Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Orca Card Vending Machine
Guide to Orca Card Vending Machine
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for orca card vending machine
- Understanding orca card vending machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of orca card vending machine
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for orca card vending machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for orca card vending machine
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for orca card vending machine Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential orca card vending machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for orca card vending machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the orca card vending machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of orca card vending machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for orca card vending machine
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for orca card vending machine
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, the orca card vending machine stands as a pivotal solution for public transportation systems and various commercial sectors. These machines not only streamline the process of purchasing transit cards but also enhance user experience by providing a seamless and efficient payment method. As urbanization continues to rise in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for reliable and user-friendly vending solutions is more crucial than ever.
This guide offers a comprehensive overview tailored specifically for international B2B buyers. It delves into various types of orca card vending machines, the materials used in their construction, and the manufacturing and quality control processes that ensure their reliability. Buyers will also find valuable insights into leading suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends that shape the landscape of this niche industry.
Moreover, the guide addresses frequently asked questions, empowering buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed sourcing decisions. By understanding the intricacies of orca card vending machines, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and improve customer satisfaction. Whether you are an emerging enterprise or an established player in the transportation sector, this resource equips you with the essential tools to navigate the global market effectively.
Understanding orca card vending machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Kiosk | Touchscreen interface, accepts cash and card payments | Public transport, parking | Pros: User-friendly, versatile payment options. Cons: Higher upfront costs. |
| Mobile Vending Unit | Compact design, portable, solar-powered options | Events, temporary locations | Pros: Flexibility in deployment, eco-friendly. Cons: Limited capacity for transactions. |
| Multi-Function Vending | Combines card vending with additional services (e.g., ticketing) | Transit hubs, airports | Pros: Multi-use functionality, reduces need for multiple machines. Cons: Complexity may lead to higher maintenance. |
| Automated Retail Machine | Fully automated, remote monitoring capabilities | Retail environments, campuses | Pros: Low staffing costs, real-time inventory updates. Cons: Initial investment can be significant. |
| Custom Configured Units | Tailored to specific business needs and branding | Niche markets, specialized events | Pros: Unique branding and service offerings. Cons: Longer lead time for production and installation. |
Standard Kiosk
Standard kiosks are the most common type of orca card vending machines, featuring a touchscreen interface that allows users to purchase cards using cash or credit/debit cards. These kiosks are ideal for public transport systems and parking facilities where ease of use and accessibility are paramount. When considering a standard kiosk, buyers should evaluate the machine’s software capabilities, customer support options, and whether it meets local regulatory requirements for payment processing.
Mobile Vending Unit
Mobile vending units are designed for portability, making them suitable for events or temporary locations. Many models come with solar-powered options, allowing for operation in areas without electrical access. This type is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to expand their reach without the overhead of permanent installations. Buyers should consider the unit’s transaction capacity and battery life, as these factors can significantly impact operational efficiency.
Multi-Function Vending
These machines combine multiple services, such as card vending and ticketing, into a single unit. This versatility makes them particularly useful in transit hubs and airports, where space is limited, and various services are needed. While they can streamline operations and reduce the number of machines required, buyers must be aware that the complexity of these machines may lead to higher maintenance costs and potential downtime.
Automated Retail Machine
Automated retail machines are fully automated and often equipped with remote monitoring capabilities. They are especially suitable for retail environments and campuses where a low-staffing model is desirable. The key advantages of this type include reduced labor costs and real-time inventory management. However, buyers should prepare for a significant initial investment and ensure that they have a robust maintenance plan in place to address any technical issues that may arise.
Custom Configured Units
Custom configured units allow businesses to tailor vending solutions to their specific needs, including branding and unique service offerings. This flexibility can be advantageous in niche markets or specialized events where standard solutions may not suffice. When considering a custom unit, buyers should factor in the longer lead times for production and installation, as well as the potential for increased costs compared to off-the-shelf options.
