Master Sourcing Vending Machine Components for Optimal
Guide to Vending Machine Components
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vending machine components
- Understanding vending machine components Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of vending machine components
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vending machine components
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vending machine components
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vending machine components Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential vending machine components Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vending machine components
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vending machine components Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vending machine components
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vending machine components
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vending machine components
In today’s dynamic global economy, the demand for vending machines and their components is on the rise, driven by evolving consumer behaviors and technological advancements. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of vending machine components is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. These components are not merely functional parts; they are the backbone of operational efficiency, impacting everything from customer satisfaction to profit margins.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse landscape of vending machine components, covering essential types such as payment systems, product dispensers, refrigeration units, and control boards. It will also explore the materials used in manufacturing these components, ensuring buyers are equipped with knowledge about durability and compatibility. Quality control measures and manufacturing standards are addressed to help buyers evaluate suppliers effectively, while cost considerations provide a framework for budgeting and investment.
With insights into market trends and frequently asked questions, this guide aims to empower international buyers with the information necessary to navigate the global market confidently. By leveraging this resource, businesses can optimize their sourcing strategies, enhance operational performance, and ultimately drive growth in their respective markets. Understanding these elements is essential for capitalizing on opportunities within the vending machine sector.
Understanding vending machine components Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Dispensing | Uses mechanical systems for product delivery | Snacks, beverages, and small items | Reliable and low maintenance, but limited product range |
| Electronic Payment Systems | Accepts various payment methods, including cash and cards | High-traffic locations, urban areas | Increases sales potential, but higher initial costs |
| Refrigerated Units | Temperature-controlled for perishable items | Food service, pharmaceuticals | Essential for freshness, but requires power and maintenance |
| Interactive Touchscreens | User-friendly interface for selections | Technology-centric environments | Enhances user experience, but can be costly to implement |
| Smart Inventory Management | Tracks stock levels and sales in real-time | Large-scale operations, retail | Optimizes restocking, but requires reliable internet access |
Mechanical Dispensing
Mechanical dispensing systems are characterized by their use of physical mechanisms, such as levers and pulleys, to deliver products. These machines are particularly suitable for dry snacks, beverages, and small items. For B2B buyers, the key consideration is reliability and low maintenance costs. However, the limitation in product range may deter businesses looking to diversify their offerings.
Electronic Payment Systems
Electronic payment systems have revolutionized the vending industry by allowing machines to accept various payment methods, including credit cards, mobile payments, and even cryptocurrencies. This feature is especially beneficial in high-traffic urban areas where consumer convenience drives sales. While they significantly increase potential revenue, B2B buyers must consider the higher initial investment and potential technical support needs.
Refrigerated Units
Refrigerated vending machines are designed to maintain a controlled temperature, making them ideal for selling perishable items like sandwiches, salads, and beverages. These units are crucial for businesses in the food service and pharmaceutical sectors where product freshness is paramount. Buyers should weigh the benefits of maintaining quality against the operational costs related to power consumption and regular maintenance.
Interactive Touchscreens
Interactive touchscreens enhance the user experience by providing a visually engaging interface for product selection. These machines are particularly suited for technology-centric environments, such as office buildings or tech campuses, where users expect modern amenities. While the user-friendly design can boost sales, B2B buyers should be prepared for the higher costs associated with technology integration and potential repair needs.
Smart Inventory Management
Smart inventory management systems utilize technology to track stock levels and sales in real-time, optimizing restocking processes and reducing waste. These systems are especially beneficial for large-scale operations and retail environments where efficiency is critical. Buyers must consider the infrastructure required for reliable internet access and the potential complexity of integrating these systems into existing operations.
