Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Invest In Vending Machines
Guide to Invest In Vending Machines
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for invest in vending machines
- Understanding invest in vending machines Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of invest in vending machines
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for invest in vending machines
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for invest in vending machines
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for invest in vending machines Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential invest in vending machines Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for invest in vending machines
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the invest in vending machines Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of invest in vending machines
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for invest in vending machines
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for invest in vending machines
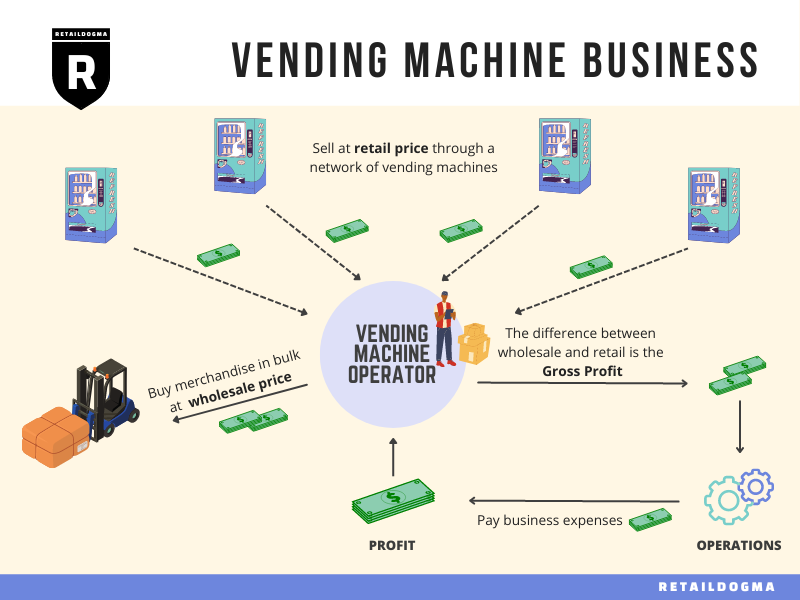
In today’s fast-paced global market, investing in vending machines has emerged as a lucrative opportunity for B2B buyers seeking to diversify their portfolios and tap into new revenue streams. With the growing demand for convenient and accessible retail solutions, vending machines provide a unique avenue for businesses to reach consumers directly, particularly in urban areas where foot traffic is high. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, empowering international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in markets like the UAE and Saudi Arabia—to make informed sourcing decisions.
Within this guide, we delve into various aspects of vending machine investments, including types of machines, materials used in manufacturing, and quality control measures essential for ensuring product longevity and reliability. We also explore the landscape of suppliers, allowing buyers to identify reputable partners who can meet their specific needs. Understanding the cost dynamics and the overall market trends will further equip buyers to navigate potential challenges and seize opportunities.
Additionally, we address frequently asked questions to clarify common concerns and provide actionable insights. By leveraging the information in this guide, B2B buyers will be better positioned to capitalize on the vending machine market, ensuring that their investments are not only profitable but also strategically aligned with consumer demands and technological advancements.
Understanding invest in vending machines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Vending | Dispenses snacks and beverages via mechanical systems | Offices, schools, public spaces | Pros: Low maintenance, familiar technology. Cons: Limited product range, lower profit margins. |
| Smart Vending | Equipped with IoT technology for real-time inventory | Airports, malls, tech hubs | Pros: Data-driven insights, flexible inventory. Cons: Higher upfront costs, requires tech support. |
| Healthy Vending | Focused on nutritious food and beverages | Gyms, schools, health facilities | Pros: Meets growing health trends, attracts health-conscious consumers. Cons: Higher sourcing costs, niche market. |
| Specialty Vending | Offers unique products (e.g., electronics, cosmetics) | Events, trade shows, boutiques | Pros: High-profit margins, caters to specific customer needs. Cons: Limited customer base, inventory risk. |
| Automated Retail | Combines vending with retail for a broader selection | Urban centers, transportation hubs | Pros: Enhanced customer experience, diverse product offerings. Cons: Complex logistics, maintenance challenges. |
Traditional Vending
Traditional vending machines are the most recognizable type, dispensing snacks and beverages through mechanical systems. They are commonly found in offices, schools, and public spaces. B2B buyers appreciate their low maintenance requirements and familiarity, making them easy to manage. However, the limited product range and lower profit margins can be drawbacks, especially in competitive environments where differentiation is key.
