Master the 3 Things in a Vending Machine for Optimal B2B
Guide to 3 Things In A Vending Machine
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3 things in a vending machine
- Understanding 3 things in a vending machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of 3 things in a vending machine
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3 things in a vending machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3 things in a vending machine
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3 things in a vending machine Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential 3 things in a vending machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3 things in a vending machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the 3 things in a vending machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3 things in a vending machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3 things in a vending machine
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3 things in a vending machine
In today’s fast-paced global marketplace, vending machines have evolved from simple snack dispensers to complex systems that cater to diverse consumer preferences. For B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the critical components of vending machines is essential for optimizing inventory and maximizing profit margins. This guide illuminates the three key elements that every vending machine should encompass, ensuring that buyers can make informed sourcing decisions.
Navigating this comprehensive resource, you will explore various types of vending machine products, delve into the materials used in manufacturing, and scrutinize quality control processes that ensure product safety and compliance. Furthermore, we provide insights into identifying reliable suppliers, estimating costs, and understanding market trends that impact product availability and pricing.
With FAQs addressing common concerns and challenges, this guide empowers international B2B buyers with actionable insights and strategic sourcing strategies. By leveraging this information, businesses can not only enhance their vending machine offerings but also cultivate robust supplier relationships, ensuring a competitive edge in their respective markets. Embrace the opportunity to refine your vending machine product selection and drive your business towards sustainable growth.
Understanding 3 things in a vending machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snack Vending Machines | Offers a variety of packaged snacks, often customizable | Offices, schools, gyms | Pros: High demand, easy to refill; Cons: Limited shelf life of products. |
| Drink Vending Machines | Dispenses beverages, including soft drinks and water | Corporate environments, public spaces | Pros: High turnover, diverse options; Cons: Requires refrigeration and maintenance. |
| Combo Vending Machines | Combines snacks and drinks in one unit | Airports, malls, entertainment venues | Pros: Maximizes space and variety; Cons: More complex to manage inventory. |
| Coffee Vending Machines | Provides hot beverages, including coffee and tea | Offices, waiting areas, convenience stores | Pros: High profit margins, caters to coffee culture; Cons: Requires frequent servicing. |
| Specialized Vending Machines | Custom machines for niche products like electronics or health items | Hospitals, tech stores, gyms | Pros: Targets specific markets, potential for high margins; Cons: Limited customer base and higher initial investment. |
Snack Vending Machines
Snack vending machines are designed to dispense a variety of packaged snacks, such as chips, candy, and granola bars. They are particularly suitable for environments with high foot traffic, like offices and schools, where quick and convenient access to snacks is desired. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the machine’s capacity, ease of refilling, and the variety of products it can accommodate. Additionally, it’s important to assess the shelf life of the snacks to ensure they remain fresh and appealing to customers.
Drink Vending Machines
Drink vending machines specialize in offering a wide range of beverages, including soft drinks, bottled water, and juices. They are commonly found in corporate environments and public spaces, where hydration is a priority. B2B buyers should focus on the machine’s capacity for cold storage and the variety of drink options available. While these machines can generate high turnover due to consistent demand, buyers must also consider the maintenance requirements, such as regular cleaning and refrigerant checks, to ensure optimal performance.
Combo Vending Machines
Combo vending machines combine snacks and drinks in a single unit, making them an efficient choice for locations like airports, malls, and entertainment venues. Their versatility allows businesses to cater to a broader customer base, maximizing space and variety. Buyers should weigh the advantages of offering multiple product types against the challenges of managing inventory for different categories. Additionally, considering the machine’s size and layout will help ensure it meets the specific needs of the intended location.
Coffee Vending Machines
Coffee vending machines provide hot beverages, including coffee and tea, catering to the growing coffee culture in many regions. These machines are ideal for offices, waiting areas, and convenience stores, where customers seek quality coffee on-the-go. B2B purchasers should evaluate the machine’s brewing capabilities, maintenance requirements, and the range of beverage options it offers. While coffee machines can yield high profit margins, they also require regular servicing to maintain product quality and customer satisfaction.