Key Industrial Applications of vending machine components
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vending machine components | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Automated retail solutions | Increased customer engagement, reduced labor costs | Supplier reliability, technology integration capabilities |
| Hospitality | In-room vending services | Enhanced guest experience, 24/7 availability | Customization options, payment system compatibility |
| Healthcare | Medical supply vending machines | Quick access to essential supplies, improved efficiency | Compliance with health regulations, robust security features |
| Education | Campus vending solutions | Convenient access to snacks and supplies for students | Durability, energy efficiency, and user-friendly design |
| Transportation | Vending machines at transit hubs | Streamlined service for travelers, increased revenue | Location adaptability, payment method diversity |
Retail: Automated Retail Solutions
In the retail sector, vending machine components are integral to creating automated retail solutions that enhance customer interaction and streamline sales processes. These machines can offer a variety of products, from snacks to electronics, reducing the need for staff and optimizing space. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing reliable components that ensure seamless operation is crucial, as downtime can lead to lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
Hospitality: In-Room Vending Services
In the hospitality industry, vending machines in hotel rooms provide guests with convenient access to snacks and beverages at any time. This 24/7 service can significantly enhance the guest experience and contribute to increased revenue. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing customizable vending solutions that can accommodate local preferences and payment systems, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of their clientele.
Healthcare: Medical Supply Vending Machines
Healthcare facilities are increasingly using vending machines to dispense medical supplies and medications. This application ensures that essential items are readily available, enhancing operational efficiency and patient care. For B2B buyers in this sector, it is vital to prioritize compliance with health regulations and security features to protect sensitive items. Components must be sourced from reputable suppliers who understand the specific requirements of healthcare environments.
Education: Campus Vending Solutions
Vending machines in educational institutions provide students with easy access to snacks, beverages, and essential supplies. This convenience can improve student satisfaction and engagement on campus. Buyers from the education sector should look for durable vending components that can withstand heavy usage and have energy-efficient designs, as these factors contribute to long-term cost savings and sustainability.
Transportation: Vending Machines at Transit Hubs
Vending machines located in transit hubs cater to travelers by providing quick access to refreshments and necessities. This application not only improves the overall travel experience but also generates additional revenue for businesses operating in high-traffic areas. International buyers must consider the adaptability of vending machines to different locations and the diversity of payment methods, as these factors can greatly influence customer acceptance and usage rates.
Related Video: How to Start a Vending Machine Business, Cost, Tips, How Much You Make
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vending machine components
When selecting materials for vending machine components, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in vending machine components, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various environments, including humid and coastal areas.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is one of its greatest advantages; it can last for many years without significant wear. However, it tends to be more expensive than other materials, which can impact overall project budgets. Manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is particularly compatible with food and beverage applications, ensuring hygiene and safety. Its resistance to rust makes it ideal for components exposed to moisture.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. In regions like Europe, adherence to EN standards is critical, while in Africa and South America, local regulations may vary.
Plastic (Polypropylene)
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is a lightweight plastic with good chemical resistance and moderate temperature tolerance. It is often used in components that require flexibility and impact resistance.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polypropylene is its low cost and ease of manufacturing, making it suitable for high-volume production. However, it has limited temperature resistance compared to metals and can degrade under UV exposure.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is ideal for non-load-bearing components and those that will not be exposed to extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals. It is commonly used in coin mechanisms and internal housing.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the selected polypropylene grades meet relevant food safety standards, particularly in regions with strict regulations like the EU. Understanding local recycling capabilities is also essential for sustainability.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It can be anodized for enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it easy to handle and install, while its corrosion resistance is beneficial in various environments. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may require additional coatings for specific applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for exterior components of vending machines, such as frames and panels, where weight savings and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions is essential. Buyers should also consider local sourcing options to mitigate import costs and ensure faster delivery times.
Copper
Key Properties:
Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties, making it suitable for wiring and electronic components in vending machines.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which is essential for electronic applications. However, it is susceptible to corrosion and can be more expensive than other materials, impacting overall costs.