Related Video: How to get an Orca Card in Seattle WA USA
Key Industrial Applications of orca card vending machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of orca card vending machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Transport | Automated ticketing for transit systems | Increased efficiency in ticket sales and reduced queues | Integration with existing transit systems, user interface design |
| Education | Student ID and access card dispensing | Streamlined student access to facilities and services | Security features, card customization options |
| Retail | Loyalty and gift card issuance | Enhanced customer engagement and retention | Compatibility with payment systems, card design flexibility |
| Event Management | Ticket sales for events and venues | Improved customer experience and sales tracking | Scalability for high-demand events, data management capabilities |
| Corporate Offices | Employee access control and identification | Enhanced security and ease of access management | Integration with HR systems, support for various card types |
Public Transport
In public transport systems, the orca card vending machine is utilized for automated ticketing solutions, allowing passengers to purchase transit cards and tickets seamlessly. This application addresses common challenges such as long queues and manual ticketing errors, leading to improved operational efficiency. International buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider sourcing machines that integrate easily with existing transit systems and offer user-friendly interfaces to cater to diverse populations.
Education
Educational institutions deploy orca card vending machines to dispense student IDs and access cards. This application enhances security by controlling access to facilities while providing students with a convenient method to access services. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it is crucial to ensure that these machines have robust security features and customization options to reflect institutional branding and meet local regulations.
Retail
In the retail sector, orca card vending machines are effective for issuing loyalty and gift cards. This application fosters customer engagement and retention by providing a quick and convenient way for customers to acquire cards. B2B buyers from South America and Africa should prioritize sourcing machines compatible with various payment systems and capable of offering flexible card designs to meet diverse consumer preferences.
Event Management
Event organizers utilize orca card vending machines for ticket sales, enhancing the customer experience by facilitating quick and easy access to events. This application addresses the need for efficient sales tracking and reduces the risk of ticket fraud. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should seek scalable solutions that can handle high-demand events and provide data management capabilities for better event planning and analysis.
Corporate Offices
In corporate environments, orca card vending machines are employed for employee access control and identification. This application enhances security by ensuring that only authorized personnel can enter specific areas while simplifying the management of employee access. B2B buyers should consider sourcing machines that integrate with existing HR systems and support various card types to ensure a smooth transition and operational efficiency.
Related Video: What are all the Laboratory Apparatus and their uses?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for orca card vending machine
When selecting materials for the orca card vending machine, it’s essential to consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of several common materials used in the construction of these machines, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel (e.g., AISI 304/316)
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in environments exposed to moisture and various chemicals. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for diverse applications.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel offers high durability and strength, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. However, it is more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to machine, which may increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application:
The corrosion resistance of stainless steel makes it suitable for outdoor installations, where exposure to the elements is a concern. It is compatible with a wide range of media, including water and various cleaning agents.
Specific Considerations for International B2B Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or EN for material specifications. In regions like Europe and Australia, the preference for stainless steel is often due to its longevity and aesthetic appeal.
2. Carbon Steel (e.g., A216 WCB)
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is strong and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for structural components. However, it is susceptible to corrosion if not adequately protected.
Pros & Cons:
While carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, it requires protective coatings to prevent rust, which can add to lifecycle costs. Its durability is suitable for internal components but may not be ideal for external surfaces.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is suitable for applications where exposure to harsh environments is limited. It is often used in non-corrosive environments, although care must be taken regarding media compatibility.
Specific Considerations for International B2B Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of local corrosion protection standards and consider the cost implications of coatings. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary, additional protective measures may be necessary.
3. Polycarbonate
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is a lightweight, impact-resistant plastic that can withstand a wide range of temperatures. It is transparent, allowing for visibility of internal components.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polycarbonate is its high impact resistance and lightweight nature, which simplifies installation. However, it is less durable than metals and can be prone to scratching and UV degradation over time.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is ideal for protective covers and windows in vending machines, providing visibility while protecting internal components. It is compatible with various media but may require UV stabilizers for outdoor use.
Specific Considerations for International B2B Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with safety and environmental regulations, particularly regarding the use of plastics. In Europe, for instance, REACH compliance is essential for materials used in consumer-facing products.
4. Aluminum (e.g., 6061-T6)
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various applications. It has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is relatively easy to machine and fabricate, offering a good balance between weight and strength. However, it may not be as strong as steel and can be more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is often used for structural components and casings in vending machines. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications, although it may require anodizing for enhanced protection.
Specific Considerations for International B2B Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum grades and their compliance with international standards. In the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, selecting the right aluminum grade is crucial for maintaining performance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for orca card vending machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (e.g., AISI 304/316) | Structural components, outdoor installations | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, machining complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel (e.g., A216 WCB) | Internal components, non-corrosive environments | Cost-effective, good strength | Susceptible to corrosion, requires coatings | Low |
| Polycarbonate | Protective covers, visibility panels | Lightweight, impact-resistant | Prone to scratching, UV degradation | Med |
| Aluminum (e.g., 6061-T6) | Structural components, casings | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Less strong than steel, higher cost | Med |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for orca card vending machines, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with local standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for orca card vending machine
The manufacturing of orca card vending machines involves a series of meticulously planned stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets both functional and quality standards. Understanding these processes and the associated quality assurance measures is essential for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing orca card vending machines involves sourcing and preparing materials. Common materials include high-grade metals for structural integrity, plastics for housing, and electronic components for functionality.