Specialized Vending Machines
Specialized vending machines are designed to dispense niche products such as electronics, health items, or personal care products. These machines are particularly useful in settings like hospitals, tech stores, and gyms, where specific customer needs must be met. Buyers should consider the initial investment and the potential customer base when purchasing specialized machines, as they may target a narrower market. However, the potential for high margins in niche markets can make these machines a lucrative investment for businesses looking to diversify their offerings.
Related Video: All Machine Learning Models Clearly Explained!
Key Industrial Applications of 3 things in a vending machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 3 things in a vending machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Dispensing medical supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) | Immediate access to essential supplies, enhancing patient care | Compliance with health regulations, supplier reliability |
| Education | Providing snacks and beverages in schools and universities | Improved student satisfaction and retention | Nutritional standards, diverse product offerings |
| Corporate Offices | Coffee and snack vending for employee satisfaction | Boosts morale and productivity, reduces downtime | Quality of products, payment systems, maintenance support |
| Manufacturing | Offering safety gear and tools in factory break rooms | Increases operational efficiency, reduces downtime | Durability of products, supplier lead times |
| Hospitality | Providing quick access to snacks and drinks in hotels | Enhances guest experience, increases ancillary revenue | Product variety, compliance with food safety regulations |
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, vending machines that dispense medical supplies and PPE play a crucial role in ensuring that healthcare workers have immediate access to essential items. This application addresses the challenge of stock shortages during critical times, such as pandemics or emergencies. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing compliant medical products is paramount. Buyers must ensure that suppliers adhere to health regulations and can provide reliable delivery schedules to maintain operational continuity.
Education
Vending machines in educational institutions provide snacks and beverages, catering to the diverse needs of students. This application not only enhances student satisfaction but also contributes to better retention rates. In South America and Europe, educational policies may dictate nutritional standards for food sold on campuses. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who offer healthy options while ensuring compliance with local regulations regarding food safety and quality.
Corporate Offices
Corporate vending machines that offer coffee and snacks are vital for maintaining employee morale and productivity. By providing convenient access to refreshments, companies can reduce downtime and foster a positive work environment. For B2B buyers in Europe and Africa, it is essential to source high-quality products and reliable payment systems to ensure smooth operations. Additionally, establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and customized offerings tailored to employee preferences.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing settings, vending machines that provide safety gear and tools can significantly enhance operational efficiency. By reducing downtime during breaks, workers can quickly access necessary equipment, ensuring uninterrupted production. International buyers in regions like Nigeria and South America should focus on sourcing durable products that meet industry standards. Understanding local sourcing regulations and supplier capabilities is essential to ensure timely availability and compliance.
Hospitality
Vending machines in hotels offer guests quick access to snacks and drinks, enhancing their overall experience and contributing to additional revenue streams. This application is particularly relevant in Europe, where travelers expect convenience. B2B buyers must consider product variety and compliance with food safety regulations when sourcing. Partnering with suppliers who can provide popular items and seasonal offerings can help hotels stay competitive and cater to diverse guest preferences.
Related Video: How to Start a Vending Machine Business, Cost, Tips, How Much You Make
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3 things in a vending machine
When selecting materials for components in a vending machine, it’s critical to consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials. This analysis focuses on three common materials used in vending machine applications: Stainless Steel, Plastic, and Aluminum. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its suitability for specific components, such as machine casings, product dispensing mechanisms, and internal structures.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and durability. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust and stains, which is crucial for vending machines that may be exposed to moisture. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials and can be challenging to fabricate due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for external casings and internal components that require hygiene and durability, such as food and beverage dispensers. Its compatibility with a variety of media makes it a preferred choice for vending machines that dispense consumables.
International Considerations: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local health and safety standards is essential. Familiarity with ASTM and ISO standards can help ensure that the selected stainless steel meets regulatory requirements.
Plastic
Key Properties: Plastic materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are lightweight and versatile. They offer good impact resistance and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic is its low cost and ease of manufacturing, allowing for rapid production of components. However, plastics may have lower temperature resistance and can degrade over time when exposed to UV light or harsh chemicals.
Impact on Application: Plastics are commonly used for internal components, such as trays and product dividers, where weight savings and cost efficiency are priorities. They are suitable for non-food items or when the machine is located in environments with controlled temperatures.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with food safety regulations, especially when vending consumables. Understanding local regulations regarding plastic materials can help avoid compliance issues.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It is also relatively easy to machine and fabricate.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for structural components that require both lightness and durability. However, it is more expensive than plastic and may not be as robust as stainless steel in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in vending machine frames and structural supports, where a balance between weight and strength is necessary. It is also suitable for components that may be exposed to moisture but not harsh chemicals.