Impact on Application:
Copper is particularly useful in electrical components, such as circuit boards and connectors, where performance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the varying regulations regarding copper use in electronics across different regions. Compliance with standards such as IEC 60068 for environmental testing is crucial for ensuring product reliability.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for vending machine components | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Exterior panels, internal frames, and food-related parts | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastic (Polypropylene) | Coin mechanisms, internal housing | Low cost and easy to manufacture | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| Aluminum | Frames, panels, and decorative elements | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | More expensive than steel | Medium |
| Copper | Wiring and electronic components | Superior electrical conductivity | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides critical insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with performance requirements, budget constraints, and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vending machine components
Manufacturing Processes for Vending Machine Components
When sourcing vending machine components, understanding the manufacturing processes is crucial for ensuring quality, reliability, and performance. The main stages of manufacturing typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques that are vital for producing high-quality components.
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing is selecting and preparing the raw materials. Common materials for vending machine components include:
- Metals (e.g., steel, aluminum) for structural parts
- Plastics (e.g., ABS, polycarbonate) for exterior casings and internal components
- Electronic components (e.g., circuit boards, sensors)
Techniques in this phase involve cutting, shaping, and treating materials to ensure they meet the specifications required for subsequent processes. For instance, metals may undergo processes such as die-cutting or laser cutting, while plastics may be injection molded for efficiency and precision.
Forming
Once materials are prepared, they are formed into the desired shapes. This stage is critical as it determines the functionality and fit of the components. Key techniques include:
- Stamping: Used for metal parts, this involves pressing material into molds to create specific shapes.
- Extrusion: Commonly used for plastics, where material is forced through a die to produce long shapes that can be cut to length.
- CNC Machining: This computer-controlled process allows for precise shaping of both metal and plastic components, ensuring high accuracy.
Assembly
After individual components are formed, they need to be assembled. This process may involve manual labor or automated systems, depending on the complexity of the components. Key assembly methods include:
- Screwing and Bolting: Common for structural integrity, ensuring that parts remain securely attached.
- Soldering and Welding: Used for joining electronic components and metal parts.
- Adhesive Bonding: Involves using strong adhesives to bond various materials, especially in plastic assemblies.
Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes that enhance the appearance and durability of components. Techniques include:
- Painting and Coating: To protect against corrosion and wear, often important for outdoor vending machines.
- Polishing: For aesthetic appeal, especially in visible components.
- Quality Surface Treatments: Such as anodizing for aluminum parts to improve their resistance to oxidation.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance is essential to ensure that vending machine components meet international standards and customer expectations. International standards such as ISO 9001 govern quality management systems, while industry-specific certifications like CE marking and API standards may apply depending on the component’s function and market.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is typically structured through several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing to monitor compliance with quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive check of the finished products before they are shipped to customers.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of common testing methods that suppliers may employ, including:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that components perform as expected under operational conditions.
- Durability Testing: Assesses the longevity and wear resistance of components.
- Electrical Safety Testing: Particularly important for electronic components to prevent failures or hazards.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical. Here are actionable steps to ensure supplier reliability:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regularly scheduled audits can provide insight into a supplier’s manufacturing and QC processes.
- Request Quality Assurance Documentation: Ask for certificates and reports that demonstrate compliance with relevant standards (e.g., ISO 9001, CE).
- Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can provide unbiased assessments of quality and compliance.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers should be aware of the nuances related to quality certification:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific regulations that affect product compliance. For instance, European standards may be stricter compared to those in Africa or South America.
- Language Barriers: Documentation may be in different languages, necessitating translation or local expertise to ensure understanding.
- Cultural Differences: Approaches to quality and manufacturing may vary across regions. Understanding these cultural differences can enhance communication and cooperation with suppliers.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for B2B buyers in the vending machine component industry. By focusing on the details of material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, along with robust quality control measures, buyers can make informed decisions and build strong partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vending machine components Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Vending Machine Components
When sourcing vending machine components, it is essential to grasp the various cost components that contribute to the final pricing. The key elements include:
- Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences costs. High-quality metals and plastics may lead to higher upfront expenses but can result in better durability and lower maintenance costs over time.
