lock design, assembly may be conducted manually or via automated systems.
-
Integration of Security Features: High-security features, such as pick-resistant pins or electronic components, are incorporated during this phase.
-
Supplier Insights: Buyers should evaluate the assembly process, focusing on the balance between human craftsmanship and automation, as both play a role in quality control.
4. Finishing
The final stage in the manufacturing process is finishing, which enhances both appearance and functionality.
- Techniques:
- Electroplating: Provides a protective layer against corrosion while improving aesthetic appeal.
-
Powder Coating: Offers a durable finish that can withstand harsh environments, particularly beneficial for outdoor vending machines.
-
Importance for Buyers: The finishing process not only affects the lock’s look but also its durability. Buyers should request information on the finishing techniques employed and their expected performance.
Quality Assurance (QA) Processes
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of vending machine locks is essential to ensure product reliability and safety. International B2B buyers need to be well-versed in the relevant standards and quality checkpoints.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
Vending machine locks must comply with several international standards, which may include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, ensuring that products meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Indicates that the lock meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for locks that may be used in environments requiring high-security measures, such as military or critical infrastructure.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Implementing a robust quality control system involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to catch defects early in the process.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo thorough testing to ensure they meet all specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods play a crucial role in verifying the quality of vending machine locks:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that locks operate smoothly and securely.
- Durability Testing: Simulates wear and tear to assess how the locks perform over time.
- Environmental Testing: Exposes locks to extreme conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity) to evaluate their resilience.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are actionable strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control systems in place. This provides firsthand insights into their operations.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports, including inspection results, testing data, and compliance certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to evaluate the supplier’s quality control measures independently. This adds an extra layer of assurance.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understand that quality expectations and regulatory compliance may differ across regions. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and practices.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Delays in shipping or customs can impact the delivery of quality products. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can mitigate risks associated with international procurement.
Conclusion
For B2B buyers in the vending machine lock market, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is paramount. By focusing on material selection, forming techniques, assembly methods, and finishing processes, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure the procurement of high-quality locks. Additionally, implementing rigorous quality control measures and verifying supplier standards will safeguard against potential issues, ultimately contributing to successful business operations.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vending machine lock Sourcing
In the realm of sourcing vending machine locks, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis covers the key components of cost, factors influencing price, and actionable insights to optimize purchasing strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost of vending machine locks. Common materials include stainless steel, zinc alloys, and plastic. High-quality materials often lead to higher costs but can enhance durability and security.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the overall pricing. Countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but it’s essential to consider the trade-off between cost and quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs of production, including utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs, which can be reflected in pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific lock designs can add to initial costs. However, investing in specialized tooling may be necessary for high-volume orders, which can reduce per-unit costs over time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes ensure that products meet specifications and standards. While implementing stringent QC can increase costs, it ultimately protects brand reputation and reduces returns.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on location and Incoterms. Understanding these costs is crucial, especially when importing locks to regions like Africa or South America, where logistics may involve longer transit times and higher tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position, brand reputation, and service offerings.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating for better terms based on projected future orders can be advantageous.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized locks may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: Premium materials may drive up costs, but they can also provide enhanced security and longevity. Assessing the total cost of ownership (TCO) can reveal that investing in quality materials is beneficial in the long run.
-
Quality/Certifications: Locks that meet international standards or have certifications may be priced higher. However, they provide assurance of quality and compliance, which can be crucial in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service level can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but often provide better support and product guarantees.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is vital as they dictate who bears the costs and risks during shipping. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) may shift costs to the buyer once the goods are loaded, impacting overall pricing.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can result in more favorable terms and discounts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the TCO rather than just the purchase price. Evaluate maintenance, replacement, and potential security implications of lower-cost options.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, sourcing from suppliers in Europe may offer higher quality but at a premium, while suppliers in Africa or South America may provide more competitive rates.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to benchmark pricing and understand local supply chain dynamics. This insight can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize procurement platforms to compare prices and suppliers efficiently. Data-driven decisions can lead to better sourcing outcomes.