International Considerations: When sourcing aluminum, buyers should be aware of the various grades and their respective properties. Compliance with international standards such as JIS and DIN can ensure that the aluminum used is appropriate for the intended application.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for 3 things in a vending machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | External casings, food and beverage dispensers | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost, difficult to fabricate | High |
| Plastic | Internal trays, product dividers | Low cost, easy to mold | Lower temperature resistance, UV degradation | Low |
| Aluminum | Structural supports, frames | Good strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive than plastic, less robust than stainless steel | Medium |
This material selection guide provides a foundational understanding for international B2B buyers in the vending machine industry. By considering the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3 things in a vending machine
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for products typically found in vending machines are critical components for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section will explore the manufacturing processes for three common vending machine items: snacks, beverages, and personal care items, along with the relevant quality assurance measures that ensure compliance and reliability.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Snacks (e.g., chips, nuts, candy)
Main Stages:
– Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials. For snacks, this includes sourcing quality grains, nuts, or other ingredients. Suppliers often use bulk purchasing to reduce costs.
-
Forming: Depending on the type of snack, forming techniques vary. For chips, ingredients are mixed, rolled out, and cut into shapes before frying. For nuts, they may be roasted and seasoned.
-
Assembly: Once formed, snacks are packaged into bags or boxes. Automated packaging lines ensure efficiency and consistency.
-
Finishing: The final product undergoes cooling and labeling. Packaging must comply with local regulations regarding nutritional information and allergens.
Key Techniques:
– Extrusion: Commonly used for snacks like puffs or cereals, where ingredients are cooked and shaped under high pressure.
– Frying and Baking: Essential for chips and other crispy snacks, where the cooking method significantly affects taste and texture.
2. Beverages (e.g., soft drinks, juices)
Main Stages:
– Material Preparation: Ingredients such as water, sugar, and flavorings are sourced from certified suppliers. Quality checks on raw materials are critical.
-
Forming: Beverages are blended according to proprietary recipes. This stage may involve carbonation for soft drinks or pasteurization for juices.
-
Assembly: Bottling or canning occurs in a sterile environment to prevent contamination. Automated filling machines are used to ensure accuracy.
-
Finishing: The products are labeled and packed into cartons for distribution. Quality control measures ensure that each batch meets specifications.
Key Techniques:
– Carbonation: The process of dissolving carbon dioxide in a liquid, crucial for soft drinks.
– Pasteurization: A heat treatment process that extends shelf life and ensures safety, especially for juices.
3. Personal Care Items (e.g., hand sanitizers, tissues)
Main Stages:
– Material Preparation: Ingredients are sourced from certified suppliers, focusing on safety and efficacy, particularly for consumables.
-
Forming: For hand sanitizers, ingredients are mixed in precise proportions. For tissues, raw materials like paper are processed and cut to size.
-
Assembly: Products are filled, packaged, and prepared for distribution. Automated assembly lines are common in this sector.
-
Finishing: Final inspection ensures that packaging is intact and compliant with safety standards.
Key Techniques:
– Emulsification: Used in products like lotions and sanitizers to blend oil and water-based ingredients.
– Laminating: In tissue production, where multiple layers of paper are bonded for strength and softness.
Quality Assurance
To maintain product integrity and compliance, various quality assurance measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process.
Relevant International Standards
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable across industries. It emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) Standards: For personal care items, particularly those that are medicinal, adherence to API standards ensures safety and efficacy.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process to monitor quality and prevent defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product before packaging. This includes sensory evaluations for snacks and beverages, as well as safety tests for personal care items.
Common Testing Methods
- Chemical Analysis: Ensures that the product composition meets regulatory standards.
- Microbiological Testing: Critical for consumables to ensure they are free from harmful pathogens.
- Sensory Evaluation: Used for snacks and beverages to assess taste, texture, and aroma.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers, especially when sourcing internationally.
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of supplier facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can help assess supplier compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to evaluate supplier facilities can ensure unbiased assessments of quality practices.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When dealing with suppliers across different regions, it’s vital to understand the local regulations and certification requirements. For instance:
-
Africa: Regulatory bodies may have varying standards for food safety and personal care products. It’s crucial to align with local compliance measures.