Smart Vending
Smart vending machines leverage IoT technology, providing real-time inventory tracking and data analytics. They are particularly suited for high-traffic areas such as airports, malls, and tech hubs, where consumer behavior can be closely monitored. The advantages include data-driven insights that help optimize inventory and improve sales. However, the initial investment is higher, and ongoing technical support may be necessary, which could deter some buyers.
Healthy Vending
Healthy vending machines focus on providing nutritious food and beverages, catering to the increasing demand for healthier options. They are ideal for gyms, schools, and health facilities, attracting health-conscious consumers. The pros include alignment with current health trends, making them a compelling choice for businesses looking to enhance their brand image. However, sourcing higher-quality ingredients can lead to increased costs, and the market may be more niche compared to traditional offerings.
Specialty Vending
Specialty vending machines offer unique products, such as electronics or cosmetics, often found at events, trade shows, or boutiques. These machines can yield high-profit margins due to their specialized offerings. B2B buyers can leverage these machines to cater to specific customer needs and stand out in crowded markets. The challenges include a limited customer base and the risk of unsold inventory, requiring careful market analysis before investment.
Automated Retail
Automated retail combines vending with traditional retail, offering a broader selection of products. These machines are increasingly found in urban centers and transportation hubs, providing convenience to busy consumers. The primary benefits include an enhanced customer experience and a diverse product offering that can attract a wider audience. However, the complexity of logistics and ongoing maintenance can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers considering this investment.
Related Video: How to Invest – The BCG Matrix
Key Industrial Applications of invest in vending machines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Invest in Vending Machines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Healthy snack and beverage vending | Increases employee satisfaction and productivity | Supplier reliability, product variety, health certifications |
| Corporate Offices | Office supply vending | Reduces downtime for employees needing supplies | Inventory management, refill frequency, payment options |
| Healthcare | Medication dispensing | Ensures timely access to medication for patients | Regulatory compliance, security features, user accessibility |
| Education | Campus convenience stores | Enhances student experience and boosts revenue | Location analysis, product selection, cashless payment systems |
| Transportation Hubs | Travel essentials vending | Provides travelers with convenience and comfort | Location visibility, product assortment, high turnover rate |
Food and Beverage
Investing in vending machines that offer healthy snacks and beverages addresses the growing demand for wellness in workplaces. By providing nutritious options, companies can enhance employee satisfaction and productivity, reducing the likelihood of absenteeism. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing machines that comply with local health standards and offer a variety of culturally relevant snacks is crucial. Buyers should also consider the reliability of suppliers to ensure product freshness and availability.
Corporate Offices
Vending machines for office supplies streamline operations by reducing downtime when employees need materials like pens, paper, and other essentials. This application is particularly beneficial in fast-paced corporate environments across Europe and South America, where quick access to supplies can enhance efficiency. Buyers should focus on vendors that offer comprehensive inventory management solutions and can provide flexible payment options to accommodate diverse workforce needs.
Healthcare
In healthcare settings, vending machines that dispense medications can significantly improve patient care by ensuring timely access to essential drugs. This application is vital in hospitals and clinics, especially in regions where pharmacy access may be limited. International B2B buyers must prioritize regulatory compliance and security features to protect sensitive medications. Additionally, user accessibility is essential to cater to patients with varying needs.
Education
Vending machines in educational institutions serve as convenient mini-stores for students, offering snacks, drinks, and even school supplies. This application not only enhances the student experience but also generates additional revenue for schools and universities. Buyers in regions like Europe and South America should conduct thorough location analyses to determine optimal placement, ensuring high visibility and foot traffic. Furthermore, integrating cashless payment systems can cater to the tech-savvy student demographic.