Disclaimer
Prices and costs mentioned are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct due diligence before finalizing any procurement decisions.
Spotlight on Potential vending machine lock Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for vending machine lock.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vending machine lock
When considering vending machine locks for procurement, understanding the technical specifications and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here, we outline essential properties and terms that will aid international B2B buyers in navigating this specialized market.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality of the materials used in the construction of the lock, such as steel or brass.
– Importance: Higher-grade materials enhance durability, corrosion resistance, and security. For buyers, selecting locks made from appropriate material grades ensures longevity and reduces the frequency of replacements, which is especially important in high-traffic areas. -
Lock Mechanism Type
– Definition: Refers to the design of the locking mechanism, such as pin tumbler, disc detainer, or electronic.
– Importance: Different mechanisms offer varying levels of security and ease of use. Buyers must assess their security needs; for example, electronic locks may provide advanced features like remote access or audit trails, while traditional locks might be easier to maintain. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable variation in the dimensions of the lock parts.
– Importance: Precise tolerances ensure that components fit together correctly, affecting the lock’s performance and resistance to tampering. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels is critical for ensuring compatibility with existing vending machine designs. -
Keying Options
– Definition: The configuration of the lock’s key system, such as standard, master, or restricted keys.
– Importance: Different keying options provide varying levels of access control. A master key system allows for a single key to operate multiple locks, which can streamline operations for businesses managing numerous machines. -
Finish and Coating
– Definition: The surface treatment applied to the lock, such as chrome plating or powder coating.
– Importance: The finish affects both aesthetics and functionality, including resistance to rust and wear. Buyers should consider the environment in which the lock will be used; for instance, a powder-coated finish may be preferable in humid climates.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Usage: When sourcing vending machine locks, buyers may prefer OEM parts for reliability and compatibility with existing machinery. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Usage: Understanding the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning. Buyers must evaluate whether the MOQ aligns with their operational needs to avoid excess stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific product.
– Usage: An RFQ is a crucial step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms. It’s advisable to provide detailed specifications to receive accurate quotes. -
Incoterms
– Definition: International commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Usage: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost implications. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) clarify who bears the costs and risks at various stages of shipping. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time between placing an order and receiving it.