- Labor: Labor costs vary by region. Countries with higher labor costs may produce components at a premium, while regions with lower wages might offer more competitive pricing. Understanding local labor markets can provide strategic sourcing advantages.
- Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Buyers should inquire about these costs as they can vary widely across different suppliers.
- Tooling: Custom tooling for specific components can represent a significant initial investment. Buyers should evaluate whether the tooling costs can be amortized over larger production runs to enhance cost-effectiveness.
- Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that components meet specified standards, which can add to the overall cost. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term operational issues and warranty claims.
- Logistics: Transportation costs can fluctuate based on distance, shipping methods, and fuel prices. Understanding the logistics involved in sourcing from different regions is crucial for accurate cost estimations.
- Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on their market position and the level of competition. Buyers should aim to understand these margins as they directly impact the final pricing.
Key Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the price of vending machine components:
- Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically lead to lower unit prices. Buyers should assess their demand and negotiate favorable terms based on volume.
- Specifications and Customization: Custom components tailored to specific needs may incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against standard solutions.
- Material Quality and Certifications: Components that meet specific industry certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should verify the necessity of these certifications for their target markets.
- Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and financial stability can impact pricing. Conducting thorough due diligence is essential to ensure a trustworthy partnership.
- Incoterms: The terms of shipping and responsibility for costs can significantly affect the overall price. Buyers must clarify these terms to avoid unexpected expenses.
Tips for International B2B Buyers
When sourcing vending machine components, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following actionable insights:
- Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures and potential discounts. Leverage volume purchases or long-term contracts to negotiate better terms.
- Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operation, and disposal costs. This holistic view can lead to more informed sourcing decisions.
- Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the currency exchange rates, import duties, and taxes that can affect pricing. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage in negotiations.
- Supplier Diversification: Consider sourcing from multiple suppliers to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Diversifying your supplier base can also lead to competitive pricing.
- Stay Informed: Regularly review market trends and pricing fluctuations in the vending machine components sector to adapt your sourcing strategy accordingly.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for vending machine components can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. Buyers should approach pricing discussions with suppliers with an understanding that the figures may fluctuate based on market conditions, order specifications, and other influencing factors. Always seek detailed quotes tailored to specific needs and requirements.
Spotlight on Potential vending machine components Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for vending machine components.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vending machine components
Key Technical Properties of Vending Machine Components
Understanding the technical properties of vending machine components is essential for international B2B buyers. These specifications can significantly impact product performance, durability, and overall customer satisfaction. Here are some critical technical properties:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the type and quality of materials used in manufacturing components, such as plastics, metals, and electronic parts.
– Importance: Selecting the right material grade ensures durability and resistance to wear and tear. For instance, stainless steel is preferred for external parts due to its corrosion resistance, while specific plastics may be chosen for internal mechanisms to reduce weight and cost. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance specifies the allowable variation in dimensions of a component. It is critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly and function as intended.
– Importance: In vending machines, precise tolerances are crucial to avoid jams and malfunctions. A tolerance that is too wide can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased maintenance costs. -
Load Capacity
– Definition: This property indicates the maximum weight or load that a component can support without failure.
– Importance: For components like shelves or dispensing mechanisms, understanding load capacity helps ensure that the vending machine can handle the intended product range without damage, thereby reducing replacement costs and downtime. -
Power Consumption
– Definition: This metric refers to the amount of electrical energy required for components to operate.
– Importance: Low power consumption is increasingly important for energy efficiency and sustainability. Buyers should consider components that minimize energy use, which can lead to lower operational costs and compliance with energy regulations. -
Operating Temperature Range
– Definition: This indicates the temperature range within which a component can operate effectively.