Transportation Hubs
Vending machines offering travel essentials such as snacks, drinks, and personal care items cater to the needs of travelers in airports, train stations, and bus terminals. This convenience enhances the overall travel experience, particularly in busy hubs across Africa and the Middle East. Buyers should focus on sourcing machines that can handle high turnover rates and provide a diverse product assortment to meet various traveler needs. Additionally, visibility and strategic placement are critical to maximizing sales in these locations.
Related Video: Kooler Ice Vending Machines – IM600XL vs. IM1000
Strategic Material Selection Guide for invest in vending machines
When investing in vending machines, selecting the right materials is crucial for ensuring product performance, longevity, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze several common materials used in vending machines, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and staining, which is essential for maintaining hygiene in food-related applications. However, it is more expensive than other materials like carbon steel, which may impact initial investment costs. Manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including beverages and snacks. Its non-reactive nature ensures that the quality of the products remains intact.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EU regulations) is critical. Buyers should ensure that the grade of stainless steel used meets local and international standards, such as ASTM or EN.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel offers good strength and toughness, with a temperature rating suitable for most vending machine applications. However, it lacks inherent corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
Carbon steel is cost-effective and easy to machine, making it a popular choice for non-corrosive applications. The downside is its susceptibility to rust, which necessitates protective coatings or regular maintenance to prolong its lifespan.
Impact on Application:
This material is ideal for vending machines that dispense non-perishable items or are located in controlled environments. Its compatibility with various mechanical components is also a plus.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must consider local climate conditions, as high humidity or exposure to moisture can accelerate corrosion. Compliance with standards like ASTM is also essential to ensure quality and safety.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It is suitable for applications where weight is a concern.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce shipping costs and ease installation. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can be more expensive than carbon steel, depending on the alloy used.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is often used in vending machine frames and panels, especially in environments where weight savings are critical. It is also suitable for various media, although care must be taken with acidic or alkaline products.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that aluminum grades meet local standards for strength and corrosion resistance. Compliance with international standards such as JIS or ASTM is also important for quality assurance.
Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)
Key Properties:
GRP is a composite material known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons:
GRP is highly durable and resistant to chemicals, making it suitable for vending machines that dispense beverages. However, it can be more expensive to manufacture and may not have the same aesthetic appeal as metal options.
Impact on Application:
GRP is ideal for applications where weight and corrosion resistance are critical, particularly in outdoor settings. It is compatible with a range of products but may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with local regulations regarding plastic materials, especially in food applications. Understanding the environmental impact and recyclability of GRP is also essential for sustainability-focused buyers.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for invest in vending machines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food and beverage dispensing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher initial cost | High |
| Carbon Steel | General service, non-corrosive fluids | Cost-effective, good strength | Susceptible to corrosion if not protected | Low |
| Aluminum | Lightweight frames and panels | Low weight, good thermal conductivity | Less durable than stainless steel | Med |
| Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) | Outdoor vending machines | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion-resistant | Higher manufacturing cost | Med |
This guide aims to provide international B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for vending machines, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for invest in vending machines
Manufacturing Processes for Vending Machines
Investing in vending machines involves understanding the intricate manufacturing processes that bring these machines to life. The typical stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, each playing a critical role in ensuring the end product meets quality and functionality standards.
1. Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of raw materials. Vending machines are primarily constructed from metals like steel and aluminum, plastics, and electronic components.
- Key Activities:
- Sourcing: Identify reliable suppliers that provide high-quality materials, ensuring compliance with international standards.
- Material Inspection: Conduct incoming quality control (IQC) checks to assess material quality and specifications.
This stage is crucial as the durability and performance of the vending machines depend heavily on the quality of the materials used.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next phase involves forming them into the desired shapes. This process may include cutting, bending, and welding.
- Techniques:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining allows for precise cuts and shapes, enhancing the accuracy of the components.