- Sourcing: Suppliers should be vetted for quality and sustainability. Prefer suppliers who adhere to international standards like ISO 14001 for environmental management.
- Material Inspection: Before use, materials undergo Incoming Quality Control (IQC) to ensure they meet predefined specifications. This includes checking for defects and verifying material certifications.
2. Forming
This stage involves shaping the materials into the necessary components of the vending machine.
- Techniques: Techniques such as CNC machining, injection molding for plastic parts, and sheet metal forming are commonly used. Each technique should be chosen based on the material properties and component requirements.
- Precision: High precision is vital, particularly for parts that will house electronic components. Tolerances should align with industry standards to ensure compatibility and performance.
3. Assembly
Once the components are formed, they move to the assembly stage.
- Assembly Line: A streamlined assembly line can enhance efficiency. Workers should be trained in best practices to minimize errors.
- Automation: Incorporating automation in assembly can improve consistency and speed. Robots can handle repetitive tasks, while humans can focus on quality checks and complex assembly.
4. Finishing
The final stage includes surface treatment and final assembly, ensuring both aesthetic appeal and functionality.
- Coatings and Treatments: Surface treatments such as powder coating or galvanization enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors. This is especially crucial for machines installed in outdoor settings.
- Final Assembly: This involves integrating all components, including electronics, display interfaces, and payment systems. Attention to detail is critical to ensure all parts fit perfectly and function correctly.
Quality Assurance
International Standards
Quality assurance in manufacturing orca card vending machines is governed by several international standards.
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers should implement ISO 9001 to ensure consistent quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: For machines sold in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For machines involved in financial transactions, adherence to Application Programming Interface (API) standards ensures secure and reliable communication between devices.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verifies the quality of raw materials before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing to catch defects early. This may involve visual inspections and functional tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product before shipment. This includes performance testing, safety checks, and compliance verification.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods vary based on component functionality but typically include:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that all features of the vending machine operate as intended. This includes testing the card reader, payment systems, and display functionality.
- Environmental Testing: Simulates conditions the machine may face in its operational environment, checking for durability against heat, cold, moisture, and dust.
- Electrical Safety Testing: Ensures compliance with electrical standards, protecting users and preventing equipment damage.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. This can include reviewing their QMS, production methods, and inspection records.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports from suppliers, including metrics on defect rates and corrective actions taken. This transparency can provide insights into their commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party quality inspectors to verify compliance with international standards. This adds an extra layer of assurance, particularly for buyers unfamiliar with local manufacturing practices.
Navigating QC Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers must be aware of the nuances in quality control across different regions:
- Regional Standards: Familiarize yourself with regional standards and certifications. For example, in Europe, compliance with CE marking is mandatory, while in the Middle East, local regulations may vary significantly.
- Cultural Considerations: Cultural differences can impact manufacturing practices and quality perceptions. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication and understanding of quality expectations.
- Documentation: Ensure all quality assurance documents are available in a language you understand. This includes certifications, inspection reports, and compliance documents.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for orca card vending machines is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside rigorous quality control standards and verification methods, businesses can ensure they source reliable and high-quality vending machines that meet their operational needs. This knowledge not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also fosters long-term supplier relationships, essential for success in diverse markets.