– Importance: Vending machines often operate in various environments, from hot outdoor settings to climate-controlled indoor areas. Components must be chosen based on their ability to function reliably across these temperature extremes to prevent failures.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the vending machine components market. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding whether a component is OEM or aftermarket can influence quality and compatibility decisions. Buyers should prioritize OEM parts for reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory costs and production planning. Suppliers with lower MOQs are often more accessible for smaller businesses or new entrants in the market. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ is essential for comparing offers from different suppliers. A well-structured RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, enhancing negotiation power. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
– Importance: Incoterms clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps mitigate risks and avoid misunderstandings during international transactions.
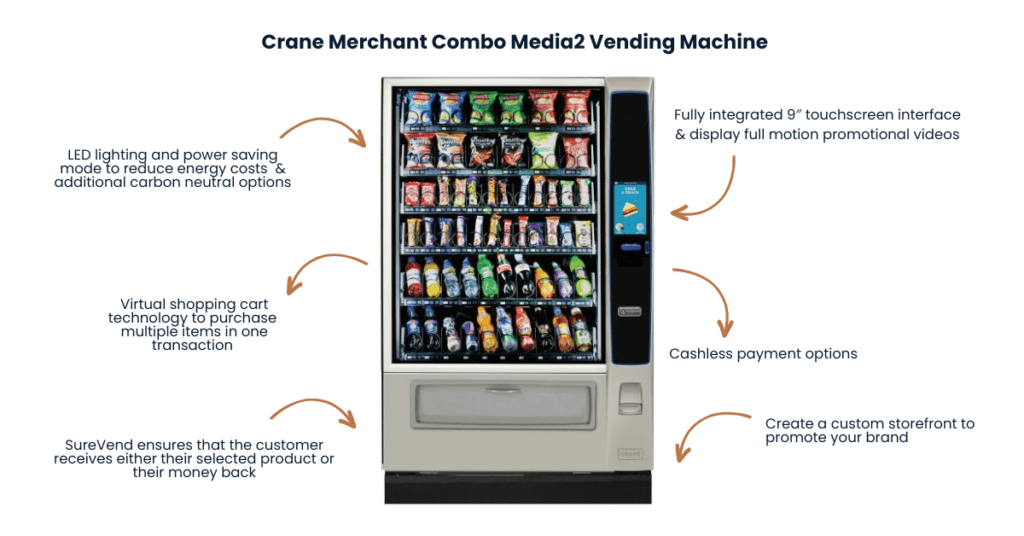
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should consider lead times when sourcing components to ensure timely delivery and avoid disruptions in operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, streamline procurement processes, and enhance the overall efficiency of their vending machine operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vending machine components Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The vending machine components sector is witnessing significant transformations driven by globalization, technological advancement, and changing consumer preferences. One of the primary global drivers is the increasing demand for automated retail solutions, which has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Businesses are looking for innovative ways to engage customers while minimizing human interaction, leading to a surge in the development of advanced vending machines equipped with cashless payment systems and IoT capabilities.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for inventory management and predictive analytics, which helps companies optimize their supply chains. For international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these trends is crucial. Adopting smart vending solutions can enhance operational efficiency and improve customer satisfaction, making it a competitive advantage in the market.