- Stamping and Bending: Used for creating the machine’s outer shell and internal brackets, ensuring they fit together seamlessly.
The forming stage lays the groundwork for a robust and reliable vending machine.
3. Assembly
Assembly is where the individual components come together to create the final product. This stage is often labor-intensive and requires meticulous attention to detail.
- Key Steps:
- Component Assembly: Integrating mechanical parts, electronic systems, and payment modules.
- Testing During Assembly: Implementing in-process quality control (IPQC) measures to identify defects early, reducing costs associated with rework.
A well-executed assembly process is essential for ensuring that the vending machine operates efficiently and effectively.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves finishing touches that enhance the machine’s aesthetics and functionality. This includes painting, coating, and surface treatments.
- Processes:
- Powder Coating: Provides a durable and attractive finish, resistant to scratches and corrosion.
- Quality Testing: Conducting final quality control (FQC) inspections to ensure that the machine meets all operational standards before shipping.
Finishing not only improves the visual appeal of the vending machines but also contributes to their longevity.
Quality Assurance in Vending Machine Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of vending machines, ensuring that each unit meets international and industry-specific standards.
Relevant International Standards
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes. Additionally, compliance with CE marking indicates conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, while API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply for machines designed for specific environments.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
QC Checkpoints
Quality control is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Ensures that raw materials meet specified quality standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Involves continuous monitoring during the assembly phase to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the completed machines, including functional tests and visual inspections, before they leave the factory.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are used to ensure quality:
- Functional Testing: Verifying that all electronic and mechanical components operate correctly.
- Stress Testing: Simulating real-world conditions to test the machine’s durability and performance under load.
- Compliance Testing: Ensuring that the machines meet all regulatory standards relevant to the target market.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to assess manufacturing capabilities and quality control practices. This provides insight into their processes and commitment to quality.
- Request Quality Assurance Reports: Ask for documentation that outlines their quality management systems, including records of past inspections and audits.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent third-party inspection services to evaluate the manufacturing facilities and processes. This adds an extra layer of assurance regarding quality.
QC/Certifications for International Buyers
International buyers must be aware of specific quality control nuances:
- Regulatory Compliance: Understand the compliance requirements for vending machines in your region, such as local health and safety regulations.
- Certification Processes: Familiarize yourself with certification processes required in your target markets, which may vary significantly between regions. For instance, machines exported to Europe must adhere to CE marking standards.
- Cultural Considerations: Be aware of cultural differences in quality expectations and business practices, especially in emerging markets. Building strong relationships with suppliers can help bridge these gaps.
Conclusion
Investing in vending machines requires a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, along with robust quality control measures, B2B buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality machines. Additionally, verifying supplier capabilities through audits and third-party inspections can significantly mitigate risks associated with international procurement, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Related Video: Most Satisfying Factory Production Processes And Heavy-Duty Factory Machines!
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for invest in vending machines Sourcing
Investing in vending machines entails a multifaceted cost structure that international B2B buyers must navigate carefully. Understanding these costs and the factors influencing pricing can lead to more informed purchasing decisions and better negotiation outcomes.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as metal, plastic, and electronic components, is a significant portion of the total investment. Prices can fluctuate based on global supply chains and demand, so it’s essential to establish reliable suppliers.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In developing markets, labor might be cheaper, but this can come with trade-offs in quality. Ensure that the workforce is adequately trained and that the supplier adheres to local labor laws.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facilities, and administrative expenses. Understanding the supplier’s operational efficiency can provide insight into their pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Custom vending machines may require specialized tooling, which can add to initial costs. Buyers should clarify whether tooling costs are included in the quoted price or will be charged separately.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet specified standards is crucial. Quality control processes can add to the overall cost but are necessary to avoid future expenses related to product failures.
-
Logistics: Transportation, warehousing, and handling costs must be factored in. International shipping can significantly impact the total cost, so understanding Incoterms is vital.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on market conditions and the supplier’s business model.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing significantly. Bulk purchases usually lead to lower per-unit costs, so buyers should assess their demand forecasts carefully.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features will increase costs. Buyers should balance the desire for customization with their budget constraints.