– Usage: Understanding lead times is critical for inventory management and planning. Buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating contracts to ensure timely delivery of locks for their vending machines.
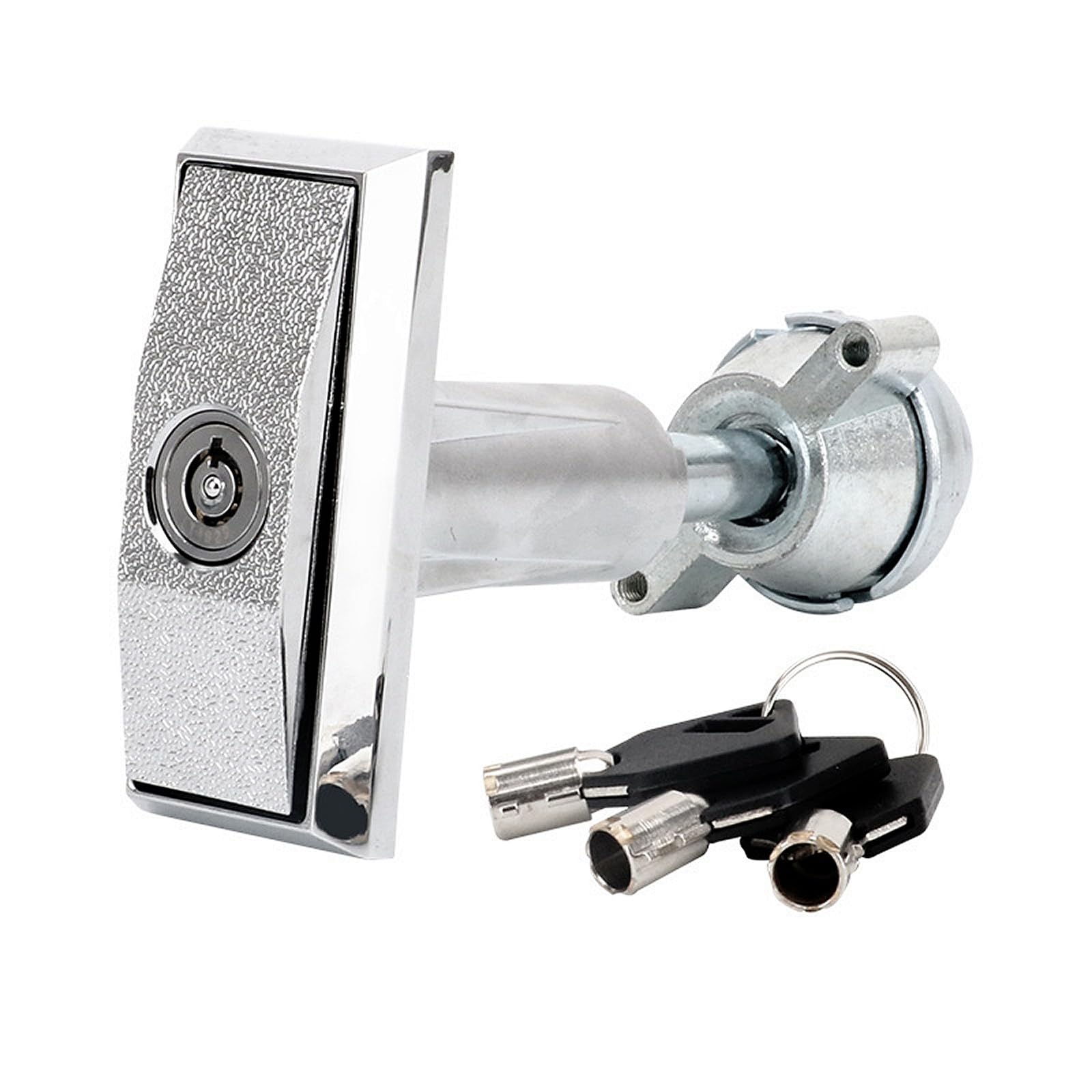

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and ultimately enhance the security and functionality of their vending machine operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vending machine lock Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The vending machine lock sector is experiencing significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. Global drivers include the rising emphasis on security, automation, and the need for seamless customer experiences. As vending machines become more integrated with digital payment systems and IoT technologies, the demand for sophisticated locking mechanisms has surged. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must stay ahead of these trends to remain competitive.
Current and emerging B2B tech trends include the adoption of smart locks that provide remote access and monitoring capabilities. These innovations not only enhance security but also offer operational efficiencies, allowing machine operators to manage multiple units from a centralized system. Moreover, the integration of biometric security features is gaining traction, appealing to businesses prioritizing high-security solutions.
Market dynamics indicate a growing preference for modular and customizable lock solutions, enabling businesses to tailor their security systems to specific operational needs. As the global market expands, suppliers that can offer flexibility and adaptability in their product lines will likely capture a larger share. Buyers should consider suppliers with proven track records in innovation and responsiveness to market changes to ensure they are sourcing the most relevant products.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of the procurement process in the vending machine lock sector. Environmental impact considerations, such as the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing and transporting locking mechanisms, are increasingly influencing purchasing decisions. B2B buyers must evaluate the sustainability practices of their suppliers, focusing on those committed to reducing waste and energy consumption.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should seek suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and source materials responsibly. This commitment not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with consumer expectations for corporate social responsibility.
In terms of ‘green’ certifications and materials, look for suppliers who utilize recycled materials or environmentally friendly production processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By prioritizing these aspects, B2B buyers can contribute to a more sustainable vending machine lock industry while also meeting the increasing demand for eco-conscious products.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of vending machine locks has been closely tied to advancements in technology and changes in consumer behavior. Historically, these locks were simple mechanical devices that provided basic security. However, with the advent of digital technology in the late 20th century, the industry began to shift towards more complex solutions, integrating electronic components that enhanced security and user accessibility.