-
South America: Import regulations can be stringent, and products may require specific certifications to enter markets.
-
Middle East and Europe: Understanding the nuances of CE marking and other regional certifications is essential for compliance and market access.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, international B2B buyers can ensure that the products they source for vending machines meet the highest standards of quality and safety, ultimately leading to greater customer satisfaction and business success.
Related Video: How Things Are Made | An Animated Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3 things in a vending machine Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing strategies for sourcing products for vending machines is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the components that drive costs and the influencers on pricing can significantly enhance procurement decisions.
Cost Components in Vending Machine Product Sourcing
-
Materials: The type of products stocked in vending machines directly affects the material costs. For instance, sourcing snacks may involve lower material costs compared to beverages or fresh food items, which often require specialized packaging to maintain freshness.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect costs associated with manufacturing and logistics. For instance, if products are sourced from countries with lower labor costs, this can lead to significant savings. However, it’s essential to consider the trade-offs in quality and compliance with international labor standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs related to production facilities, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturers often spread these costs over a larger volume of production, which can lower the overall cost per unit.
-
Tooling: If custom products are required, tooling costs can increase significantly. This is particularly relevant for products that need unique molds or designs, impacting the initial investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures is critical, especially for consumables. These costs can vary based on the complexity of the products and the certifications required to comply with local regulations.
-
Logistics: Transportation and storage costs can fluctuate widely based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, shipping methods, and local infrastructure. International buyers should consider the implications of Incoterms on logistics costs.
-
Margin: Finally, the profit margin that suppliers add to their costs can vary based on competition, product exclusivity, and market demand. Understanding the typical margins in your target market can help in negotiation.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically reduce the unit cost, making it more economical for buyers. However, international buyers should balance the benefits of bulk purchasing with storage capabilities and cash flow considerations.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom products may incur higher costs due to additional tooling and production time. Buyers should assess the necessity of customization against potential savings from standard products.
-
Materials: High-quality materials often lead to higher prices, but they can also enhance product appeal and longevity, thereby increasing sales potential.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific health and safety standards may command higher prices. Buyers must weigh the benefits of compliance against cost, especially in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: Reliability, reputation, and the supplier’s ability to meet delivery timelines can influence pricing. Establishing long-term partnerships can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is vital for international buyers as they dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, impacting total costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiate: Always negotiate pricing and terms, especially when establishing new supplier relationships. Leverage volume commitments to secure better pricing.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the initial purchase price and consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes logistics, storage, and potential wastage.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing structures based on local demand, competition, and economic conditions. Tailoring your approach based on regional insights can lead to better procurement outcomes.
-
Stay Informed: Regularly review market trends and supplier performance to make informed sourcing decisions. Engaging in industry forums can provide valuable insights into pricing dynamics.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed are indicative and can vary significantly based on market conditions, specific product requirements, and geographic factors. It is advisable to conduct thorough market research and engage with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing information tailored to your specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential 3 things in a vending machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘3 things in a vending machine’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3 things in a vending machine
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with vending machine components is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge helps in making informed purchasing decisions and navigating the complexities of global supply chains. Below are critical specifications and terms relevant to three common items found in vending machines: snack products, beverages, and payment systems.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of materials based on their mechanical and physical properties, such as strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
– Importance: High-quality materials ensure longevity and reliability of vending machine components, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance costs. -
Shelf Life
– Definition: The duration for which a product remains usable or saleable under specified storage conditions.
– Importance: Understanding shelf life is critical for stocking perishable items. It helps prevent losses due to expired products, which can negatively impact customer satisfaction and profitability.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measurement.
– Importance: Tolerance levels are essential for ensuring that components fit together correctly, especially in mechanical parts like dispensing mechanisms. Poor tolerances can lead to operational failures. -
Packaging Standards
– Definition: Specifications regarding the materials and methods used to package products for protection and marketing.
– Importance: Adhering to packaging standards is vital for compliance with local regulations and for ensuring the product’s safety and presentation. This is particularly important for edible items. -
Weight Distribution
– Definition: The balance of weight within the vending machine, affecting how items are stored and dispensed.