-
Materials: Higher quality materials will increase the price but may enhance durability and user satisfaction.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers with quality certifications (e.g., ISO) may charge higher prices. However, these certifications can be crucial for ensuring product reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more, but they often offer better support and product guarantees.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is essential for calculating total landed costs. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect the final price.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations to achieve better pricing. Leverage quotes from multiple suppliers to foster competition.
-
Cost Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. A lower initial price may result in higher long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of exchange rates, tariffs, and import duties that can affect the overall cost. It’s advisable to work with local partners who understand the regional market dynamics.
-
Quality Assurance: Before finalizing a purchase, request samples and conduct quality checks to mitigate risks associated with poor product quality.
Disclaimer
Pricing for vending machines can vary widely based on the specifications and market conditions at the time of purchase. This analysis provides indicative costs and should be used as a guideline rather than a definitive pricing structure. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing.
Spotlight on Potential invest in vending machines Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘invest in vending machines’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for invest in vending machines
When considering an investment in vending machines, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed decisions. Below are key specifications and terms that international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be familiar with.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality and type of materials used in the construction of vending machines, such as stainless steel, plastic, or glass.
– Importance: High-grade materials ensure durability and longevity, which are critical for machines operating in high-traffic environments. This affects not only the lifespan but also maintenance costs. -
Power Consumption
– Definition: The amount of electrical energy the vending machine uses during operation, typically measured in watts.
– Importance: Lower power consumption translates to reduced operational costs, making the machine more economically viable, especially in regions with high electricity prices. -
Capacity
– Definition: The total volume of products that a vending machine can hold, often expressed in terms of item count or weight.
– Importance: Understanding capacity helps in determining product variety and turnover rate. A machine with a larger capacity may be more beneficial in busy locations, minimizing restocking frequency. -
Payment Options
– Definition: The types of payment methods accepted by the vending machine, such as cash, credit/debit cards, mobile payments, and contactless options.
– Importance: Offering diverse payment methods can increase sales, as it caters to a wider customer base. This is particularly relevant in regions where cashless transactions are becoming the norm. -
Dimensions and Weight
– Definition: The physical size and weight of the vending machine, which can affect its placement and stability.
– Importance: Understanding dimensions is vital for logistics, installation, and compliance with space regulations. Heavier machines may require additional support or specific installation protocols.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Significance: In the vending machine industry, working with an OEM can ensure high-quality components and support for maintenance and repairs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Significance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their demand forecasts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers asking for a price quote for specific products or services.
– Significance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, fostering competitive pricing and better negotiation outcomes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
– Significance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements, reducing misunderstandings related to costs and liability during transport. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Significance: Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory planning and ensuring that machines are available when and where they are needed.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their vending machine investments, ensuring they meet market demands while optimizing operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the invest in vending machines Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global vending machine market is witnessing significant growth, driven by factors such as increasing consumer demand for convenience, the rise of contactless payment solutions, and the proliferation of smart vending technologies. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to invest, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The market is expected to reach approximately $25 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 10%.
Emerging trends include the integration of IoT technology, allowing for real-time inventory management and customer interaction analytics. Smart vending machines equipped with sensors and connected to mobile apps can enhance customer engagement and improve operational efficiency. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the demand for touchless solutions, prompting many manufacturers to innovate and adapt to health and safety standards. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers in the Middle East, where a tech-savvy population is eager for modern solutions.