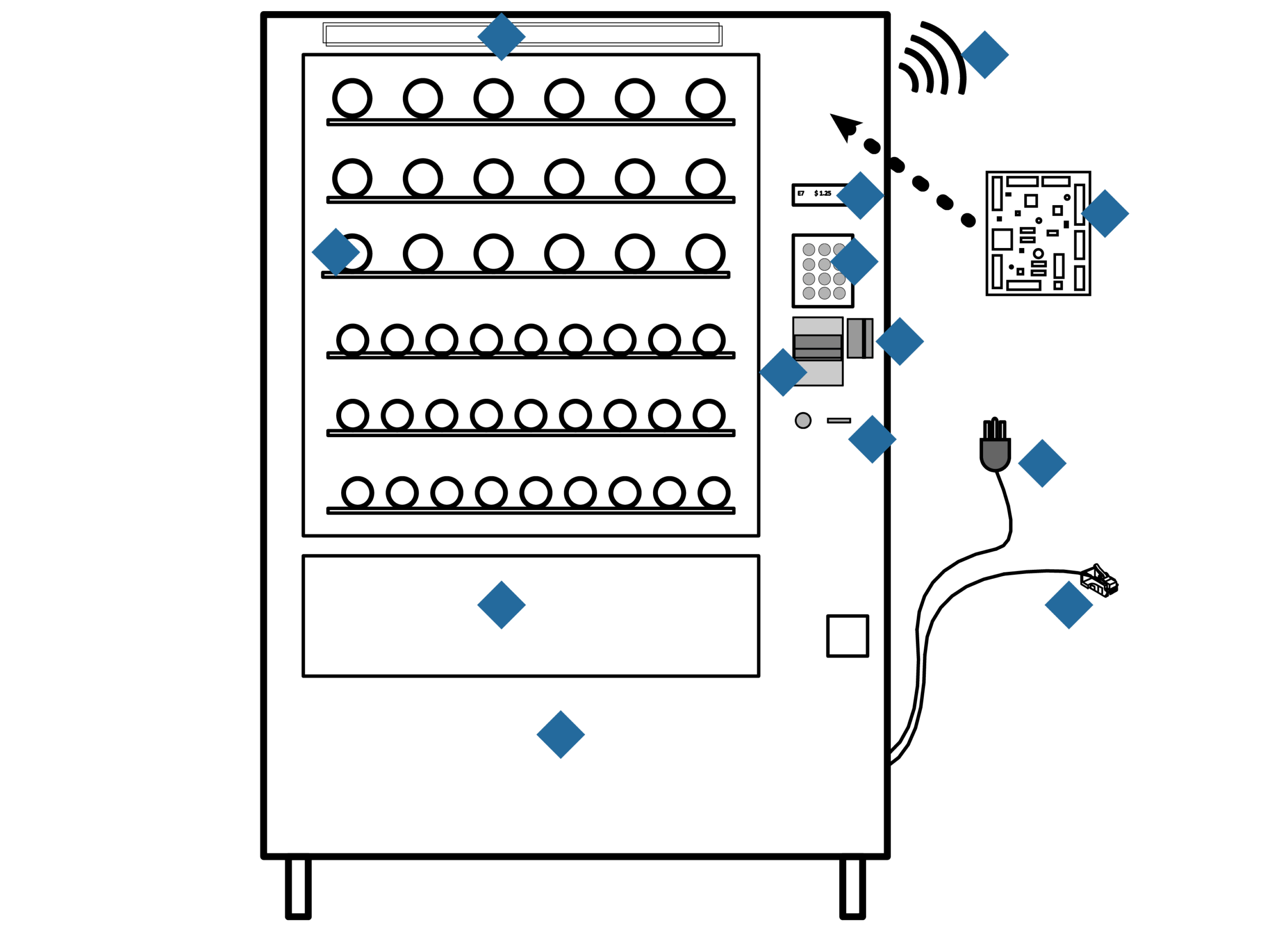
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Furthermore, the market dynamics for vending machine components are influenced by regional economic conditions. In Europe, for instance, there is a push for greater customization and product variety, reflecting diverse consumer tastes. Conversely, markets in Africa and South America may focus on cost-effective solutions that cater to local purchasing power. Therefore, B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer flexibility and scalability in their product offerings to adapt to local market conditions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the vending machine components sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of vending machines and their components cannot be overlooked. As international buyers seek to improve their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles, the importance of ethical supply chains is more pronounced.
Buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste in their production processes. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other ‘green’ certifications indicate a commitment to sustainability. Additionally, sourcing from manufacturers who prioritize eco-friendly materials, such as biodegradable plastics or sustainably sourced metals, can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Incorporating sustainability into purchasing decisions not only contributes to environmental preservation but also aligns with global trends favoring ethical consumption. By prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with environmental regulations and enhance their market position.