Related Video: The Production Planning Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for orca card vending machine Sourcing
To effectively navigate the sourcing of orca card vending machines, international B2B buyers must understand the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics. This understanding not only aids in budgeting but also in negotiating favorable terms with suppliers.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary costs arise from raw materials used in manufacturing vending machines, including metals, plastics, and electronic components. Prices for these materials can fluctuate based on global supply chain conditions, affecting overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages paid to workers involved in the assembly and production of vending machines. These costs vary significantly by region, with labor-intensive manufacturing locations typically offering lower rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent for manufacturing facilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient management of overhead can significantly impact the cost structure.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools and equipment necessary for the production of vending machines is crucial. These costs can be amortized over production runs, making them a significant factor for buyers ordering in bulk.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that machines meet safety and quality standards incurs costs related to inspections, testing, and compliance certifications. High-quality standards may lead to increased upfront costs but can reduce long-term expenses related to repairs and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and handling fees, play a significant role in total expenditure. The choice of shipping methods and routes can greatly influence logistics costs, especially for international orders.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs. Understanding the industry standard margins can help buyers assess fair pricing and negotiate better deals.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Higher volumes usually lead to lower unit costs due to economies of scale, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate orders.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized features or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should balance the desire for customization with budget constraints, considering whether standard models could meet their needs.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: The choice of materials and the certifications that accompany them (e.g., ISO, CE) can influence both price and perceived value. Higher quality materials often command higher prices but can enhance durability and user satisfaction.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and production capabilities affect pricing. Engaging with reputable suppliers who have a history of delivering quality products can mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact overall costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, particularly if you can commit to larger volumes or longer-term contracts. Being informed about market rates can strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A lower purchase price may not always equate to better value if operational costs are high.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. Additionally, tariffs and trade agreements can influence costs, especially for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where trade dynamics can vary significantly.
Disclaimer
Prices for orca card vending machines can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions and specific buyer requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential orca card vending machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘orca card vending machine’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for orca card vending machine
Understanding the technical properties and terminology associated with the orca card vending machine is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section outlines critical specifications and industry jargon that can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
The orca card vending machine is typically constructed from high-grade materials such as stainless steel or reinforced plastic. The choice of material affects durability, resistance to weather conditions, and overall maintenance costs. For buyers in regions with extreme climates, selecting machines with higher material grades can lead to longer lifespans and reduced downtime. -
Power Supply Specifications
These machines often require specific voltage and amperage to operate efficiently. Understanding the power supply specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility with local electrical systems. Buyers should verify that the machines can operate on the voltage available in their region to avoid installation complications.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
User Interface Design
A user-friendly interface is vital for enhancing customer experience. Features such as touchscreen capabilities, multilingual options, and intuitive navigation can significantly impact user satisfaction. For international buyers, ensuring that the interface can accommodate local languages and preferences can boost usage rates. -