– Importance: Proper weight distribution ensures that machines operate smoothly and reduces the risk of jams or malfunctions, enhancing user experience and operational efficiency.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source high-quality components that meet specific design standards, ensuring compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory effectively and negotiate better terms with suppliers, especially in bulk purchasing situations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Relevance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare quotes from different suppliers, aiding in cost-effective decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, ensuring smoother international transactions.
-
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods.
– Relevance: Understanding lead times is essential for inventory management, especially in markets where demand can fluctuate significantly. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Regulatory requirements that products must meet to ensure safety, quality, and compliance.
– Relevance: Being aware of relevant certification standards is crucial for compliance, particularly in regions with strict regulations, such as the EU or certain African markets.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and build more effective partnerships in the vending machine industry. This knowledge not only aids in sourcing the right products but also in negotiating better deals and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the 3 things in a vending machine Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The vending machine sector is experiencing a transformative phase, driven by globalization, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Key trends include the rise of cashless payment systems, which cater to the increasing demand for convenience and speed among consumers. Contactless payments and mobile wallets are becoming standard, enabling vendors to enhance user experience and streamline transactions.
Moreover, smart vending machines equipped with IoT technology are emerging as a game-changer. These machines collect real-time data on sales patterns and inventory levels, allowing businesses to optimize their supply chains and reduce operational costs. In regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure may be less developed, mobile technology integration can facilitate better inventory management and customer engagement strategies.
Additionally, sourcing trends are shifting towards local suppliers to reduce lead times and transportation costs. This is particularly relevant in Europe and the Middle East, where regulations around sustainability and local sourcing are becoming more stringent. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate agility and responsiveness to market shifts, ensuring they can adapt quickly to emerging consumer demands and regulatory changes.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer a mere buzzword; it is an essential criterion for B2B buyers in the vending machine sector. The environmental impact of sourcing practices is significant, affecting everything from product packaging to the materials used in the machines themselves. Ethical sourcing involves selecting suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using biodegradable packaging or sourcing ingredients from fair-trade suppliers.
B2B buyers should actively seek green certifications for the products they source, such as Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, or organic certifications. These not only enhance the marketability of vending machine offerings but also align with the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly products. In regions like Europe, where consumers are increasingly environmentally conscious, offering sustainable products can significantly boost sales.
Furthermore, adopting sustainable practices is not just about compliance; it can lead to cost savings in the long run. Energy-efficient vending machines can reduce electricity consumption, while locally sourced products can minimize transportation costs and carbon footprints. By prioritizing sustainability, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation, attract a broader customer base, and contribute positively to their communities.
Brief Evolution/History
The vending machine industry has evolved dramatically since its inception in the late 19th century. Initially, these machines dispensed simple products like postcards and chewing gum. The introduction of electrical vending machines in the 1930s marked a significant turning point, allowing for a broader range of products, including beverages and snacks.
As technology advanced, the 21st century saw the rise of digital vending machines equipped with payment systems that accept credit cards and mobile payments. Today, the focus is shifting toward smart vending solutions that leverage data analytics to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is vital to leveraging technological advancements in vending operations and staying competitive in a rapidly changing market.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3 things in a vending machine
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers for vending machine products?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the vending industry and seek references from other businesses they supply. Verify their compliance with local regulations, especially regarding food safety and labeling standards. Additionally, assess their financial stability and ability to provide consistent product quality. Request samples to evaluate product quality firsthand, and consider visiting their facilities if possible. Establishing clear communication and understanding their logistical capabilities can further ensure they meet your operational needs. -
What customization options are typically available for vending machine products?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including product selection, packaging design, and branding. This can help differentiate your offerings in the market. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to explore available options, such as private labeling or bespoke product formulations. Additionally, inquire about minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized products, as these can vary significantly between suppliers. Customization can enhance customer engagement and improve sales, particularly in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. -
What should I know about minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times?
Understanding MOQs and lead times is critical for inventory management. Suppliers often set MOQs based on their production costs and logistics. Negotiate these quantities to find a balance that suits your budget while ensuring sufficient stock levels. Lead times can vary widely based on the supplier’s location and production capabilities, so clarify these timelines upfront. Consider local suppliers to reduce lead times and shipping costs, and always account for additional time in case of unforeseen delays. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification for the products I source?