Brief Evolution/History
The vending machine industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century, transitioning from simple coin-operated machines to sophisticated automated retail solutions. Initially, vending machines offered basic products like snacks and beverages. However, the rise of technology in the 21st century has transformed them into smart machines capable of offering a wide array of products, including healthy options and non-food items.
The introduction of cashless payment options and IoT connectivity has revolutionized the way consumers interact with vending machines, allowing for real-time inventory tracking and enhanced user experiences. This evolution reflects broader consumer trends toward convenience and personalization, making it imperative for B2B buyers to stay abreast of technological advancements in the vending machine components sector. As the market continues to evolve, embracing innovation will be key to maintaining competitiveness and meeting the demands of a dynamic consumer landscape.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vending machine components
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of vending machine components?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and financial stability. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate quality management practices. Request references from existing clients and analyze their feedback. Additionally, assess their production capabilities, lead times, and logistical efficiency, especially for international shipping, to ensure they can meet your specific demands. -
Can I customize vending machine components to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for vending machine components. When discussing customization, be clear about your requirements, including size, materials, and functionality. It’s beneficial to work with suppliers who have experience in your industry segment and can provide prototypes or samples for evaluation before full-scale production. This ensures that the final product aligns with your expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for components?
MOQs can vary significantly among suppliers, often ranging from 50 to 1,000 units, depending on the component type and manufacturer. Lead times typically span from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by the complexity of the components and the supplier’s production schedule. Always clarify these details during negotiations to avoid unexpected delays and to align your inventory needs with supplier capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely, but common practices include 30% upfront and 70% upon shipment. Be mindful of the payment methods accepted; options such as letters of credit or escrow services can provide additional security. Always confirm the currency of transaction and any potential fees for currency conversion, as these can impact your overall costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) and certifications for components?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes and any relevant certifications. This might include testing standards specific to your region, such as CE marking in Europe or ANSI standards in the U.S. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or utilizing third-party inspection services to verify compliance with your quality expectations before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing components?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of components. Evaluate the supplier’s shipping methods and their experience with customs clearance in your region. Understand the total landed cost, which includes shipping, tariffs, and taxes. Establish a clear communication channel with your supplier for tracking shipments and resolving any potential delays. -
How can I handle disputes with international suppliers effectively?
Disputes can arise due to misunderstandings or quality issues. Establish a clear contract that outlines terms, including dispute resolution processes such as mediation or arbitration. Maintain open lines of communication with your supplier and document all interactions. If a dispute escalates, consider involving a legal advisor familiar with international trade laws to navigate the complexities of cross-border transactions. -
What trends should I be aware of in the vending machine components market?
Emerging trends include the integration of smart technology, such as cashless payment systems and IoT connectivity, enhancing user experience. Sustainability is also gaining traction, with a focus on eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient components. Stay informed about market developments through industry publications and trade shows to identify potential opportunities for innovation and competitive advantage in your sourcing strategy.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vending machine components
In conclusion, strategic sourcing for vending machine components is essential for international buyers seeking to enhance their supply chain efficiency and product offerings. By prioritizing partnerships with reliable suppliers, leveraging local insights, and focusing on quality and cost-effectiveness, businesses can significantly improve their competitive edge in the rapidly evolving vending market.
Key takeaways for B2B buyers include the importance of understanding regional market dynamics, fostering relationships with suppliers who prioritize innovation, and utilizing data analytics to inform purchasing decisions. Moreover, as sustainability becomes increasingly critical, sourcing components that align with eco-friendly practices can not only enhance brand reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for responsible products.
Looking ahead, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should proactively explore emerging technologies and trends in the vending sector. By adapting to these changes and embracing a strategic sourcing approach, companies can position themselves for long-term success. Now is the time to take action—evaluate your sourcing strategies, engage with key suppliers, and prepare to capitalize on the future of vending machine components.