Transaction Speed
The efficiency of the vending machine is often measured by its transaction speed, which can affect customer flow, especially in high-traffic areas. A machine that processes transactions quickly can enhance user experience and reduce wait times, which is especially important in urban centers or during peak hours. -
Payment Options
Modern orca card vending machines should support multiple payment methods, including cash, credit/debit cards, and mobile payments. This flexibility is important for catering to diverse customer preferences, particularly in regions where cashless transactions are becoming more prevalent. -
Security Features
Security is paramount, especially for machines that handle cash or sensitive customer data. Features such as tamper-proof locks, surveillance cameras, and encryption protocols for online transactions can protect against theft and fraud. Buyers should prioritize machines with robust security measures to safeguard their investments.
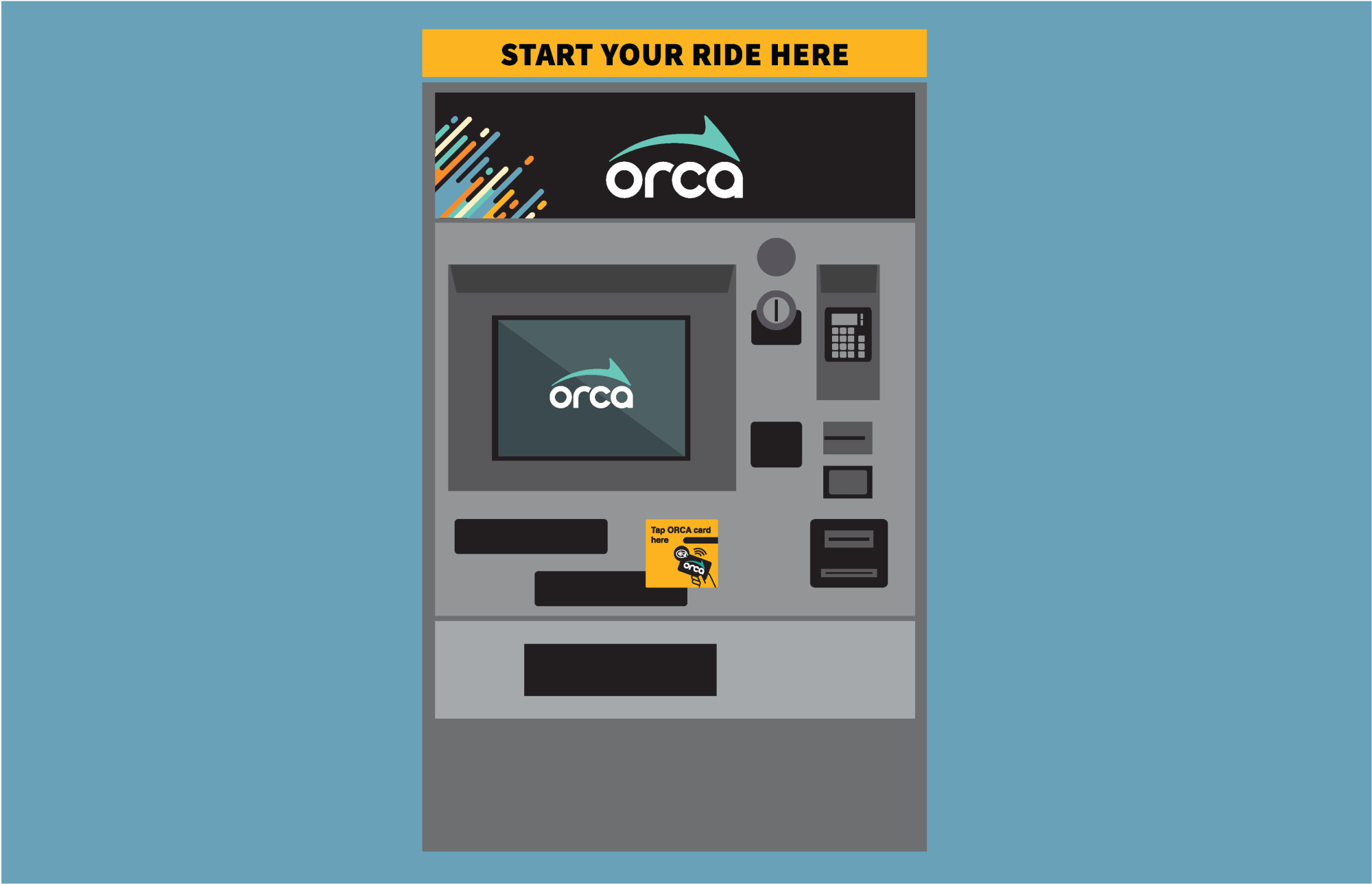
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for quality assurance and reliability in their vending machine suppliers. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers need to be aware of MOQ requirements to avoid overcommitting to stock levels that may not align with their demand forecasts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It is essential for B2B transactions as it helps buyers compare costs and negotiate terms effectively before making a purchasing decision. -
Incoterms
Short for International Commercial Terms, Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global transactions. Familiarity with terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for understanding shipping responsibilities and cost allocations. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. For buyers, understanding lead times is critical for planning inventory and ensuring timely delivery to meet customer demands. -
Warranty Period
This indicates the duration for which a manufacturer guarantees the machine against defects. Knowing the warranty period can inform buyers about potential future costs and the reliability of the equipment.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding the procurement of orca card vending machines, ultimately leading to better operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the orca card vending machine Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The orca card vending machine sector is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for contactless payment solutions and the integration of smart technologies. In markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, urbanization and the expansion of public transport networks are propelling the need for efficient fare collection systems. Particularly in countries like Egypt and Brazil, governments are investing in modernizing transport infrastructure, which includes deploying advanced vending machines that support multiple payment methods, including mobile payments.
Emerging B2B trends include the adoption of IoT-enabled machines that allow for real-time data collection and analytics, which are critical for optimizing operations and improving user experience. International buyers should also consider the rise of software integration capabilities, where vending machines connect seamlessly with transit authorities’ backend systems to streamline operations. Additionally, with the growing emphasis on user-friendly designs, machines that offer multilingual support and intuitive interfaces are becoming increasingly popular.
Market dynamics are shifting towards sustainability and energy efficiency, as stakeholders prioritize eco-friendly solutions. For instance, machines that utilize solar energy or are made from recycled materials are gaining traction. Buyers in regions like Europe are particularly focused on compliance with stringent environmental regulations, making it essential for suppliers to highlight the sustainability credentials of their products.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the orca card vending machine market, with environmental impacts influencing purchasing decisions. As international buyers increasingly seek to align with sustainability goals, understanding the ecological footprint of vending machines is crucial. This includes assessing energy consumption, waste generation, and the lifecycle of materials used in production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to responsible sourcing practices, ensuring that raw materials are obtained in a manner that respects both the environment and human rights. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC for sustainable forestry can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, there is a growing trend towards using green materials in manufacturing, such as biodegradable plastics or recycled metals. As customers become more environmentally conscious, integrating these materials not only enhances brand reputation but can also lead to cost savings in waste management and regulatory compliance.