In addition, sustainability is becoming a central theme in procurement strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including energy-efficient machines and recyclable materials. By aligning with these trends, international buyers can position themselves competitively in their respective markets.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer optional; it is a fundamental aspect of the vending machine industry that affects brand reputation and customer loyalty. The environmental impact of traditional vending machines, from energy consumption to waste generation, has prompted a shift toward greener alternatives. B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that utilize energy-efficient technologies and sustainable materials.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. This involves ensuring that the supply chain adheres to responsible labor practices and minimizes environmental harm. Buyers should look for certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade, which indicate a commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. Furthermore, the use of biodegradable packaging and recyclable components is gaining traction, providing an avenue for buyers to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
Investing in vending machines that reflect these values not only meets consumer demand for sustainability but also positions companies favorably in a competitive market increasingly focused on ethical considerations.
Brief Evolution/History
The vending machine industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 1880s when simple machines dispensed postcards and stamps. The introduction of food and beverage vending machines in the mid-20th century marked a turning point, catering to the growing demand for convenience in urban settings.
The late 1990s saw the advent of electronic vending machines, which revolutionized payment systems and product offerings. Today, the market is characterized by advanced technologies such as cashless payment options, remote monitoring, and AI-driven analytics. This evolution reflects broader trends in consumer behavior and technology, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about historical shifts that shape current market dynamics. Understanding this context can aid in making strategic investment decisions that align with future trends.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of invest in vending machines
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for vending machines?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their experience, reputation, and product quality. Request references and check online reviews or industry forums to gauge customer satisfaction. Verify their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate compliance with quality management practices. Additionally, assess their financial stability to ensure they can support long-term business relationships and service commitments. -
Can vending machines be customized to suit my market needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for vending machines. You can select specific features such as payment methods (cash, card, mobile payments), machine size, branding, and product selection tailored to local preferences. Discuss your requirements with the supplier upfront to ensure they can meet your needs and provide samples or prototypes if necessary. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for vending machines?
MOQs vary by supplier and machine type, often ranging from 5 to 50 units for bulk orders. Lead times can depend on customization and production schedules, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. It’s crucial to clarify these details during negotiations to plan your inventory and cash flow effectively, especially for new market entries. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing vending machines internationally?
Payment terms may include options like full upfront payment, a deposit with the balance upon delivery, or letter of credit arrangements. Ensure you discuss and agree on terms that protect your interests, such as escrow services or third-party verification for larger transactions. Understanding currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees is also essential. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification for vending machines?
Request documentation for quality assurance processes, such as ISO certifications, safety standards, and product testing results. Many suppliers will provide a quality control plan that outlines inspection methods and criteria. Consider conducting a factory audit or hiring a third-party inspection service to verify product quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing vending machines?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling machinery to navigate potential complexities. Ensure that you have all required documentation, such as bills of lading and import permits, to avoid delays. It’s also advisable to consider insurance coverage for your shipment. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers over vending machine quality or delivery?
Establish clear communication channels and a dispute resolution process in your contract. If issues arise, address them promptly by documenting the problem and engaging in discussions with the supplier. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration to resolve the dispute amicably. Having a legal framework outlined in your agreement can help protect your interests. -
What are the best practices for maintaining vending machines post-purchase?
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity of vending machines. Establish a routine for cleaning, restocking, and inspecting machines for potential issues. Consider training local staff or partnering with a service provider for repairs and upkeep. Additionally, implement a monitoring system to track sales and inventory levels, allowing for proactive management and optimization of your vending operations.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for invest in vending machines
In conclusion, investing in vending machines presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The strategic sourcing of vending machines not only enhances accessibility to consumer goods but also opens avenues for businesses to tap into emerging markets with growing demand for convenience. By leveraging local partnerships and understanding regional consumer preferences, businesses can optimize their vending machine offerings to maximize profitability.
Key Takeaways:
- Market Insights: Understand regional trends and consumer behaviors that influence purchasing decisions.
- Supplier Relations: Build strong relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure quality and support.
- Technology Integration: Embrace smart vending solutions that cater to the modern consumer’s needs for convenience and efficiency.
As the vending machine industry continues to evolve, international buyers must stay informed and agile. The future is promising for those who strategically source and adapt their offerings to local markets. Now is the time to act—evaluate your options, partner with local experts, and position your business for success in this dynamic sector.