Request detailed quality assurance protocols from your suppliers, including any certifications they hold, such as ISO or HACCP. These certifications indicate adherence to industry standards and can be crucial for food safety and compliance. Establish a quality control process that includes regular audits of the supplier’s production facilities and random product testing. This proactive approach helps prevent issues before they arise, ensuring that the products meet your specifications and legal requirements in your target markets. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing vending machine products?
Logistics play a pivotal role in the success of your vending business. Assess the supplier’s shipping capabilities, including their experience with international shipping and customs regulations. Opt for suppliers with reliable logistics partners to ensure timely delivery. Additionally, consider the cost implications of shipping methods and explore options for consolidated shipments to minimize expenses. Incorporating logistics into your overall sourcing strategy can streamline operations and improve product availability in your vending machines. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers?
Disputes can arise in any business relationship; having a clear plan in place is essential. Start by establishing a formal communication channel for addressing issues, ensuring both parties understand the escalation process. Document all agreements and communications to provide a reference point during disputes. If a resolution cannot be reached through direct negotiation, consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to legal action, which can be costly and time-consuming. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can often prevent disputes from escalating. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with international suppliers?
Negotiating favorable payment terms is crucial for managing cash flow. Common payment methods include letters of credit, wire transfers, or payment upon delivery. Evaluate the risks associated with each method, especially in international transactions where currency fluctuations can impact costs. Aim for terms that allow you sufficient time to sell products before payment is due, such as net 30 or net 60 days. Always conduct due diligence on the supplier’s financial background to minimize the risk of non-payment.