Brief Evolution/History
The orca card vending machine has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 20th century. Initially designed for simple fare collection, these machines have transformed into sophisticated systems capable of handling a variety of payment methods and providing real-time data analytics. The introduction of contactless payment options in the early 2000s marked a pivotal shift, enhancing user convenience and operational efficiency.
Over the past decade, the focus has expanded from merely facilitating transactions to offering integrated solutions that improve the overall public transport experience. This evolution reflects broader technological advancements and changing consumer expectations, positioning the orca card vending machine as a vital component in modern urban mobility solutions. As the sector continues to innovate, international B2B buyers must stay informed about technological advancements and sustainability practices that define the future of fare collection systems.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of orca card vending machine
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for orca card vending machines?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their experience in the industry, reputation, and customer reviews. Verify their credentials and certifications to ensure compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients, especially those in your region, to gauge reliability. Additionally, assess their production capacity and technological capabilities to meet your specific requirements, including potential customization options. -
Can I customize the orca card vending machine to suit my business needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options. You can specify features such as payment methods (credit card, mobile payment), branding, and machine size. Discuss your requirements upfront with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities. It’s essential to ensure that any customizations comply with local regulations and standards in your target market to avoid issues during implementation. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for orca card vending machines?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and specific machine features. Generally, you might expect an MOQ of 10 to 50 units. Lead times typically range from 6 to 12 weeks, depending on customization requirements and production schedules. Always confirm these details with your supplier and consider potential delays in logistics and shipping, especially for international orders. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted by suppliers of orca card vending machines?
Payment terms can vary, but many suppliers require a deposit (usually 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due before shipment. Some may offer financing options or letters of credit, particularly for larger orders. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Ensure that all payment terms are clearly documented in your contract to avoid disputes later. -
What quality assurance certifications should I look for in orca card vending machines?
Look for suppliers that hold relevant quality certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and CE marking for compliance with European safety standards. Depending on your region, other certifications like UL or FCC might be necessary. Request documentation of these certifications and inquire about their quality control processes to ensure the machines meet your expectations. -
How do logistics and shipping work for international orders of orca card vending machines?
Logistics can be complex, involving freight forwarders and customs clearance. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including Incoterms (like FOB, CIF) to understand who bears the risk and costs at each stage. Ensure that the supplier has experience with international shipping and can provide necessary documentation for customs. Consider potential tariffs and import regulations in your country when calculating total costs. -
What should I do if there is a dispute with my supplier regarding the orca card vending machines?
In case of a dispute, start by reviewing the terms of your contract to understand your rights and obligations. Communicate directly with the supplier to resolve issues amicably. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as outlined in your agreement. It’s advisable to maintain clear documentation of all communications and agreements to support your position if legal action becomes necessary. -
Are there any specific regulations or compliance standards for orca card vending machines in my region?
Yes, regulations vary by region and may include safety, environmental, and consumer protection laws. For instance, in Europe, machines must comply with the Machinery Directive and other relevant EU regulations. In Africa or South America, local authorities may have specific requirements regarding electronic payments and consumer safety. Always consult with local regulatory bodies or legal experts to ensure compliance before importing machines.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for orca card vending machine
The strategic sourcing of ORCA card vending machines presents an array of opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways highlight the importance of integrating advanced technology, ensuring user-friendly interfaces, and providing reliable support systems that cater to diverse operational needs.
Value of Strategic Sourcing
Investing in ORCA card vending machines not only enhances public transport accessibility but also streamlines revenue collection and improves customer satisfaction. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to innovation and sustainability, as these attributes are increasingly vital in today’s global market.
Looking Ahead
As urbanization continues to rise, the demand for efficient and adaptable vending solutions will only increase. International buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who offer comprehensive service agreements and customization options tailored to local market dynamics. Embracing strategic sourcing now will position businesses to capitalize on future advancements in technology and customer service.
Call to Action
Explore partnerships that align with your strategic goals and invest in ORCA card vending machines to lead the way in transforming public transport systems across your region. The future of smart transportation is here—be part of it.