In recent years, the focus has expanded to include features such as remote monitoring and smart access control, reflecting broader trends in automation and connectivity. As vending machines continue to evolve into multifunctional units, the locking mechanisms that secure them must also adapt, ensuring that they meet the demands of modern consumers and operators alike. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with current market needs.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vending machine lock
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for vending machine locks?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, client references, and quality certifications such as ISO 9001. Check for their production capacity and reliability in fulfilling orders, especially for international shipments. Evaluate their compliance with local regulations in your region, such as CE marking in Europe or other safety standards relevant to Africa and South America. Additionally, consider their communication and responsiveness, as effective dialogue is crucial for successful international trade relationships. -
Can I customize vending machine locks to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for vending machine locks. This may include unique keying systems, sizes, materials, and finishes to suit your vending machine specifications. When discussing customization, provide clear specifications and inquire about the design process, including any associated costs and timeframes. Ensure that the supplier has experience with custom orders, as this can significantly impact the quality and functionality of the final product. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for vending machine locks?
MOQs for vending machine locks can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product. Generally, expect MOQs to range from 100 to 500 units. Lead times may also differ based on customization and production schedules but typically range from 4 to 12 weeks. When negotiating terms, clarify these factors upfront to align your purchasing strategy with your business needs, especially if you are operating in regions with longer shipping times. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing vending machine locks internationally?
International payment terms can vary, but common methods include letters of credit, wire transfers, and payment platforms like PayPal. Negotiate terms that offer security for both parties, such as a partial upfront payment with the remainder due upon delivery. Consider the exchange rates and potential transaction fees associated with international payments. It’s also advisable to establish a clear agreement on payment timelines to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to disputes.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How can I ensure quality assurance and necessary certifications for vending machine locks?
Request product samples to evaluate the quality before placing a bulk order. Additionally, ask for certifications that confirm compliance with international quality and safety standards. Suppliers should provide documentation such as test reports and quality control processes. If you’re dealing with suppliers in regions with different regulatory standards, ensure that they can meet the requirements of your local market to prevent issues with product acceptance. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing vending machine locks?
When importing, consider factors such as shipping methods (air freight vs. sea freight), customs regulations, and import duties. Collaborate with your supplier to understand packaging requirements and ensure the locks are suitable for transport. Utilize a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping to streamline the process. Be proactive in obtaining necessary import permits and ensure compliance with local regulations to avoid delays at customs. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding vending machine locks?
To handle disputes effectively, maintain clear and documented communication throughout the purchasing process. Establish a detailed contract outlining terms, responsibilities, and dispute resolution mechanisms. If a disagreement arises, attempt to resolve it amicably through negotiation. Should that fail, consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation, as these methods can be more cost-effective and less time-consuming in international trade scenarios. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with a vending machine lock supplier?
To foster a successful long-term relationship, prioritize transparent communication and regular updates on order status. Provide constructive feedback on product quality and service, and be open to discussing improvements. Consider partnering for joint marketing efforts or product development initiatives, which can enhance collaboration. Finally, consistently honor payment terms and commitments to build trust and reliability, ensuring both parties benefit from the partnership.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vending machine lock
In conclusion, strategic sourcing for vending machine locks is vital for enhancing operational efficiency and securing valuable assets. B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness when selecting suppliers. Engaging with manufacturers that offer customizable solutions and robust after-sales support can significantly reduce long-term maintenance costs and improve overall service delivery.
Key Takeaways:
- Supplier Diversification: Consider multiple suppliers to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
- Quality Assurance: Invest in high-quality locks that meet international standards to ensure longevity and security.
- Technological Integration: Explore smart locking solutions that provide advanced security features and remote management capabilities.
As the market evolves, staying abreast of trends in security technology and consumer preferences will be crucial. By adopting a proactive approach to sourcing, international B2B buyers can not only enhance their competitive edge but also foster sustainable partnerships that drive innovation.
Take the next step in your strategic sourcing journey—evaluate your current suppliers and explore new partnerships that align with your growth objectives. Embrace the future of vending machine security with confidence.