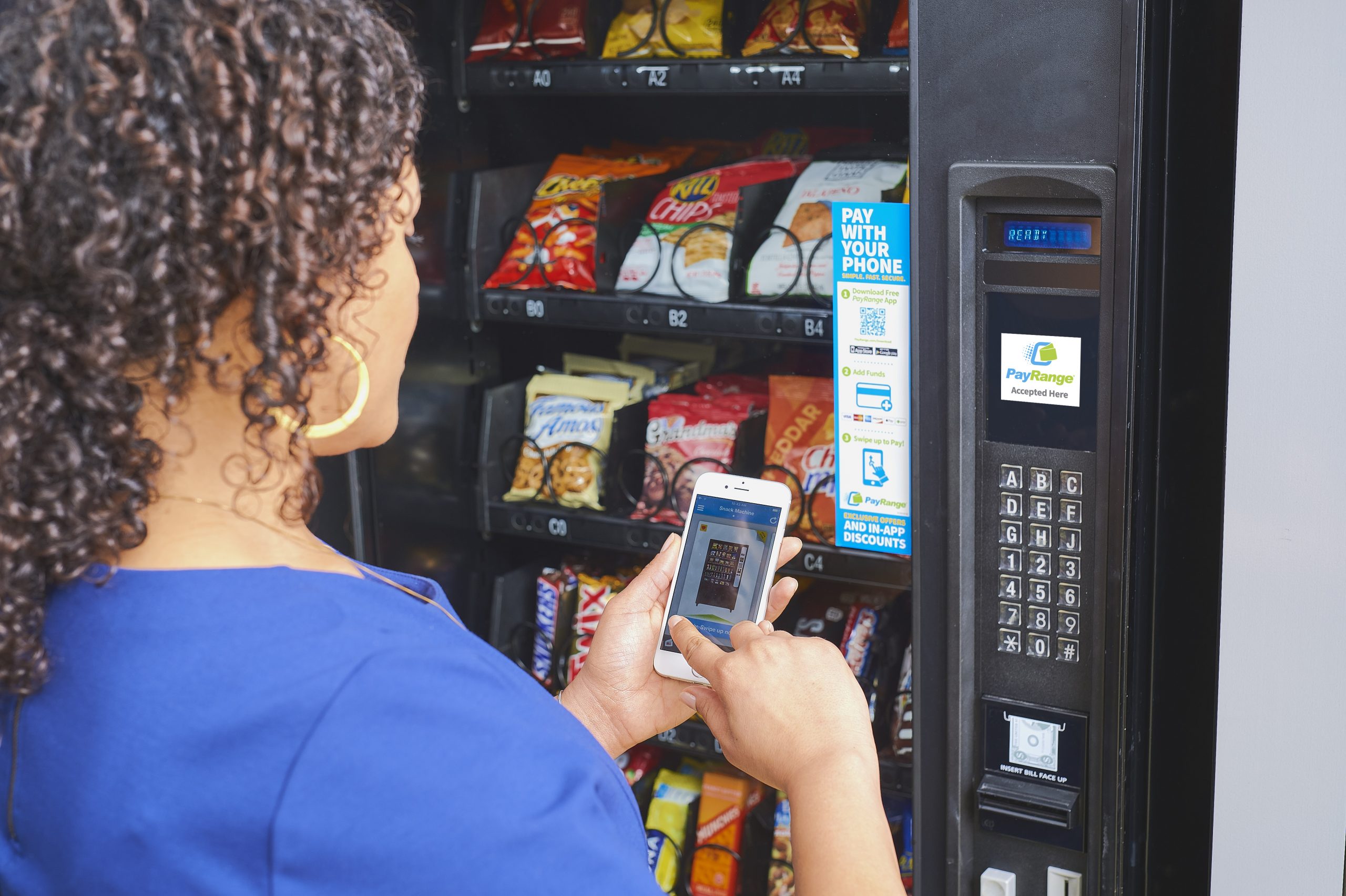

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- What are the key regulatory compliance issues I should be aware of?
Regulatory compliance varies by country and region, impacting product sourcing for vending machines. Familiarize yourself with local laws regarding food safety, labeling, and import regulations to avoid penalties. Products may require specific certifications or permits before they can be sold in your target market. Collaborate with suppliers who are knowledgeable about these regulations and can provide necessary documentation. Staying informed about changes in regulations can help you maintain compliance and build trust with customers.
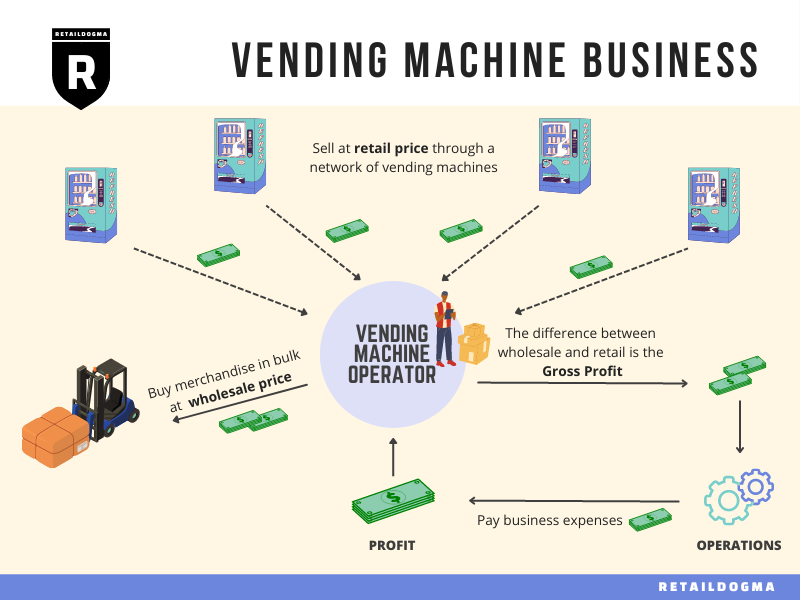
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3 things in a vending machine
In summary, the successful operation of a vending machine business hinges on strategic sourcing of products that resonate with your target market. International B2B buyers must prioritize three core elements: selecting reliable suppliers, ensuring product compliance with local regulations, and staying attuned to market trends. By cultivating strong partnerships with suppliers, businesses can secure favorable pricing and exclusive product offerings, thereby enhancing profitability.
Moreover, understanding the legal landscape surrounding vending operations is crucial. This not only mitigates risks but also fosters trust with customers and stakeholders. As you navigate the complexities of product sourcing, remember that effective inventory management aligned with consumer preferences can significantly elevate your competitive edge.
Looking ahead, the vending machine market continues to evolve, influenced by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to embrace these changes. Leverage strategic sourcing to position your business for growth and adaptability. Engage with local suppliers, explore innovative products, and remain proactive in addressing market demands. Your commitment to strategic sourcing will empower your vending operations to thrive in an increasingly dynamic landscape.